Discovering Dynamic Plant Enzyme Complexes in Yeast for Kratom Alkaloid Pathway Identification**
A previous version of this manuscript has been deposited on a preprint server (https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.16.524293).
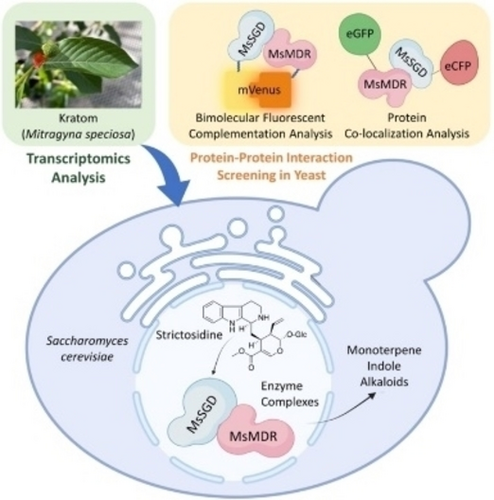
Graphical Abstract
Yeast-based protein-protein interaction (PPI) screening identified dynamic enzyme complexes and biosynthetic pathways they organize from a rare plant, kratom. PPI screening identified four functional medium-chain dehydrogenases (MsMDRs) interacting with strictosidine β-D-glucosidase (MsSGD), leading to four novel pathway branches. This study highlights how leveraging post-translational regulation features can accelerate the discovery of biosynthetic pathways in plants.
Abstract
Discovering natural product biosynthetic pathways of medicinal plants is challenging and laborious. Capturing the coregulation patterns of pathway enzymes, particularly transcriptomic regulation, has proven an effective method to accelerate pathway identification. In this study, we developed a yeast-based screening method to capture the protein-protein interactions (PPI) between plant enzymes, which is another useful pattern to complement the prevalent approach. Combining this method with plant multiomics analysis, we discovered four enzyme complexes and their organized pathways from kratom, an alkaloid-producing plant. The four pathway branches involved six enzymes, including a strictosidine synthase, a strictosidine β-D-glucosidase (MsSGD), and four medium-chain dehydrogenase/reductases (MsMDRs). PPI screening selected six MsMDRs interacting with MsSGD from 20 candidates predicted by multiomics analysis. Four of the six MsMDRs were then characterized as functional, indicating the high selectivity of the PPI screening method. This study highlights the opportunity of leveraging post-translational regulation features to discover novel plant natural product biosynthetic pathways.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.