Hydrodeoxygenation of Lignin-Derived Phenols into Alkanes by Using Nanoparticle Catalysts Combined with Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquids†
Ning Yan Dr.
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne (Switzerland)
Search for more papers by this authorYuan Yuan Dr.
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne (Switzerland)
Search for more papers by this authorRyan Dykeman
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne (Switzerland)
Search for more papers by this authorYuan Kou Prof. Dr.
PKU Green Chemistry Center, Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorPaul J. Dyson Prof. Dr.
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne (Switzerland)
Search for more papers by this authorNing Yan Dr.
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne (Switzerland)
Search for more papers by this authorYuan Yuan Dr.
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne (Switzerland)
Search for more papers by this authorRyan Dykeman
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne (Switzerland)
Search for more papers by this authorYuan Kou Prof. Dr.
PKU Green Chemistry Center, Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorPaul J. Dyson Prof. Dr.
Institut des Sciences et Ingénierie Chimiques, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), 1015 Lausanne (Switzerland)
Search for more papers by this authorThis research was performed in the framework of Sino–Swiss Science & Technology Cooperation Program (No. 2010DFA42110).
Graphical Abstract
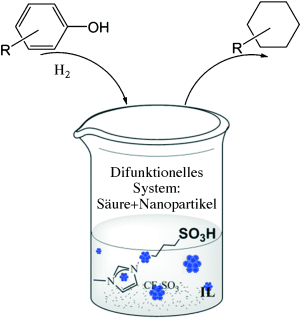
Wertschöpfung im Tandem: Ein katalytisches System bestehend aus Metall-Nanopartikeln (NPs) und einer funktionalisierten Brønsted-sauren ionischen Flüssigkeit (IL) in einer nichtfunktionalisierten IL wird beschrieben (siehe Bild). Das System ist hoch effizient für die Umsetzung von Lignin abgeleiteter phenolischer Verbindungen zu Alkanen, wobei die Hydrierung und Dehydratisierung als Tandemprozess ablaufen.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ange_201001531_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf1,014.1 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1G. W. Huber, S. Iborra, A. Corma, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4044–4098.
- 2For some recent reviews see:
- 2aS. Lee, J. G. Speight, S. K. Loyalka, Handbook of Alternative Fuel Technologies, CRC, Boca Raton, 2007, pp. 377–393;
10.1201/9781420014518.ch12 Google Scholar
- 2bS. Albertazzi, F. Basile, G. Fornasari, F. Trifiro, A. Vaccari, Catalysis for Renewables: From Feedstock to Energy Production, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2007, pp. 147–162.
10.1002/9783527621118.ch7 Google Scholar
- 3For examples see:
- 3aD. Meier, R. Ante, O. Faix, Bioresour. Technol. 1992, 40, 171–177;
- 3bA. Oasmaa, R. Alen, Bioresour. Technol. 1993, 45, 189–194;
- 3cD. Meier, J. Berns, O. Faix, U. Balfanz, W. Baldauf, Biomass Bioenergy 1994, 7, 99–105;
- 3dR. W. Thring, J. Breau, Fuel 1996, 75, 795–800;
- 3eN. Yan, C. Zhao, P. J. Dyson, C. Wang, L. Liu, Y. Kou, ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 626–629.
- 4J. S. Shabtai, W. W. Zmierczak, E. Chornet, US Patent 5959167, 1999.
- 5For example see:
- 5aM. Kudsy, H. Kumazawa, E. Sada, Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1995, 73, 411–415;
- 5bM. Kudsy, H. Kumazawa, Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1999, 77, 1176–1184;
- 5cM. M. Hepditch, R. W. Thring, Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2000, 78, 226–231.
- 6For some recent examples see:
- 6aP. F. Britt, A. C. Buchanan, M. J. Cooney, D. R. Martineau, J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 1376–1389;
- 6bG. Dobele, I. Urbanovich, A. Volpert, V. Kampars, E. Samulis, BioResources 2007, 2, 699–706;
- 6cA. A. Boateng, C. A. Mullen, N. Goldberg, K. B. Hicks, H. G. Jung, J. F. S. Lamb, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 4115–4122;
- 6dL. Ingram, D. Mohan, M. Bricka, P. Steele, D. Strobel, D. Crocker, B. Mitchell, J. Mohammad, K. Cantrell, C. U. Pittman, Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 614–625;
- 6eR. French, S. Czernik, Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 25–32.
- 7S. Czernik, A. V. Bridgwater, Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 590–598.
- 8S. Crossley, J. Faria, M. Shen, D. E. Resasco, Science 2010, 327, 68–72.
- 9For example see:
- 9aE. G. Baker, D. C. Elliott, US Patent, 5,180,868, 1993;
- 9bE. Laurent, B. Delmon, J. Catal. 1994, 146, 281–291;
- 9cA. Centeno, E. Laurent, B. Delmon, J. Catal. 1995, 154, 288–298;
- 9dE. Furimsky, F. E. Massoth, Catal. Today 1999, 52, 381–495;
- 9eJ. S. Shabtai, W. W. Zmierczak, E. Chornet, US Patent, 5,959,167, 1999;
- 9fT. R. Viljava, R. S. Komulanien, A. O. I. Krause, Catal. Today 2000, 60, 83–92.
- 10
- 10aC. Zhao, Y. Kou, A. A. Lemonidou, X. Li, J. A. Lercher, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4047–4050; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3987–3990;
- 10bC. Zhao, Y. Kou, A. A. Lemonidou, X. Li, J. A. Lercher, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 412–414.
- 11H. Panneman, A. A. C. M. Beenackers, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 1433–1440.
- 12For a recent review see: A. Pinkert, K. N. Marsh, S. Pang, M. P. Staiger, Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6712–6728.
- 13For example see:
- 13aA. P. Abbott, P. M. Cullis, M. J. Gibson, R. C. Harris, E. Raven, Green Chem. 2007, 9, 868–872;
- 13bB. A. D. Neto, M. B. Alves, A. A. M. Lapis, F. M. Nachtigall, M. N. Eberlin, J. Dupont, P. A. Z. Suarez, J. Catal. 2007, 249, 154–161;
- 13cA. A. M. Lapis, L. F. de Oliveira, B. A. D. Neto, J. Dupont, ChemSusChem 2008, 1, 759–762;
- 13dM. J. Earle, N. V. Plechkova, K. R. Seddon, Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 2045–2057.
- 14J. B. Binder, M. J. Gray, J. F. White, Z. C. Zhang, J. E. Holladay, Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1122–1130.
- 15J. Dupont, G. S. Fonseca, A. P. Umpierre, P. F. P. Fichtner, S. R. Teixeira, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4228–4229.
- 16For example see:
- 16aG. S. Fonseca, A. P. Umpierre, P. F. P. Fichtner, S. R. Teixeira, J. Dupont, Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 3263–3269;
- 16bD. Astruc, F. Lu, J. Ruiz, Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 8062–8083; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7852–7872;
- 16cL. S. Ott, R. G. Finke, Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 8382–8393;
- 16dB. Léger, A. Denicourt-Nowicki, A. Roucoux, H. Olivier-Bourbigou, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 153–159;
- 16eL. Bastien, A. Denicourt-Nowicki, H. Olivier-Bourbigou, A. Roucoux, Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 9090–9096;
- 16fV. Calò, A. Nacci, A. Monopoli, P. Cotugno, Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 1272–1279;
- 16gN. Yan, X-C Xiao, Y. Kou, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 1179–1218, and references therein.
- 17X. Yang, N. Yan, Z. Fei, R. M. Crespo-Quesada, G. Laurenczy, L. Kiwi-Minsker, Y. Kou, Y. Li, P. J. Dyson, Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 7444–7446.
- 18
- 18aN. Yan, C. Zhao, C. Luo, P. J. Dyson, H. Liu, Y. Kou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8714–8715;
- 18bC.-X. Xiao, H.-Z. Wang, X.-D. Mu, Y. Kou, J. Catal. 2007, 250, 25–32.
- 19
- 19aX. Mu, J. Meng, Z. Li, Y. Kou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9694–9695;
- 19bC. Zhao, H.-Z. Wang, N. Yan, C.-X. Xiao, X.-D. Mu, P. J. Dyson, Y. Kou, J. Catal. 2007, 250, 33–40.
- 20
- 20aK. E. Johnson, R. M. Pagni, J. Bartmess, Monatsh. Chem. 2007, 138, 1077–1101 and references therein. For more recent examples see:
- 20bA. C. Pinto, A. A. M. Lapis, S. B. Vasconcellos, R. S. Bastos, J. Dupont, B. A. D. Neto, Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 5639–5641;
- 20cA. R. Hajipour, A. Rajaei, A. E. Ruoho, Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 708–711;
- 20dM. A. Harmer, C. P. Junk, V. V. Rostovtsev, W. J. Marshall, L. M. Grieco, J. Vickery, R. Miller, S. Work, Green Chem. 2009, 11, 517–525;
- 20eR. Juárez, R. Martin, M. Alvaro, H. Garcia, Appl. Catal. A 2009, 369, 133–137.
- 21A. C. Cole, J. L. Jensen, I. Ntai, K. L. T. Tran, K. J. Weaver, D. C. Forbes, J. H. Davis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 5962–5963.
- 22C. Thomazeau, H. Olivier-Bourbigou, L. Magna, S. Luts, B. Gilbert, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 5264–5265.
- 23J. M. Pringle, C. M. Forsyth, M. Forsyth, D. R. MacFarlane, Acta. Crystallogr. Sect. E 2003, 59, o 1759-o1761.
- 24R. L. Augustine, Heterogeneous Catalysis for the Synthetic Chemist, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1996, chap. 17.
Citing Literature
This is the
German version
of Angewandte Chemie.
Note for articles published since 1962:
Do not cite this version alone.
Take me to the International Edition version with citable page numbers, DOI, and citation export.
We apologize for the inconvenience.