Synthesis and Characterization of Circumtetracene: Unraveling Structure-Property Relationships of Circumacenes
Graphical Abstract
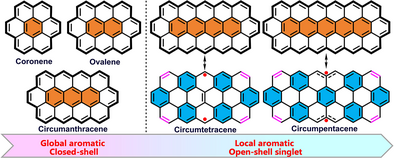
A stable circumtetracene derivative has been successfully synthesized and isolated in crystalline form. A comparison of its electronic properties (both experimentally and by theoretical calculations) with those of previously reported circumacene analogues, led to elucidation of a significant transition in the electronic structure from a closed-shell global aromatic to a singlet open-shell local aromatic configuration upon π-extension.
Abstract
Circumacenes have garnered significant interest in both fundamental science and nanoelectronics due to their unique electronic structures. However, their synthesis and investigations into the structure–property relationships present considerable challenges. In this work, we report the successful synthesis and characterization of a stable circumtetracene derivative in crystalline form. For comparison, a new circumanthracene derivative was also prepared. The electronic properties of both compounds were systematically investigated using both various experimental techniques and theoretical calculations. It was found that circumtetracene exhibits a dominant local aromatic nature with small open-shell diradical character, while circumanthracene displays a closed-shell global aromatic character. Both compounds show amphoteric redox behavior with narrow energy gaps. The dication of circumtetracene and the dianions of circumtetracene and circumanthracene can be obtained experimentally through chemical oxidation and reduction, all displaying intense NIR absorptions. Furthermore, the electronic properties of these derivatives were compared with those of previously reported circumacene analogues, revealing a transition in electronic structure from closed-shell global aromatic to singlet open-shell local aromatic configurations upon π-extension. This work provides a comprehensive exploration of the structure-property relationships within the circumacene series, offering valuable insights for the design and synthesis of novel multizigzag-edged nanographenes with tunable electronic properties.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.