Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Effect of Western Ethiopian Propolis
Corresponding Author
Tariku Neme Afata
Department of Environmental Health Science and Technology, Jimma University, Ethiopia
Oromia Region, Dambi Dollo Teachers College, Ethiopia
Search for more papers by this authorAman Dekebo
Department of Applied Chemistry, Adama Science and Technology University, Adama, Ethiopia
Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Adama Science and Technology University, Adama, Ethiopia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tariku Neme Afata
Department of Environmental Health Science and Technology, Jimma University, Ethiopia
Oromia Region, Dambi Dollo Teachers College, Ethiopia
Search for more papers by this authorAman Dekebo
Department of Applied Chemistry, Adama Science and Technology University, Adama, Ethiopia
Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Adama Science and Technology University, Adama, Ethiopia
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
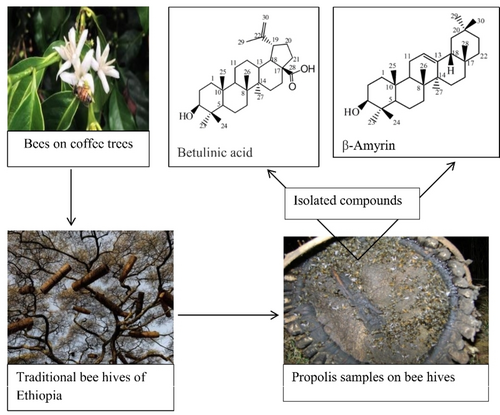
Propolis or bee glue is commonly named as a natural resinous mixture produced by honeybees (Apis mellifera) from substances collected from parts of plants, buds, and exudate. The result of the ethyl acetate - methanol (3 : 2) volume by volume fraction yielded a total of two compounds namely betulinic acid and β-amyrin isolated from Bodji Dirmaji and Fincha'a district propolis, respectively. The crude ethanolic extract was portioned with the different solvent systems by increasing the polarities in the following order of hexane, ethyl acetate, and methanol. Column chromatographic method on normal silica gel was used to isolate the compounds. The structures of the compounds were characterized using 1D NMR techniques. The study revealed that western Ethiopian propolis was rich in saponins, tannins, flavonoids, steroids, triterpenes, and glycosides. The antibacterial activity for the isolated compound (betulinic acid) showed the highest inhibition for S. aureus (11.2±1.6), E. coli (17.7±1.1), and A. niger (12.6±1.2) mm.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
- 1T. N. Afata, R. Nemo, N. Ishete, G. T. Tucho and A. Dekebo, ‘Phytochemical investigation, physicochemical characterization, and antimicrobial activities of Ethiopian propolis’, Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103931.
- 2S. Sobocanec, V. Šverko, T. Balog, A. Šarić, G. Rusak, S. Likić, B. Kušić, V. Katalinić, S. Radić and T. Marotti, ‘Oxidant/antioxidant properties of Croatian native propolis’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8018–8026.
- 3A. K. Kuropatnicki, E. Szliszka and W. Krol, ‘Historical aspects of propolis research in modern times’, Evid.based complementary and altern. med. 2013, 2013, 1–7.
- 4A. Gómez-Caravaca, M. Gómez-Romero, D. Arráez-Román, A. Segura-Carretero and A. Fernández-Gutiérrez, ‘Advances in the analysis of phenolic compounds in products derived from bees’, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 1220–1234.
- 5Y. K. Park, S. M. Alencar and C. L. Aguiar, ‘Botanical Origin and Chemical Composition of Brazilian Propolis’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2502–2506.
- 6P. Okińczyc, J. Widelski, J. Szperlik, M. Żuk, T. Mroczek, K. Skalicka-Woźniak, Z. Sakipova, G. Widelska and P. M. Kuś, ‘Impact of Plant Origin on Eurasian Propolis on Phenolic Profile and Classical Antioxidant Activity’, Biomol. Eng. 2021, 11.
- 7A. Daugsch, C. S. Moraes, P. Fort and Y. K. Park, ‘Brazilian red propolis—chemical composition and botanical origin’, Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 5, 435–441.
- 8A. Bakdash, O. H. Almohammadi, N. A. Taha, A. Abu-Rumman and S. Kumar, ‘Chemical composition of propolis from the Baha region in Saudi Arabia’, Czech J. Food Sci. 2018, 36, 00–10.
- 9H. Afrouzan, A. Tahghighi, S. Zakeri and A. Es-haghi, ‘Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activities of Iranian Propolis’, Iran. Biomed. J. 2018, 22, 50–65.
- 10A. N. Tamfu, M. Sawalda, M. T. Fotsing, R. M. T. Kouipou, E. Talla, G. F. Chi, J. J. E. Epanda, J. T. Mbafor, T. A. Baig, A. Jabeen and F. Shaheen, ‘A new isoflavonol and other constituents from Cameroonian propolis and evaluation of their anti-inflammatory, antifungal and antioxidant potential’, Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1659–1666.
- 11S. S. Alenezi, N. D. Alenezi, G. U. Ebiloma, M. J. Natto, M. A. Ungogo, J. O. Igoli, V. A. Ferro, A. I. Gray, J. Fearnley, H. P. de Koning, D. G. Watson, ‘The Antiprotozoal Activity of Papua New Guinea Propolis and Its Triterpenes’, Molecules 2022, 27, 1622.
- 12S. Ipav, J. Igoli, T. Tor-Anyiin, J. Anyam, ‘Isolation and Characterisation of Lupeol and Lupeol Acetate from Propolis Obtained from Benue State’, J. Chem. Soc. Nigeria 2022, 47, 152–157.
- 13J. Ito, F.-R. Chang, H.-K. Wang, Y. K. Park, M. Ikegaki, N. Kilgore and K.-H. Lee, ‘Anti-AIDS agents. 48. Anti-HIV activity of moronic acid derivatives and the new melliferone-related triterpenoid isolated from Brazilian propolis’, J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1278–1281.
- 14A. A. Al-Ghamdi, N. I. M. Bayaqoob, A. I. Rushdi, Y. Alattal, B. R. T. Simoneit, A. H. El-Mubarak, K. F. Al-Mutlaq, ‘Chemical compositions and characteristics of organic compounds in propolis from Yemen’, Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1094–1103.
- 15K. Haile, T. Kebede, A. Dekebo, ‘A comparative study of volatile components of propolis (bee glue) collected from Haramaya University and Assela beekeeping centers, Ethiopia’, Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2012, 26, 353–360.
- 16A. I. Rushdi, N. Adgaba, N. I. Bayaqoob, A. Al-Khazim, B. R. Simoneit, A. H. El-Mubara, K. F. Al-Mutlaq, ‘Characteristics and chemical compositions of propolis from Ethiopia’, Springerplus 2014, 3, 1–9.
- 17M. C. Marcucci, ‘Propolis: chemical composition, biological properties and therapeutic activity’, Apidologie 1995, 26, 83–99.
- 18S. M. de Figueiredo, N. S. Binda, M. Almeida Bde, S. R. Lemos Abreu, J. A. Silva de Abreu, G. M. Pastore, H. H. Sato, V. C. Toreti, E. V. Tapia, Y. K. Park, S. A. Vieira Filho, R. B. Caligiorne, ‘Green Propolis: Thirteen Constituents of Polar Extract and Total Flavonoids Evaluated During Six Years through RP-HPLC’, Curr. Drug Discovery Technol. 2015, 12, 229–239.
- 19V. Bankova, G. Boudourova-Krasteva, J. M. Sforcin, X. Frete, A. Kujumgiev, R. Maimoni-Rodella, S. Popov, ‘Phytochemical evidence for the plant origin of Brazilian propolis from São Paulo State’, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 1999, 54, 401–405.
- 20I. I. S. Alfarrayeh, Bioactivities and potential beneficial properties of propolis ethanolic extract, caffeic acid phenethyl ester, and Arabic coffee beans extract, University of Pécs Pécs, Hungary, 2021.
- 21F. K. Abd El Hady, A. G. Hegazi, ‘Egyptian propolis: 2. Chemical composition, antiviral and antimicrobial activities of East Nile Delta propolis’, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 2002, 57, 386–394.
- 22S. Fikru, ‘Review of honey bee and honey production in Ethiopia’, J. Anim. Sci. Adv. 2015, 5, 1413–1421.
- 23A. Dekebo, D. Bisrat, C. Jung, ‘Opportunities and constraints of beekeeping practices in Ethiopia’, J of Api 2019, 34, 169–180.
- 24A. Kassaye, ‘The honeybees (Apis mellifera) of Ethiopia-a morphometric study’, The honeybees (Apis mellifera) of Ethiopia-a morphometric study. 1990.
- 25N. Volpi, G. Bergonzini, ‘Analysis of flavonoids from propolis by on-line HPLC–electrospray mass spectrometry’, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 42, 354–361.
- 26A. C. H. F. Sawaya, I. Barbosa da Silva Cunha, M. C. Marcucci, ‘Analytical methods applied to diverse types of Brazilian propolis’, Chem. Cent. J. 2011, 5, 1–10.
- 27F. M. A. de Carvalho, J. K. Schneider, C. V. F. de Jesus, L. N. de Andrade, R. G. Amaral, J. M. David, L. C. Krause, P. Severino, C. M. F. Soares, E. C. Bastos, F. F. Padilha, S. V. F. Gomes, R. Capasso, A. Santini, E. B. Souto, R. L. C. de Albuquerque-Júnior, ‘Brazilian Red Propolis: Extracts Production, Physicochemical Characterization, and Cytotoxicity Profile for Antitumor Activity’, Biomol. Eng. 2020, 10, 1–15.
- 28A. Petrova, M. Popova, C. Kuzmanova, I. Tsvetkova, H. Naydenski, E. Muli, V. Bankova, ‘New biologically active compounds from Kenyan propolis’, Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 509–514.
- 29A. Ikuta, H. Itokawa, ‘Triterpenoids of Paeonia japonica callus tissue’, Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 2813–2815.
- 30S. B. Mahato, S. Sen, ‘Advances in triterpenoid research, 1990–1994’, Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 1185–1236.
- 31S. Seo, Y. Tomita, K. Tori, ‘Carbon-13 NMR spectra of urs-12-enes and application to structural assignments of components of Isodon japonicus Hara tissue cultures’, Tetrahedron Lett. 1975, 16, 7–10.
10.1016/S0040-4039(00)71763-1 Google Scholar
- 32F. Ververidis, E. Trantas, C. Douglas, G. Vollmer, G. Kretzschma, N. Panopoulos, ‘Biotechnology of flavonoids and other phenylpropanoid-derived natural products. Part I: Chemical diversity, impacts on plant biology and human health’, Biotechnol. J. 2007, 2, 1214–1234.
- 33A. Salatino, É. W. Teixeira, G. Negri, ‘Origin and chemical variation of Brazilian propolis’, Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2005, 2, 33–38.
- 34S. Ramnath, S. Venkataramegowda, C. Singh, ‘Chemical composition of bee propolis collected from different regions in India by GCMS analysis’, J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2015, 30, 1319–1328.
- 35T. Omara, A. K. Kiprop, V. J. Kosgei, ‘Isolation and characterization of compounds in ethanolic extract of Albizia coriaria (Welw ex. Oliver) leaves: a further evidence of its ethnomedicinal diversity’, Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2022, 46, 30.
10.1186/s42269-022-00716-0 Google Scholar
- 36V. F. de Castro Ishida, G. Negri, A. Salatino, M. F. C. Bandeira, ‘A new type of Brazilian propolis: prenylated benzophenones in propolis from Amazon and effects against cariogenic bacteria’, Food Chem. 2011, 125, 966–972.
- 37C. S. Machado, J. B. Mokochinski, T. O. d. Lira, F. d. C. E. de Oliveira, M. V. Cardoso, R. G. Ferreira, A. C. H. F. Sawaya, A. G. Ferreira, C. Pessoa, O. Cuesta-Rubio, ‘Comparative study of chemical composition and biological activity of yellow, green, brown, and red Brazilian propolis’, Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1–10.
- 38M. L. Silva, D. A. Luz, A. R. Q. Gomes, M. C. Monteiro, C. S. Machado, Y. R. Torres, T. O. de Lira, A. G. Ferreira, E. A. Fontes-Júnior, C. S. F. Maia, ‘Research Article Neurobehavioral and Antioxidant Effects of Ethanolic Extract of Yellow Propolis’, Oxid. Met. 2016, 2016, 1–14.
- 39A. A. Mahamat, J. N. Nyemb, I. S. Gade, A. T. Ngenge, E. Talla, H. Céline, L. Sophie, J. T. Mbafor, ‘A New fatty acid and some triterpenoids from propolis of Nkambe (North-West Region, Cameroon) and evaluation of the antiradical scavenging activity of their extracts’, Open Chem. J. 2020, 18, 239–243.
- 40S. Paul, ‘Two New Cycloartenol and Some Pentacyclic Triterpenoids from Cameroonian Propolis (Ngaoundal, AD Region) and Evaluation of their Antimicrobial Activity’, Nat Prod Chem Res 2021, 9, 415.
- 41S. Ramnath, S. Venkataramegowda, C. Singh, ‘Chemical composition of bee propolis collected from different regions in India by GCMS analysis’, International Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 2015, 30, 1319–1328.
- 42C. Chandramu, R. Manohar, D. Krupadanam, R. Dashavantha, ‘Isolation, characterization and biological activity of betulinic acid and ursolic acid from Vitex negundo L. Phytother Res’, Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 129–134.
- 43J. M. Sforcin, V. Bankova, ‘Propolis: is there a potential for the development of new drugs?’, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 253–260.
- 44N. El Menyiy, M. Bakour, A. El Ghouizi, S. El Guendouz, B. Lyoussi, ‘Influence of Geographic Origin and Plant Source on Physicochemical Properties, Mineral Content, and Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Moroccan Propolis’, Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 5570224.
- 45I. Przybyłek, T. M. Karpiński, ‘Antibacterial Properties of Propolis’, Molecules 2019, 24.
- 46Q. Ding, A. R. Sheikh, X. Gu, J. Li, K. Xia, N. Sun, R. A. Wu, L. Luo, Y. Zhang, H. Ma, ‘Chinese Propolis: Ultrasound-assisted enhanced ethanolic extraction, volatile components analysis, antioxidant and antibacterial activity comparison’, Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 313–330.
- 47R. M, A. Richardson, M. Azirun, ‘Antibacterial activity of propolis and honey against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli’, Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 1872–1878.
- 48R. P. Dantas Silva, B. A. Machado, G. A. Barreto, S. S. Costa, L. N. Andrade, R. G. Amaral, A. A. Carvalho, F. F. Padilha, J. D. Barbosa, M. A. Umsza-Guez, ‘Antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiparasitic, and cytotoxic properties of various Brazilian propolis extracts’, PLoS One 2017, 12, e0172585.
- 49K. Georgieva, M. Popova, L. Dimitrova, B. Trusheva, L. N. Thanh, D. T. L. Phuong, N. T. P. Lien, H. Najdenski, V. Bankova, ‘Phytochemical analysis of Vietnamese propolis produced by the stingless bee Lisotrigona cacciae’, PLoS One 2019, 14, e0216074.
- 50M. Jug, O. Karas, I. Kosalec, ‘The influence of extraction parameters on antimicrobial activity of propolis extracts’, Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 1934578X1701200113.
- 51M. Popova, D. Gerginova, B. Trusheva, S. Simova, A. N. Tamfu, O. Ceylan, K. Clark, V. Bankova, ‘A Preliminary Study of Chemical Profiles of Honey, Cerumen, and Propolis of the African Stingless Bee Meliponula ferruginea’, Food 2021, 10, 1–17.
- 52M. Popova, E. Giannopoulou, K. Skalicka-Woźniak, K. Graikou, J. Widelski, V. Bankova, H. Kalofonos, G. Sivolapenko, K. Gaweł-Bęben, B. Antosiewicz, I. Chinou, ‘Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Propolis from Poland’, Molecules 2017, 22.
- 53M. Popova, B. Trusheva, D. Antonova, S. Cutajar, D. Mifsud, C. Farrugia, I. Tsvetkova, H. Najdenski, V. Bankova, ‘The specific chemical profile of Mediterranean propolis from Malta’, Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1431–1435.
- 54A. Al-Daamy, N. Abdzaid, R. Salman, M. Mohamed, A. Dekel, R. Abdul-Muhsen, ‘Study of antibacterial activity in the local Iraqi propolis’, Journal of Contemporary Medical Sciences 2015, 1, 1–7.
- 55A. A. Gharib, M. Taha, ‘Antimicrobial Activity Of Propolis Against Some Bacteria and Fungi’, Zagazig Vet. J. 2013, 41, 81–97.
10.21608/zvjz.2013.94459 Google Scholar
- 56T. S. Jafarzadeh Kashi, R. Kasra Kermanshahi, M. Erfan, E. Vahid Dastjerdi, Y. Rezaei, F. S. Tabatabaei, ‘Evaluating the In-vitro Antibacterial Effect of Iranian Propolis on Oral Microorganisms’, Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research: IJPR 2011, 10, 363–368.
- 57N. Sahar, Biochemical and Biological Evaluation of Propolis, Capital University, Islamabad, 2020, pp. 23–40.
- 58I. Al-Ani, S. Zimmermann, J. Reichling, M. Wink, ‘Antimicrobial Activities of European Propolis Collected from Various Geographic Origins Alone and in Combination with Antibiotics’, Medicine (Basel) 2018, 5, 1–17.
- 59A. R. Torres, L. P. Sandjo, M. T. Friedemann, M. M. Tomazzoli, M. Maraschin, C. F. Mello, A. R. S. Santos, ‘Chemical characterization, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of propolis obtained from Melipona quadrifasciata quadrifasciata and Tetragonisca angustula stingless bees’, Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7118.
- 60E. Alday, M. Navarro-Navarro, A. Garibay-Escobar, R. Robles-Zepeda, J. Hernandez, C. Velazquez, ‘Advances in pharmacological activities and chemical composition of propolis produced in Americas’, J. Adv. Res. 2016.
- 61N. A. Abdullah, N. Zullkiflee, S. N. Z. Zaini, H. Taha, F. Hashim, A. Usman, ‘Phytochemicals, mineral contents, antioxidants, and antimicrobial activities of propolis produced by Brunei stingless bees Geniotrigona thoracica, Heterotrigona itama, and Tetrigona binghami’, Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2902–2911.
- 62D. Devequi-Nunes, B. A. S. Machado, G. A. Barreto, J. Rebouças Silva, D. F. da Silva, J. L. C. da Rocha, H. N. Brandão, V. M. Borges, M. A. Umsza-Guez, ‘Chemical characterization and biological activity of six different extracts of propolis through conventional methods and supercritical extraction’, PLoS One 2018, 13, e0207676.
- 63T. G. do Nascimento, R. E. Dos Santos Arruda, E. T. da Cruz Almeida, J. M. Dos Santos Oliveira, I. D. Basílio-Júnior, I. C. Celerino de Moraes Porto, A. Rodrigues Sabino, J. Tonholo, A. Gray, R. E. Ebel, C. Clements, T. Zhang, D. G. Watson, ‘Comprehensive multivariate correlations between climatic effect, metabolite-profile, antioxidant capacity and antibacterial activity of Brazilian red propolis metabolites during seasonal study’, Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18293.
- 64M. S. N. Regueira, S. R. Tintino, A. R. P. da Silva, M. D. S. Costa, A. A. Boligon, E. F. F. Matias, V. de Queiroz Balbino, I. R. A. Menezes, H. D. Melo Coutinho, ‘Seasonal variation of Brazilian red propolis: Antibacterial activity, synergistic effect and phytochemical screening’, Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 572–580.
- 65F. Marletto, ‘Propolis characteristics in relation to the floral origin and the bees’ utilization of it’, Apicoltore Moderno (Italy) 1983, 74, 187–191.
- 66E. Muli, J. Maingi, ‘Antibacterial activity of Apis mellifera L. propolis collected in three regions of Kenya’, J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2007, 13, 655–663.
- 67M. A. Wikler, ‘Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically: approved standard’, CLSI (NCCLS) 2006, 26, M7-A7.
- 68B. Pharmacopoeia, ‘The pharmaceutical press’, Her Majesty's Stationary Office, London 1998, 1, 125.