Interleukin-19 ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalitis
Graphical Abstract
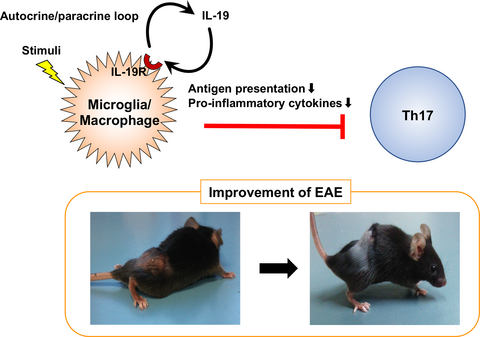
Interleukin-19 serves as a negative feedback regulator to limit the pro-inflammatory response of macrophages and microglia in autocrine/paracrine manners. Interleukin-19 suppresses microglia/macrophage antigen presentation, T helper 17 cell expansion and subsequent inflammation in the central nervous system, resulting in improvement in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.