Rate and Selectivity Enhancements Mediated by OH Radicals in the Oxidative Coupling of Methane Catalyzed by Mn/Na2WO4/SiO2†
This study was supported by BP as part of the Methane Conversion Cooperative Research Program at the University of California at Berkeley.
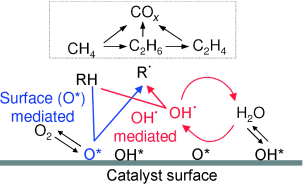
Graphical Abstract
Radically Improved: OH radicals formed by quasi-equilibrated steps on oxide surfaces introduce homogeneous pathways that lead to higher rates and C2 yields in oxidative methane coupling relative to those attained by CH4 activation with chemisorbed oxygen (see picture; O*: dissociated oxygen atom; R: abstractor). The reactivity of OH. leads to a weaker influence of the CH bond energies on the relative rates of H abstraction from CH4, C2H6, and C2H4.