The Catalytic Z to E Isomerization of Stilbenes in a Photosensitizing Porous Coordination Network†
This research was supported by the CREST project of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), for which M.F. is the principal investigator, and also in part by KAKENHI (20044006), JSPS, and Global COE Program (Chemistry Innovation through Cooperation of Science and Engineering), MEXT (Japan).
Graphical Abstract
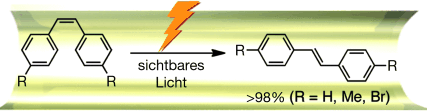
Einbahnreaktion: Die Z→E-Photoisomerisierung von Stilben durch sichtbares Licht geschieht in einem porösen Koordinationsnetzwerk (siehe Bild). Die Reaktion verläuft in einer Pore über die Photoanregung des Ladungstransfer-Komplexes zwischen einem elektronenarmen Liganden und dem Stilben. Das in situ gebildete E-Isomer wird schnell gegen nicht umgesetztes Z-Isomer aus der Lösung ausgetauscht, daher genügt eine katalytische Menge des Netzwerkes, um die Reaktion voranzutreiben.