Hydrogen-Bonded Sugar-Alcohol Trimers as Hexadentate Silicon Chelators in Aqueous Solution†
Polyol metal complexes, Part 41. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft within the framework of the program “Principles of Biomineralization” (grant Kl 624/7-1). We are indebted to Dipl.-Chem. M. Bootz (LMU Munich) for DFT calculations, and Dr. J. Senker (LMU Munich) for the 29Si and 13C solid-state NMR experiments.—Part 40: P. Klüfers, O. Krotz, M. Oßberger, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 6, 1919–1923.
Graphical Abstract
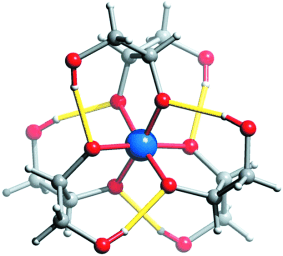
Building bridges: Fumed colloidal silica can be dissolved in alkaline aqueous solutions of the open-chain sugar alcohols mannitol, xylitol, and threitol. These polyols are able to form six-coordinate silicon complexes that are stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonds. The prototypical core is shown (yellow bars: the intramolecular H bonds).