Palladium-Catalyzed Skeletal Rearrangement of Substituted 2-Silylaryl Triflates via 1,5-C−Pd/C−Si Bond Exchange
Daigo Hayashi
Division of Chemistry, Department of Materials Engineering Science, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-8531 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Tomohiro Tsuda
Division of Chemistry, Department of Materials Engineering Science, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-8531 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Ryo Shintani
Division of Chemistry, Department of Materials Engineering Science, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-8531 Japan
Innovative Catalysis Science Division, Institute for Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives (ICS-OTRI), Osaka University, Suita, Osaka 565-0871 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorDaigo Hayashi
Division of Chemistry, Department of Materials Engineering Science, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-8531 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Tomohiro Tsuda
Division of Chemistry, Department of Materials Engineering Science, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-8531 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Ryo Shintani
Division of Chemistry, Department of Materials Engineering Science, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, Toyonaka, Osaka 560-8531 Japan
Innovative Catalysis Science Division, Institute for Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives (ICS-OTRI), Osaka University, Suita, Osaka 565-0871 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
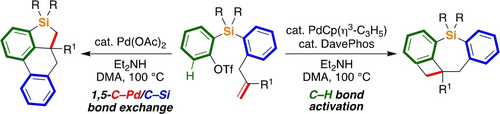
A palladium-catalyzed skeletal rearrangement of 2-(2-allylarylsilyl)aryl triflates has been developed to give tetrahydrophenanthrosiloles via 1,5-C−Pd/C−Si bond exchange. The reaction pathways can be switched by tuning the reaction conditions to give fused dihydrodibenzosilepin derivatives from the same starting materials. The inspection of the reaction conditions revealed the importance of carboxylates in promoting the C−Pd/C−Si bond exchange.
Abstract
A palladium-catalyzed skeletal rearrangement of 2-(2-allylarylsilyl)aryl triflates has been developed to give highly fused tetrahydrophenanthrosilole derivatives via unprecedented 1,5-C−Pd/C−Si bond exchange. The reaction pathways can be switched toward 4-membered ring-forming C(sp2)−H alkylation by tuning the reaction conditions to give completely different products, fused dihydrodibenzosilepin derivatives, from the same starting materials. The inspection of the reaction conditions revealed the importance of carboxylates in promoting the C−Pd/C−Si bond exchange.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202313171-sup-0001-6d.cif2.2 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202313171-sup-0001-7s.cif741.5 KB | Supporting Information |
| anie202313171-sup-0001-8p.cif675.3 KB | Supporting Information |
| anie202313171-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf12.5 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For selected recent reviews:
- 1aD. L. Priebbenow, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 1927;
- 1bL. Li, Y.-L. Wei, L.-W. Xu, Synlett 2020, 31, 21;
- 1cP. Xiao, L. Gao, Z. Song, Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 2407;
- 1dJ.-S. Li, J. Wu, ChemPhotoChem 2018, 2, 839;
- 1eT. Komiyama, Y. Minami, T. Hiyama, Synlett 2017, 28, 1873; See also:
- 1fP. Sahoo, M. Majumdar, Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 1281.
- 2For reviews:
- 2aR. Ramesh, D. S. Reddy, J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3779;
- 2bE. Rémond, C. Martin, J. Martinez, F. Cavelier, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 11654;
- 2cA. K. Franz, S. O. Wilson, J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 388;
- 2dG. A. Showell, J. S. Mills, Drug Discovery Today 2003, 8, 551.
- 3For reviews:
- 3aZ. Chen, S. Feng, D. Wang, Polymer 2023, 15, 332;
- 3bL. D. Pham, N. Q. Nguyen, M. O. Hight, T. A. Su, J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 11605;
- 3cY. Zuo, Z. Gou, W. Quan, W. Lin, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 438, 213887;
- 3dJ. Y. Corey, Adv. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 59, 181;
- 3eW. W. H. Wong, J. F. Hooper, A. B. Holmes, Aust. J. Chem. 2009, 62, 393;
- 3fJ. Chen, Y. Cao, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 1714.
- 4For examples of biologically active silacycles:
- 4aJ. O. Daiss, C. Burschka, J. S. Mills, J. G. Montana, G. A. Showell, I. Fleming, C. Gaudon, D. Ivanova, H. Gronemeyer, R. Tacke, Organometallics 2005, 24, 3192;
- 4bJ. O. Daiss, C. Burschka, J. S. Mills, J. G. Montana, G. A. Showell, J. B. H. Warneck, R. Tacke, Organometallics 2006, 25, 1188;
- 4cR. Tacke, V. Müller, M. W. Büttner, W. P. Lippert, R. Bertermann, J. O. Daiß, H. Khanwalkar, A. Furst, C. Gaudon, H. Gronemeyer, ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1797;
- 4dJ. Wang, C. Ma, Y. Wu, R. A. Lamb, L. H. Pinto, W. F. DeGrado, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 13844;
- 4eR. Ramesh, D. S. Reddy, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 4093;
- 4fH. Toyama, M. Nakamura, Y. Hashimoto, S. Fujii, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 2982.
- 5For selected recent examples:
- 5aX.-B. Wang, Z.-J. Zheng, J.-L. Xie, X.-W. Gu, Q.-C. Mu, G.-W. Yin, F. Ye, Z. Xu, L.-W. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 790;
- 5bY. Qin, J.-L. Han, C.-W. Ju, D. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8481;
- 5cM.-H. Zhu, X.-W. Zhang, M. Usman, H. Cong, W.-B. Liu, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 5703;
- 5dW. Wang, S. Zhou, L. Li, Y. He, X. Dong, L. Gao, Q. Wang, Z. Song, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 11141;
- 5eY. Qin, L. Li, J.-Y. Liang, K. Li, D. Zhao, Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 14224;
- 5fX. Tang, Y. Zhang, Y. Tang, Y. Li, J. Zhou, D. Wang, L. Gao, Z. Su, Z. Song, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 5185;
- 5gH. Chen, J. Peng, Q. Pang, H. Du, L. Huang, L. Gao, Y. Lan, C. Yang, Z. Song, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212889.
- 6For selected recent examples:
- 6aW.-T. Zhao, Z.-Q. Lu, H. Zheng, X.-S. Xue, D. Zhao, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7997;
- 6bF. Chen, Y. Shao, M. Li, C. Yang, S.-J. Su, H. Jiang, Z. Ke, W. Zeng, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3304;
- 6cY. Xu, W. Xu, X. Chen, X. Luo, H. Lu, M. Zhang, X. Yang, G. Deng, Y. Liang, Y. Yang, Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 11756;
- 6dY. Zeng, X.-J. Fang, R.-H. Tang, J.-Y. Xie, F.-J. Zhang, Z. Xu, Y.-X. Nie, L.-W. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202214147; See also:
- 6eT. Tsuda, S.-M. Choi, R. Shintani, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1641;
- 6fT. Ikeuchi, K. Hirano, M. Uchiyama, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4879;
- 6gH. Liu, P. He, X. Liao, Y. Zhou, X. Chen, W. Ou, Z. Wu, C. Luo, L. Yang, J. Xu, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 9864;
- 6hX.-X. Zhang, Y. Gao, Y.-X. Zhang, J. Zhou, J.-S. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217724.
- 7For reviews:
- 7aW.-T. Zhao, F. Gao, D. Zhao, Synlett 2018, 29, 2595;
- 7bL. Li, Y. Zhang, L. Gao, Z. Song, Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1466;
- 7cL. L. Wang, Z. Duan, Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 307;
- 7dJ. Hermanns, B. Schmidt, J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1998, 2209.
- 8For recent reviews on 1,n-metal migration reactions:
- 8aM.-Y. Li, D. Wei, C.-G. Feng, G.-Q. Lin, Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200456;
- 8bJ. Corpas, P. Mauleón, R. G. Arrayás, J. C. Carretero, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 7513;
- 8cX. Dong, H. Wang, H. Liu, F. Wang, Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 3530;
- 8dA. Rahim, J. Feng, Z. Gu, Chin. J. Chem. 2019, 37, 929.
- 9For pioneering examples:
- 9aM. A. Campo, R. C. Larock, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14326;
- 9bQ. Huang, A. Fazio, G. Dai, M. A. Campo, R. C. Larock, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7460.
- 10For pioneering examples:
- 10aK. Oguma, M. Miura, T. Satoh, M. Nomura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10464;
- 10bT. Hayashi, K. Inoue, N. Taniguchi, M. Ogasawara, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9918.
- 11
- 11aC. Bour, J. Suffert, Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 653;
- 11bY. Sato, C. Takagi, R. Shintani, K. Nozaki, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9211;
- 11cJ.-L. Han, Y. Qin, C.-W. Ju, D. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6555.
- 12
- 12aM. Tobisu, J. Hasegawa, Y. Kita, H. Kinuta, N. Chatani, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 11437;
- 12bN. Ishida, Y. Shimamoto, T. Yano, M. Murakami, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 19103;
- 12cT. Matsuda, I. Yuihara, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7393;
- 12dM. Font, B. Cendón, A. Seoane, J. L. Mascareñas, M. Gulías, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8255.
- 13
- 13aT. Seiser, N. Cramer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 10163; See also:
- 13bQ.-W. Zhang, K. An, W. He, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5667.
- 14
- 14aY. Liang, S. Zhang, Z. Xi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9204;
- 14bY. Liang, W. Geng, J. Wei, Z. Xi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1934;
- 14cT. Meng, K. Ouyang, Z. Xi, RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 14273;
- 14dY. Shi, X. Shi, J. Zhang, Y. Qin, B. Li, D. Zhao, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6697.
- 15
- 15aM. Tobisu, M. Onoe, Y. Kita, N. Chatani, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7506;
- 15bM. Onoe, K. Baba, Y. Kim, Y. Kita, M. Tobisu, N. Chatani, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19477.
- 16T. Tsuda, Y. Kawakami, S.-M. Choi, R. Shintani, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8057.
- 17For selected reviews on C−H bond activation under transition-metal catalysis:
- 17aP. Wedi, M. van Gemmeren, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13016;
- 17bC. Sambiagio, D. Schönbauer, R. Blieck, T. Dao-Huy, G. Pototschnig, P. Schaaf, T. Wiesinger, M. F. Zia, J. Wencel-Delord, T. Besset, B. U. W. Maes, M. Schnürch, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6603;
- 17cC. Liu, J. Yuan, M. Gao, S. Tang, W. Li, R. Shi, A. Lei, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12138;
- 17dN. Kuhl, M. N. Hopkinson, J. Wencel-Delord, F. Glorius, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10236.
- 18Deposition numbers 2247988, 2247989, and 2247990 contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service.
- 19For relevant benzocyclobutene synthesis:
- 19aJ. Ye, Z. Shi, T. Sperger, Y. Yasukawa, C. Kingston, F. Schoenebeck, M. Lautens, Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 361;
- 19bF. Ye, Y. Ge, A. Spannenberg, H. Neumann, M. Beller, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5383; See also:
- 19cM. Catellani, G. P. Chiusoli, S. Ricotti, J. Organomet. Chem. 1985, 296, C11;
- 19dX. Wu, J. Zhou, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11035;
- 19eL. Zhang, L. Liu, T. Huang, Q. Dong, T. Chen, Organometallics 2020, 39, 2189.
- 20S. D. Walker, T. E. Barder, J. R. Martinelli, S. L. Buchwald, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1871.
- 21X. Huang, K. W. Anderson, D. Zim, L. Jian, A. Klapars, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6653.
- 22D. W. Old, J. P. Wolfe, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9722.
- 23The C−H bond activation presumably proceeds through diethylamine-assisted deprotonation-palladation.
- 23aN. Misawa, T. Tsuda, R. Shintani, K. Yamashita, K. Nozaki, Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 2566;
- 23bX. Yan, M. Yang, Y.-B. She, Y.-F. Yang, Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 737. See also the Supporting Information.
- 24
- 24aM. Chaumontet, R. Piccard, N. Audic, J. Hitce, J.-L. Peglion, E. Clot, O. Baudoin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15157;
- 24bS. Rousseaux, M. Davi, J. Sofack-Kreutzer, C. Pierre, C. E. Kefalidis, E. Clot, K. Fagnou, O. Baudoin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10706;
- 24cC. E. Kefalidis, M. Davi, P. M. Holstein, E. Clot, O. Baudoin, J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 11903;
- 24dB. Xu, D. Ji, L. Wu, L. Zhou, Y. Liu, Z.-M. Zhang, J. Zhang, Chem 2022, 8, 836; See also:;
- 24eP. A. Provencher, J. F. Hoskin, J. J. Wong, X. Chen, J.-Q. Yu, K. N. Houk, E. J. Sorensen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 20035.
- 25For reviews:
- 25aL. Ackermann, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1315;
- 25bD. Lapointe, K. Fagnou, Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 1118; For a pioneering work:;
- 25cM. Lafrance, K. Fagnou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16496.
- 26See the Supporting Information for details.
- 27Et2NH was chosen as the ligand for palladium, following the relevant literature precedent: Reference [23b].
- 28B. Su, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12137.
- 29D. Sarkar, A. V. Gulevich, F. S. Melkonyan, V. Gevorgyan, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6792.
- 30
- 30aA. Kovács, A. Vasas, J. Hohmann, Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1084;
- 30bJ. Qi, D. Zhou, W. Jiang, G. Chen, W. Li, N. Li, Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 13, 480.
- 31
- 31aY. Shoyama, I. Nishioka, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1978, 26, 3641;
- 31bF. S. El-Feraly, Y.-M. Chan, J. Nat. Prod. 1981, 44, 557;
- 31cM. Asim, D. Klonowska, C. Choueiri, I. Korobkov, K. E. Carlson, J. A. Katzenellenbogen, T. Durst, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3713.
- 32K. Šindelář, J. O. Jílek, V. Bártl, J. Metyšová, B. Kakáč, J. Holubek, E. Svátek, J. Pomykáček, M. Protiva, Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1976, 41, 910.
- 33
- 33aV. H. Rawal, M. P. Cava, Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 5581;
- 33bY. Nishida, S. Sugahara, K. Wada, D. Toyohisa, T. Tanaka, M. Ono, S. Yasuda, Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1351;
- 33cC. Zhang, F. Li, Y. Yu, A. Huang, P. He, M. Lei, J. Wang, L. Huang, Z. Liu, J. Liu, Y. Wei, J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3618.