A Synergistic Photocatalysis–Electrocatalysis System for Efficient Hydrogen Generation and Energy-Saving Benzylamine Oxidative Upgrading
Graphical Abstract
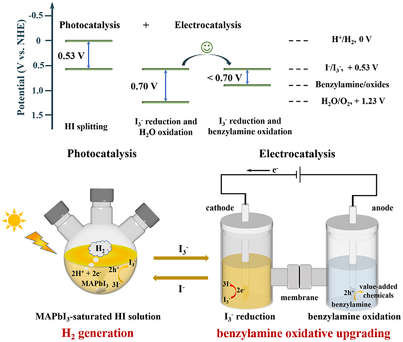
A synergistic photocatalysis–electrocatalysis system addresses the I3− light shielding in HI splitting and achieves efficient H2 generation and energy-saving benzylamine oxidative upgrading. The Re0.5Mo0.5S2-modified MAPbI3 photocatalyst generates 875.4 µmol of H2 in 4 h, and the electrocatalytic I3− reduction coupled with benzylamine oxidation can operate at a low potential of 0.44 V for 10 mA cm−2.
Abstract
Photocatalytic hydrogen iodide (HI) splitting represents a promising tactic for H2 generation, but the light-shielding effect induced by the generated I3− greatly impedes subsequent reactions. A critical challenge in this field lies in achieving the timely reduction of I3− while avoiding the use of additional sacrificial agents, such as H3PO2. Herein, we develop a synergistic photocatalysis–electrocatalysis system to address this challenge and achieve efficient H2 generation and benzylamine oxidative upgrading. The photocatalytic component features a Re0.5Mo0.5S2 cocatalyst-modified MAPbI3 with efficient charge separation and ample active sites, achieving a remarkable H2 generation of 875.4 µmol within 4 h through HI splitting. The subsequent electrocatalytic module can operate at a low potential (only 0.44 V to reach 10 mA cm−2) to reduce the generated I3− and oxidize benzylamine to value-added chemicals. After the electrolysis, the regenerated HI solution can be recycled for subsequent photocatalytic H2 generation. The synergistic system establishes a sustainable catalytic cycle mediated by I−/I3− redox couples, enabling continuous photocatalytic H2 generation from HI splitting and energy-saving electrocatalytic benzylamine oxidative upgrading.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.