Microalgae Octapeptide IIAVEAGC Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Neurotoxicity in 6-OHDA-Induced SH-SY5Y Cells by Regulating the Nrf2/HO-1and Jak2/Stat3 Pathways
Abstract
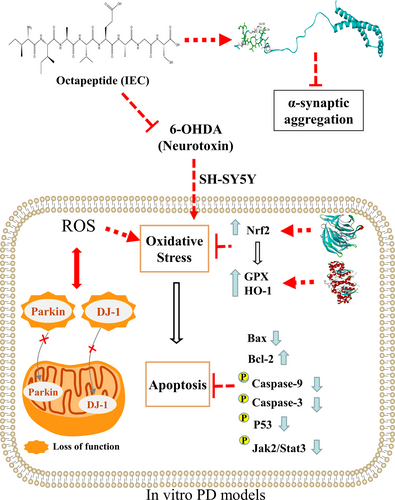
Neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by the progressive loss of selectively vulnerable populations of neurons, and many factors are involved in its causes. Neurotoxicity and oxidative stress, are the main related factors. The octapeptide Ile-Ile-Ala-Val-Glu-Ala-Gly-Cys (IEC) was identified from the microalgae Isochrysis zhanjiangensis and exhibited potential anti-oxidative stress activity. In this study, the stability of α-synaptic protein binding to IEC was modeled using molecular dynamics, and the results indicated binding stabilization within 60 ns. Oxidative stress in neurons is the major cause of α-synaptic protein congestion. Therefore, we next evaluated the protective effects of IEC against oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in 6-ohdainduced Parkinson's disease (PD) model SH-SY5Y cells in vitro. In oxidative stress, IEC appeared to increase the expression of the antioxidant enzymes HO-1 and GPX through the antioxidant pathway of Nrf2, and molecular docking of IEC with Nrf2 and GPX could generate hydrogen bonds. Regarding apoptosis, IEC protected cells by increasing the Bcl-2/Bax ratio, inhibiting the caspase cascade, acting on p53, and modulating the Jak2/Stat3 pathway. The results indicated that IEC exerted neuroprotective effects through the inhibition of α-synaptic protein aggregation and antioxidant activity. Therefore, microalgal peptides have promising applications in the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
Research data are not shared.