Superfast Protein Desulfurization Triggered by Low-Energy Visible Light
Dongyang Han
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiangyu Deng
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYan Cui
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXianglai Zhu
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorGuiyu Deng
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorLu-Jun Liang
Center for BioAnalytical Chemistry, Hefei National Laboratory of Physical Science at Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guo-Chao Chu
Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230022 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lei Liu
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDongyang Han
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiangyu Deng
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYan Cui
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXianglai Zhu
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorGuiyu Deng
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorLu-Jun Liang
Center for BioAnalytical Chemistry, Hefei National Laboratory of Physical Science at Microscale, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guo-Chao Chu
Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230022 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lei Liu
New Cornerstone Science Laboratory, Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, MOE Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
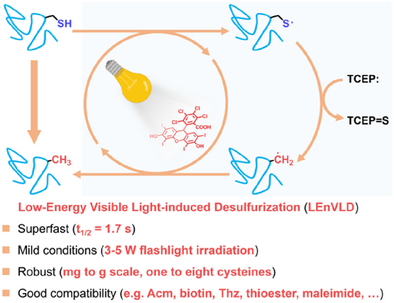
A practical strategy of low-energy visible light-induced desulfurization (LEnVLD) has been developed to enable superfast and clean desulfurization under exceptionally mild conditions. The utility of LEnVLD was demonstrated through the clean desulfurization of a wide range of peptide and protein substrates, and its convenience and robustness facilitated the application of LEnVLD in versatile reaction scenarios such as solid-supported desulfurization and flow chemistry-based desulfurization.
Abstract
The combination of transthioesterification-based ligation of thiol-derived amino acids and the post-ligation desulfurization has greatly expanded the scope of modern chemical protein synthesis. Here, we report a new strategy of low-energy visible light-induced desulfurization (LEnVLD) that enables superfast and clean protein desulfurization (half life = 1.7 s) with improved reaction selectivity compared to the previous methods. The LEnVLD method can be easily carried out under very mild conditions using only a catalytic amount of fluorescent dye and household flashlight (ca. 5 W) irradiation, eliminating the need for any pyrophoric reagent, thiol additives, or excessive radical initiators, and its practicality was demonstrated by the fast and high-yielding desulfurization of more than 30 peptide and protein substrates bearing a variety of sensitive functional groups (e.g., Thz, N-alkylated maleimide, and thioester). Moreover, the convenience and robustness of LEnVLD enable its extension to versatile reaction scenarios (e.g., solid-supported desulfurization and flow chemistry-based desulfurization) that would enhance the practical capability of chemical protein synthesis.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202502884-sup-0001-SupMat.docx6.4 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1S. B. Kent, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 338–351.
- 2V. R. Pattabiraman, J. W. Bode, Nature 2011, 480, 471–479.
- 3Z.-Q. Sun, H. Liu, X.-C. Li, Chem 2023, 10, 767–799.
- 4S. Bondalapati, M. Jbara, A. Brik, Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 407–418.
- 5H.-S. Ai, M. Pan, L. Liu, ACS Cent. Sci. 2024, 10, 1442–1459.
- 6J.-S. Zheng, S. Tang, Y.-K. Qi, Z.-P. Wang, L. Liu, Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2483–2495.
- 7Y.-K. Qi, J.-S. Zheng, L. Liu, Chem 2024, 10, 2930–2407.
- 8A. T. Balana, A.-L. Mahul-Mellier, B. A. Nguyen, M. Horvath, A. Javed, E. R. Hard, Y. Jasiqi, P. Singh, S. Afrin, S. Pedretti, V. Singh, V. M.-Y. Lee, K. C. Luk, L. Saelices, H. A. Lashuel, M. R. Pratt, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2024, 20, 646–655.
- 9M. Pan, Q.-Y. Zheng, T. Wang, L.-J. Liang, J.-X. Mao, C. Zuo, R.-C. Ding, H.-S. Ai, Y. Xie, S. Dong, Y.-Y. Yu, L. Liu, M.-L. Zhao, Nature 2021, 600, 334–338.
- 10G.-C. Chu, L.-J. Liang, R. Zhao, Y.-Y. Guo, C.-T. Li, C. Zuo, H. Ai, X. Hua, Z.-C. Li, Y.-M. Li, L. Liu, CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 2031–2043.
- 11H. Ai, M. Sun, A. Liu, Z. Sun, T. Liu, L. Cao, L. Liang, Q. Qu, Z. Li, Z. Deng, Z. Tong, G. Chu, X. Tian, H. Deng, S. Zhao, J.-B. Li, Z. Lou, L. Liu, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 972–980.
- 12M. L. Merz, S. Habeshian, B. Li, J.-A. G. L. David, A. L. Nielsen, X.-J. Ji, K. I. Khwildy, M. M. D. Benitez, P. Phothirath, C. Heinis, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2024, 20, 624–633.
- 13S.-W. Dong, J.-S. Zheng, Y.-M. Li, H. Wang, G. Chen, Y.-X. Chen, G.-M. Fang, J. Guo, C.-M. He, H.-G. Hu, X.-C. Li, Y.-M. Li, Z.-G. Li, M. Pan, S. Tang, C.-L. Tian, P. Wang, B. Wu, C.-L. Wu, J.-F. Zhao, L. Liu, Sci. Chin. Chem. 2024, 67, 1060–1096.
- 14Z. Tong, H. Ai, Z. Xu, K. He, G.-C. Chu, Q. Shi, Z. Deng, Q. Xue, M. Sun, Y. Du, L. Liang, J.-B. Li, M. Pan, L. Liu, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2024, 31, 300–310.
- 15H. Ai, Z. He, Z. Deng, G.-C. Chu, Q. Shi, Z. Tong, J.-B. Li, M. Pan, L. Liu, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2024, 31, 1745–1755.
- 16P. E. Dawson, T. W. Muir, I. Clark-Lewis, S. B. Kent, Science 1994, 266, 776–779.
- 17Y.-C. Huang, G.-M. Fang, L. Liu, Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 107–116.
- 18A. Miseta, P. Csutora, Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 1232–1239.
- 19L. Z. Yan, P. E. Dawson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 526–533.
- 20Q. Wan, S. J. Danishefsky, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 9248–9252.
- 21K. Jin, T.-L. Li, H. Y. Chow, H. Liu, X.-C. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14607–14611.
- 22S. N. Bavikar, L. Spasser, M. Haj-Yahya, S. V. Karthikeyan, M. Moyal, K. S. A. Kumar, A. Brik, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 758–763.
- 23R. Jing, M. A. Walczak, Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 2590–2595.
- 24R. Desmet, C. Boidin-Wichlacz, R. Mhidia, A. Tasiemski, A. Agouridas, O. Melnyk, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302648.
- 25T. S. Chisholm, D. Clayton, L. J. Dowman, J. Sayers, R. J. Payne, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 9020–9024.
- 26L. Kambanis, A. Ayoub, M. J. Bedding, P. H. G. Egelund, J. W. C. Maxwell, C. Franck, L. Lambrechts, P. M. E. Hawkins, T. S. Chisholm, J. P. Mackay, E. Sierecki, Y. Gambin, S. S. Kulkarni, R. J. Payne, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 22027–22035.
- 27N. M. Venneti, G. Samala, R. M. I. Morsy, L. G. Mendoza, A. Isidro-Llobet, J. K. Tom, J. L. Stockdill, M. E. Kopach, J. L. Stockdill, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 1053–1061.
- 28D. Han, Y. Cui, X. Deng, C. Li, X. Zhu, B. Wang, G.-C. Chu, Z. A. Wang, S. Tang, J.-S. Zheng, L.-J. Liang, L. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 4135–4146.
- 29M. Waliczek, P. Stefanowicz, Org. Lett. 2025, 27, 1159–1163.
- 30N. Metanis, E. Keinan, P. E. Dawson, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7049–7053.
- 31L. R. Malins, N. J. Mitchell, S. McGowan, R. J. Payne, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12716–12721.
- 32V. Diemer, E. Roy, V. Agouridas, O. Melnyk, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 8521–8545.
- 33S. Dery, P. S. Reddy, L. Dery, R. Mousa, R. N. Dardashti, N. Metanis, Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 6207–6212.
- 34Z.-Q. Sun, W.-J. Ma, Y.-H. Cao, T.-Y. Wei, X.-Y. Mo, H. Y. Chow, Y. Tan, C. H. P. Cheung, J.-M. Liu, H. K. Lee, E. C. M. Tse, H. Liu, X.-C. Li, Chem 2022, 8, 2542–2557.
- 35D. M. Yan, J. R. Chen, W. J. Xiao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 378–380.
- 36J. Yan, H. Tang, E. J. R. Kuek, X. Shi, C. Liu, M. Zhang, J. L. Piper, S. Duan, J. Wu, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7214–7224.
- 37J. P. Tam, Q.-T. Yu, Biopolymers 1998, 46, 319–327.
10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(19981015)46:5<319::AID-BIP3>3.0.CO;2-S CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 38C. Haase, H. Rohde, O. Seitz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6807–6810.
- 39S. Li, C. Schöneich, R. T. Borchardt, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 48, 490–500.
- 40C. Haase, H. Rohde, O. Seitz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6807–6810.
- 41E. Welker, L. Hathaway, G. Xu, M. Narayan, L. Pradeep, H. Shin, H. A. Scheraga, Biochemistry 2007, 46, 5485–5493.
- 42D. Ramadhani, R. Maharani, A. M. Gazzali, M. Muchtaridi, Molecules 2022, 27, 4428.
- 43M. H. Houshdar Tehrani, M. Gholibeikian, A. Bamoniri, B. B. F. Mirjalili, Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 600856.
- 44G.-M. Fang, Y.-M. Li, F. Shen, Y.-C. Huang, J.-B. Li, Y. Lin, H.-K. Cui, L. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7645–7649.
- 45D. T. Flood, J. C. J. Hintzen, M. J. Bird, P. A. Cistrone, J. S. Chen, P. E. Dawson, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11634–11639.
- 46T. Maruhashi, D. Sugiura, I. Okazaki, T. Okazaki, J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001014.
- 47K. Sun, S. Li, B. Zheng, Y. Zhu, T. Wang, M. Liang, Y. Yao, K. Zhang, J. Zhang, H. Li, D. Han, J. Zheng, B. Coventry, L. Cao, D. Baker, L. Liu, P. Lu, Cell Res. 2024, 34, 846–858.
- 48T. Y. Wang, W. W. Shi, G.-C. Chu, Y.-M. Li, Chin. J. Chem. 2024, 42, 2316–2322.
- 49T. Li, J. Liu, Y. Song, F. Wang, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8450–8458.
- 50B. Basu, S. Paul, J. Catal. 2013, 614829.
- 51P. Arya, G. Panda, N. V. Rao, H. Alper, S. C. Bourque, L. E. Manzer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2889–2890.
- 52A. Zhang, S. Li, L. Apone, X. Sun, L. Chen, L. M. Ettwiller, B. W. Langhorst, C. J. Noren, M.-Q. Xu, Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15887.