Introducing Functional Groups Into B←N Organic Frameworks with Permanent Porosity
Huifang Zhou
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorTiantian Jiang
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorKangjian Fu
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xinyu Guan
Hangzhou Institute of Advanced Studies, College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Zhejiang Normal University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310000 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorShilin Guan
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Bo Liu
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Hai-Long Jiang
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorHuifang Zhou
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorTiantian Jiang
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorKangjian Fu
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xinyu Guan
Hangzhou Institute of Advanced Studies, College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Zhejiang Normal University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310000 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorShilin Guan
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Bo Liu
College of Chemistry & Pharmacy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, 712100 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Hai-Long Jiang
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorHomepage: http://mof.ustc.edu.cn/
Graphical Abstract
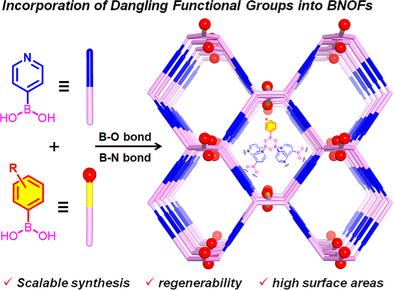
The functionality of crystalline organic frameworks incorporating dative B←N and reversible B─O bonds (BNOFs) is engineered by introducing diverse dangling groups. Notably, the carboxyl-functionalized BNOF-5 exhibits superior reversible NH₃ adsorption compared with their less- or nonfunctionalized counterparts. Combining high surface areas, low cost, and exceptional sustainability, these functionalized frameworks represent a promising platform for advanced applications.
Abstract
Crystalline organic frameworks incorporating dative B←N and reversible B─O bonds (BNOFs) have garnered increasing interest on account of their crystallinity, porosity, and processability. However, strategies for introducing functions into BNOFs remain largely unexplored. In this work, a series of functionalized BNOFs, named BNOF-n (n = 2–9), have been designed and synthesized using a mixed-monomer assembly strategy. The obtained materials share structural similarities but reveal distinct functional groups, demonstrating excellent chemical stability, high surface areas, and remarkable regenerability. Notably, BNOF-5, functionalized with abundant carboxyl groups, achieves exceptional reversible NH3 adsorption capacity (up to 10.0 mmol g−1 at 1 bar and 298 K), significantly surpassing that of the nonfunctionalized BNOF-1 (5.6 mmol g−1) and the less-functionalized BNOF-7 (7.9 mmol g−1), thereby clearly demonstrating the effectiveness of the functionalization strategy. Remarkably, the damaged BNOF-5 can be efficiently repaired through facile regeneration, highlighting its outstanding recyclability. This work demonstrates the first attempt at functionalization methodology in BNOFs, extending their potential toward diverse applications.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202509174-sup-0001-SuppMat.docx5 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202509174-sup-0002-SuppMat.zip987.1 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1H. Li, M. Eddaoudi, M. O'Keeffe, O. M. Yaghi, Nature 1999, 402, 276–279.
- 2S. Kitagawa, R. Kitaura, S.-i. Noro, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2334–2375.
- 3J.-P. Zhang, Y.-B. Zhang, J.-B. Lin, X.-M. Chen, Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1001–1033.
- 4M. O'Shaughnessy, J. Glover, R. Hafizi, M. Barhi, R. Clowes, S. Y. Chong, S. P. Argent, G. M. Day, A. I. Cooper, Nature 2024, 630, 102–108.
- 5Y. Wu, M. Tang, M. L. Barsoum, Z. Chen, F. Huang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 2906–2947.
- 6H. Furukawa, K. E. Cordova, M. O'Keeffe, O. M. Yaghi, Science 2013, 341, 1230444.
- 7B. Li, H.-M. Wen, Y. Cui, W. Zhou, G. Qian, B. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8819–8860.
- 8S. Yuan, L. Feng, K. Wang, J. Pang, M. Bosch, C. Lollar, Y. Sun, J. Qin, X. Yang, P. Zhang, Q. Wang, L. Zou, Y. Zhang, L. Zhang, Y. Fang, J. Li, H.-C. Zhou, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704303.
- 9Z. Chen, S. L. Hanna, L. R. Redfern, D. Alezi, T. Islamoglu, O. K. Farha, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 386, 32–49.
- 10H. Jiang, D. Alezi, M. Eddaoudi, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 466–487.
- 11G. Wei, Z. Chen, J. Dong, Y. Liu, Y. Cui, Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 9078–9144.
- 12W. Wang, Y. Chen, P. Feng, X. Bu, Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2403834.
- 13Q. Yin, Z.-Y. Wang, Z.-B. Fang, H.-X. Liu, Y. Hou, C. Liu, W. Deng, T.-F. Liu, CCS Chem. 2024, https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.024.202404630.
- 14C. S. Diercks, O. M. Yaghi, Science 2017, 355, eaal1585.
- 15K. Geng, T. He, R. Liu, S. Dalapati, K.-T. Tan, Z. Li, S. Tao, Y. Gong, Q. Jiang, D. Jiang, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8814–8933.
- 16J. Han, J. Feng, J. Kang, J.-M. Chen, X.-Y. Du, S.-Y. Ding, L. Liang, W. Wang, Science 2024, 383, 1014–1019.
- 17H. Zhuang, C. Guo, J. Huang, L. Wang, Z. Zheng, H.-N. Wang, Y. Chen, Y.-Q. Lan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202404941.
- 18Y. Yin, Y. Zhang, X. Zhou, B. Gui, W. Wang, W. Jiang, Y.-B. Zhang, J. Sun, C. Wang, Science 2024, 386, 693–696.
- 19F. Chen, H. Zheng, Y. Yusran, H. Li, S. Qiu, Q. Fang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 484–514.
- 20K. Wang, X. Qiao, H. Ren, Y. Chen, Z. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 8063–8082.
- 21J. Jiang, Y. Zhao, O. M. Yaghi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3255–3265.
- 22L. Hashemi, M. Y. Masoomi, H. Garcia, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 472, 214776.
- 23L. Geng, Y. Qiao, R. Sun, L. Guo, Z.-Q. Li, Y. Ma, M.-H. Yu, Z. Chang, X.-H. Bu, Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2415511.
- 24R.-B. Lin, Y. He, P. Li, H. Wang, W. Zhou, B. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1362–1389.
- 25Z.-J. Lin, S. A. R. Mahammed, T.-F. Liu, R. Cao, ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 1589–1608.
- 26Y. Zou, H.-X. Liu, L. Cai, Y.-H. Li, J.-S. Hu, C. Liu, T.-F. Liu, Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2406026.
- 27X. Meng, S. Zou, J. Li, C. Chen, J. Zhang, M. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202415346.
- 28B.-T. Liu, S.-H. Gong, X.-T. Jiang, Y. Zhang, R. Wang, Z. Chen, S. Zhang, K. O. Kirlikovali, T.-F. Liu, O. K. Farha, R. Cao, Nat. Synth. 2023, 2, 873–879.
- 29X. Song, Y. Wang, C. Wang, X. Gao, Y. Zhou, B. Chen, P. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 627–634.
- 30B. Liu, P. Guo, X. Guan, X. Tian, F. Du, W. Xie, H.-L. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202405027.
- 31W. Liu, S.-D. Jiang, Y. Yan, W. Wang, J. Li, K. Leng, S. Japip, J. Liu, H. Xu, Y. Liu, I.-H. Park, Y. Bao, W. Yu, M. D. Guiver, S. Zhang, K. P. Loh, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1633.
- 32C. Gropp, T. Ma, N. Hanikel, O. M. Yaghi, Science 2020, 370, eabd6406.
- 33M. D. Preuss, T. Schnitzer, S. A. H. Jansen, S. C. J. Meskers, T. H. R. Kuster, X. Lou, E. W. Meijer, G. Vantomme, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202402644.
- 34M. Qiao, Y. Li, Y. Li, M. Chang, X. Zhang, S. Yuan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202409951.
- 35Z.-H. Zhao, C.-H. Li, J.-L. Zuo, SmartMat 2023, 4, e1187.
- 36B. Chen, F. Jäkle, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202313379.
- 37E. Sheepwash, V. Krampl, R. Scopelliti, O. Sereda, A. Neels, K. Severin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3034–3037.
- 38H. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Chen, Y. Yang, H. Lin, S. Xiang, B. Chen, Z. Zhang, Chem 2023, 9, 242–252.
- 39W. Wang, L. Wang, F. Du, G.-D. Wang, L. Hou, Z. Zhu, B. Liu, Y.-Y. Wang, Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 533–539.
- 40Q. Dong, T. Naren, L. Zhang, W. Jiang, M. Xue, X. Wang, L. Chen, C.-S. Lee, Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202405426.
- 41D. Xiao, Z. Jin, G. Sheng, L. Chen, X. Xiao, T. Shan, J. Wang, R. Navik, J. Xu, L. Zhou, Q.-H. Guo, G. Li, Y. Zhu, J. F. Stoddart, F. Huang, Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 1906–1914.
- 42J. Cruz-Huerta, D. Salazar-Mendoza, J. Hernández-Paredes, I. F. H. Ahuactzic, H. Höpfl, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4241.
- 43N. Luisier, K. Bally, R. Scopelliti, F. T. Fadaei, K. Schenk, P. Pattison, E. Solari, K. Severin, Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 6600–6604.
- 44A. J. Stephens, R. Scopelliti, F. F. Tirani, E. Solari, K. Severin, ACS Mater. Lett. 2019, 1, 3–7.
- 45X. Wang, Z. Ke, L. Liu, J. Huang, Y. Yang, W. Dai, C. Liu, Z. Zhang, Z. Yao, S. Xiang, Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 3168–3174.
- 46C.-H. Liu, L. Chen, H. Zhang, Y. Li, H. Lin, L. Li, J. Wu, C. Liu, Z.-M. Ye, S. Xiang, B. Chen, Z. Zhang, Chem 2023, 9, 3532–3543.
- 47S. Bhandary, M. Beliš, R. Shukla, L. Bourda, A. M. Kaczmarek, K. V. Hecke, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 8659–8667.
- 48J. Xu, T. Wang, S. Deng, W. Lai, Y. Shi, Y. Zhao, F. Huang, P. Wei, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202411880.
- 49X. Wang, L. Zhang, X. Wang, T. Cheng, M. Xue, Q. Dong, Y. Peng, Q. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 35, 2401362.
- 50X. Sheng, Z. Wang, G. Sheng, C. Zhu, D. Xiao, T. Shan, X. Xiao, M. Liu, G. Li, Y. Zhu, J. L. Sessler, F. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 12547–12555.
- 51H. Lin, H. Zhang, Y. Li, F. Yuan, X. Zheng, L. He, L. Li, Y. Zhang, S. Xiang, B. Chen, Z. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202415968.
- 52L. Zhang, Z. Chen, X.-X. Li, X. Wang, Q. Gu, X. Wang, C. S. Lee, Y.-Q. Lan, Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202411018.
- 53Y. Li, H. Chen, J. Huang, H. Zhang, S. Lin, Z.-M. Ye, S. Xiang, B. Chen, Z. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 19425–19433.
- 54F. Yuan, G. Han, C. Chen, X. Fan, S. Xiang, Z. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202501875.
- 55R. F. Service, Science 2018, 361, 120–123.
- 56M. Aziz, A. T. Wijayanta, A. B. D. Nandiyanto, Energies 2020, 13, 3062.
- 57J. F. Van Humbeck, T. M. McDonald, X. Jing, B. M. Wiers, G. Zhu, J. R. Long, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2432–2440.
- 58K. Ono, T. Ishikawa, S. Masano, H. Kawai, K. Goto, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 21417–21427.
- 59C. Marsh, X. Han, J. Li, Z. Lu, S. P. Argent, I. da Silva, Y. Cheng, L. L. Daemen, A. J. Ramirez-Cuesta, S. P. Thompson, A. J. Blake, S. Yang, M. Schröder, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6586–6592.
- 60D. W. Kim, D. W. Kang, M. Kang, D. S. Choi, H. Yun, S. Y. Kim, S. M. Lee, J.-H. Lee, C. S. Hong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9672–9683.