Metal-Free Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization to Prepare Recylable Micro-Adjuvants for Dendritic Cell Vaccine
Hengyuan Zhang
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorXingyu Heng
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorHe Yang
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Rao
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorLihua Yao
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhichen Zhu
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Gaojian Chen
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Hong Chen
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorHengyuan Zhang
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorXingyu Heng
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorHe Yang
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Rao
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorLihua Yao
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhichen Zhu
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Gaojian Chen
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Hong Chen
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Soochow University, Suzhou, 215123 Jiangsu, China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
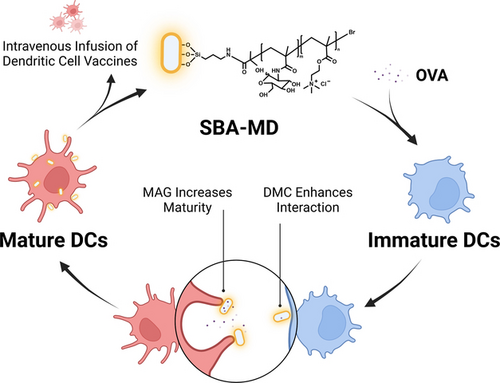
This study introduces an innovative approach that combines high efficacy with safety through the synthesis of P(MAG-co-DMC) based micro-adjuvants. The utilization of metal-free surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization enables the production of safe and recyclable adjuvants. Additionally, the adjuvants exhibit a “micro-ligand-mediated maturation enhancement” effect for DC maturation.
Abstract
In the development of dendritic cell (DC) vaccines, the maturation of DCs is a critical stage. Adjuvants play a pivotal role in the maturation of DCs, with a major concern being to ensure both efficacy and safety. This study introduces an innovative approach that combines high efficacy with safety through the synthesis of micro-adjuvants grafted with copolymers of 2-(methacrylamido) glucopyranose (MAG) and methacryloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (DMC). The utilization of metal-free surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization enables the production of safe and recyclable adjuvants. These micrometer-sized adjuvants surpass the optimal size range for cellular endocytosis, enabling the retrieval and reuse of them during the ex vivo maturation process, mitigating potential toxicity concerns associated with the endocytosis of non-metabolized nanoparticles. Additionally, the adjuvants exhibit a “micro-ligand-mediated maturation enhancement” effect for DC maturation. This effect is influenced by the shape of the particle, as evidenced by the distinct promotion effects of rod-like and spherical micro-adjuvants with comparable sizes. Furthermore, the porous structure of the adjuvants enables them to function as cargo-carrying “micro-shuttles”, releasing antigens upon binding to DCs to facilitate efficient antigen delivery.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202402853-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf936.3 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aJ. Li, H. M. Zeng, L. W. Li, Q. Yang, L. He, M. Q. Dong, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 24593–24618;
- 1bA. Nguyen, S. Kumar, A. A. Kulkarni, Small Methods 2022, 6;
- 1cC. L. Liu, M. X. Yang, D. Z. Zhang, M. Chen, D. Zhu, Front. Immunol. 2022, 13;
- 1dT. H. Tran, T. T. P. Tran, H. T. Nguyen, C. D. Phung, J. H. Jeong, M. H. Stenzel, S. G. Jin, C. S. Yong, D. H. Truong, J. O. Kim, Int. J. Pharmaceut 2018, 542, 253–265.
- 2
- 2aS. Najafi, K. Mortezaee, Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164;
- 2bX. X. Xie, T. Song, Y. Feng, H. X. Zhang, G. Yang, C. H. Wu, F. M. You, Y. Y. Liu, H. Yang, Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437;
- 2cQ. Wang, Z. Wang, X. X. Sun, Q. K. Jiang, B. J. Sun, Z. G. He, S. W. Zhang, C. Luo, J. Sun, J. Controlled Release 2022, 351, 102–122;
- 2dE. Gilboa, J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 1195–1203.
- 3
- 3aH. Dong, Q. Li, Y. Zhang, M. Ding, Z. G. Teng, Y. B. Mou, Adv. Sci. 2023, 10;
- 3bA. Gardner, A. D. Pulido, B. Ruffell, Front. Immunol. 2020, 11;
- 3cC. M. Le Gall, J. Weiden, L. J. Eggermont, C. G. Figdor, Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 474–475.
- 4I. Y. Filin, K. V. Kitaeva, C. S. Rutland, A. A. Rizvanov, V. V. Solovyeva, Front. Oncol. 2021, 11.
- 5
- 5aX. Y. Shen, C. J. Zhu, X. T. Liu, H. Q. Zheng, Q. Wu, J. J. Xie, H. Huang, Z. Y. Liao, J. Q. Shi, K. W. Nan, J. X. Wang, X. M. Mao, Z. Gu, H. J. Li, Biomater Sci-Uk 2023, 11, 1137–1152;
- 5bB. B. Zheng, J. J. Xu, G. X. Chen, S. H. Zhang, Z. Y. Xiao, W. Lu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29;
- 5cS. Kumar, R. Sunagar, E. Gosselin, Front. Immunol. 2019, 10.
- 6
- 6aY. T. Liu, K. Adu-Berchie, J. M. Brockman, M. Pezone, D. K. Y. Zhang, J. Y. Zhou, J. W. Pyrdol, H. Wang, K. W. Wucherpfennig, D. J. Mooney, P Natl Acad Sci USA 2023, 120;
- 6bL. Guo, R. X. Wei, R. Sun, Q. Yang, G. J. Li, L. Y. Wang, H. B. Luo, M. Feng, J. Controlled Release 2021, 337, 417–430;
- 6cG. J. Chen, Z. Gu, Nat Biomed Eng 2020, 4, 4–5.
- 7
- 7aW. Cho, S. Won, Y. Choi, S. Yi, J. B. Park, J. G. Park, C. E. Kim, C. Narayana, J. H. Kim, J. Yim, Y. I. Choi, D. S. Lee, S. B. Park, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62;
- 7bL. L. Cheng, P. Zhang, Y. D. Liu, Z. Y. Liu, J. J. Tang, L. T. Xu, J. Liu, Biomaterials 2023, 301;
- 7cB. I. Koo, S. M. Jin, H. Kim, D. J. Lee, E. Lee, Y. S. Nam, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2021, 10.
- 8
- 8aZ. Y. Guo, I. Noh, A. T. Zhu, Y. Y. Yu, W. W. Gao, R. H. Fang, L. F. Zhang, Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 7941–7949;
- 8bH. Tian, G. H. Wang, W. Sang, L. S. Xie, Z. Zhang, W. X. Li, J. Yan, Y. Tian, J. Li, B. Li, Y. L. Dai, Nano Today 2022, 43;
- 8cM. Y. Chen, S. Juengpanich, S. J. Li, W. Topatana, Z. Y. Lu, Q. Zheng, J. S. Cao, J. H. Hu, E. Chan, L. D. Hou, J. Chen, F. Chen, Y. Liu, S. Jiansirisomboon, Z. Gu, S. Tongpeng, X. J. Cai, Adv. Sci. 2022, 9;
- 8dJ. Xiang, L. G. Xu, H. Gong, W. W. Zhu, C. Wang, J. Xu, L. Z. Feng, L. Cheng, R. Peng, Z. Liu, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6401–6411;
- 8eM. C. Lin, Y. F. Zhang, G. S. Chen, M. Jiang, Small 2015, 11, 6065–6070.
- 9
- 9aX. Y. Heng, R. Y. Feng, L. J. Zhu, L. Y. Yu, G. J. Chen, H. Chen, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4331–4334;
- 9bL. Y. Yu, R. Y. Feng, L. J. Zhu, Q. Hao, J. C. Chu, Y. Gu, Y. Luo, Z. X. Zhang, G. J. Chen, H. Chen, Sci. Adv. 2020, 6;
- 9cY. Masuda, Y. Nakayama, T. Mukae, A. Tanaka, K. Naito, M. Konishi, Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 408–416.
- 10
- 10aN. Petrovsky, Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 1059–1074;
- 10bS. G. Reed, M. T. Orr, C. B. Fox, Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1597–1608.
- 11
- 11aQ. Huang, L. X. Yan, H. D. Wei, X. J. Ye, W. L. Wang, C. Yang, X. P. Yan, Y. Zhang, J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 121;
- 11bJ. M. Bi, C. Z. Mo, S. W. Li, M. S. Huang, Y. H. Lin, P. Y. Yuan, Z. J. Liu, B. Jia, S. M. Xu, Biomater Sci-Uk 2023, 11, 4151–4183;
- 11cC. F. Teng, C. J. Jiang, S. L. Gao, X. J. Liu, S. M. Zhai, Nanomaterials 2021, 11;
- 11dD. M. Teleanu, C. Chircov, A. M. Grumezescu, R. I. Teleanu, Nanomaterials 2019, 9;
- 11eL. Shang, K. Nienhaus, G. U. Nienhaus, J. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 12.
- 12C. H. Dong, W. Feng, W. W. Xu, L. D. Yu, H. Xiang, Y. Chen, J. Q. Zhou, Adv. Sci. 2020, 7.
- 13
- 13aH. Yang, Z. J. Xiong, X. Y. Heng, X. M. Niu, Y. C. Wang, L. H. Yao, L. L. Sun, Z. Liu, H. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023;
- 13bT. Ikazaki, E. Ishikawa, H. Tamashima, H. Akiyama, Y. Kimuro, M. Yoritate, H. Matoba, A. Imamura, H. Ishida, S. Yamasaki, G. Hirai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023;
- 13cM. H. Stenzel, Macromolecules 2022, 55, 4867–4890;
- 13dL. Su, Y. L. Feng, K. C. Wei, X. Y. Xu, R. Y. Liu, G. S. Chen, Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 10950–11029;
- 13eM. N. Zhou, C. S. Delaveris, J. R. Kramer, J. A. Kenkel, E. G. Engleman, C. R. Bertozzi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3137–3142;
- 13fY. Miura, Y. Hoshino, H. Seto, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1673–1692;
- 13gQ. Zhang, J. Collins, A. Anastasaki, R. Wallis, D. A. Mitchell, C. R. Becer, D. M. Haddleton, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4435–4439.
- 14N. Means, C. K. Elechalawar, W. R. Chen, R. Bhattacharya, P. Mukherjee, Mol. Aspects Med. 2022, 83.
- 15
- 15aY. J. Zeng, Y. F. Xiang, R. L. Sheng, H. Tomás, J. Rodrigues, Z. W. Gu, H. Zhang, Q. Y. Gong, K. Luo, Bioact Mater 2021, 6, 3358–3382;
- 15bR. Y. Feng, L. J. Zhu, X. Y. Heng, G. J. Chen, H. Chen, Acs Appl Mater Inter 2021, 13, 36859–36867;
- 15cY. Gu, B. Liu, Q. Liu, Y. J. Hang, L. Wang, J. L. Brash, G. J. Chen, H. Chen, Acs Appl Mater Inter 2019, 11, 47720–47729.
- 16X. Y. Heng, F. J. Shan, H. Yang, J. Hu, R. Y. Feng, W. D. Tian, G. J. Chen, H. Chen, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023, 12.
- 17
- 17aR. Kumar, C. F. Santa Chalarca, M. R. Bockman, C. Van Bruggen, C. J. Grimme, R. J. Dalal, M. G. Hanson, J. K. Hexum, T. M. Reineke, Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11527–11652;
- 17bJ. P. Bost, H. Barriga, M. N. Holme, A. Gallud, M. Maugeri, D. Gupta, T. Lehto, H. Valadi, E. K. Esbjörner, M. M. Stevens, S. El-Andaloussi, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18590–18591.
- 18
- 18aQ. Ma, J. S. Song, X. Zhang, Y. Jiang, L. Ji, S. H. Liao, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12;
- 18bC. W. Lu, C. P. Wang, J. Yu, J. F. Wang, F. X. Chu, Green Chem. 2019, 21, 2759–2770;
- 18cG. Yilmaz, Y. Yagci, Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 1757–1762;
- 18dV. K. Singh, C. Yu, S. Badgujar, Y. Kim, Y. Kwon, D. Kim, J. Lee, T. Akhter, G. Thangavel, L. S. Park, J. Lee, P. C. Nandajan, R. Wannemacher, B. Milián-Medina, L. Lüer, K. S. Kim, J. Gierschner, M. S. Kwon, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 794–804;
- 18eE. H. Discekici, A. Anastasaki, J. R. de Alaniz, C. J. Hawker, Macromolecules 2018, 51, 7421–7434;
- 18fN. J. Treat, H. Sprafke, J. W. Kramer, P. G. Clark, B. E. Barton, J. R. de Alaniz, B. P. Fors, C. J. Hawker, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16096–16101.
- 19
- 19aD. T. O′Hagan, E. De Gregorio, Drug Discovery Today 2009, 14, 541–551;
- 19bT. B. H. Geijtenbeek, S. I. Gringhuis, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 465–479;
- 19cG. Napolitani, A. Rinaldi, F. Bertoni, F. Sallusto, A. Lanzavecchia, Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 769–776.
- 20
- 20aP. Liu, X. Wang, M. S. Itano, A. K. Neumann, A. M. de Silva, K. Jacobson, N. L. Thompson, Traffic 2014, 15, 179–196;
- 20bA. K. Neumann, N. L. Thompson, K. Jacobson, J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 634–643.
- 21W. Kim, W. K. Kim, K. Lee, M. J. Son, M. Kwak, W. S. Chang, J. K. Min, N. W. Song, J. Lee, K. H. Bae, Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7375–7387.
- 22
- 22aA. H. Bahrami, Soft Matter 2013, 9, 8642–8646;
- 22bG. Sharma, D. T. Valenta, Y. Altman, S. Harvey, H. Xie, S. Mitragotri, J. W. Smith, J. Controlled Release 2010, 147, 408–412.