Label-free ultra-sensitive visualization of structure below the diffraction resolution limit
Corresponding Author
Sergey Alexandrov
Tissue Optics & Microcirculation Imaging Group, School of Physics, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland
Correspondence
Sergey Alexandrov, Tissue Optics & Microcirculation Imaging Group, School of Physics, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJames McGrath
Tissue Optics & Microcirculation Imaging Group, School of Physics, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland
Search for more papers by this authorColin J. R. Sheppard
Department of Nanophysics, Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Genoa, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorFrancesca Boccafoschi
Department of Health Sciences, University of Piemonte Orientale “A. Avogadro”, Novara, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCinzia Giannini
Institute of Crystallography, National Research Council, Bari, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorTeresa Sibillano
Institute of Crystallography, National Research Council, Bari, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorHrebesh Subhash
Colgate-Palmolive Global Technology Center, Piscataway, New Jersey
Search for more papers by this authorMartin Leahy
Tissue Optics & Microcirculation Imaging Group, School of Physics, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Sergey Alexandrov
Tissue Optics & Microcirculation Imaging Group, School of Physics, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland
Correspondence
Sergey Alexandrov, Tissue Optics & Microcirculation Imaging Group, School of Physics, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJames McGrath
Tissue Optics & Microcirculation Imaging Group, School of Physics, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland
Search for more papers by this authorColin J. R. Sheppard
Department of Nanophysics, Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Genoa, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorFrancesca Boccafoschi
Department of Health Sciences, University of Piemonte Orientale “A. Avogadro”, Novara, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCinzia Giannini
Institute of Crystallography, National Research Council, Bari, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorTeresa Sibillano
Institute of Crystallography, National Research Council, Bari, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorHrebesh Subhash
Colgate-Palmolive Global Technology Center, Piscataway, New Jersey
Search for more papers by this authorMartin Leahy
Tissue Optics & Microcirculation Imaging Group, School of Physics, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
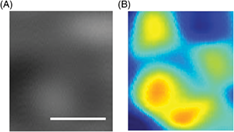
For both fundamental study of biological processes and early diagnosis of diseases, information about nanoscale changes in tissue and cell structure is crucial. Nowadays, almost all currently known nanoscopy methods rely upon the contrast created by fluorescent stains attached to the object or molecule of interest. This causes limitations due to the impact of the label on the object and its environment, as well as its applicability in vivo, particularly in humans. In this paper, a new label-free approach to visualize small structure with nano-sensitivity to structural alterations is introduced. Numerically synthesized profiles of the axial spatial frequencies are used to probe the structure within areas whose size can be beyond the diffraction resolution limit. Thereafter, nanoscale structural alterations within such areas can be visualized and objects, including biological ones, can be investigated with sub-wavelength resolution, in vivo, in their natural environment. Some preliminary results, including numerical simulations and experiments, which demonstrate the nano-sensitivity and super-resolution ability of our approach, are presented.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201700385-sup-0001-AppendixS1.docxWord 2007 document , 48.2 KB | Appendix S1. Supporting Information. |
| jbio201700385-sup-0002-AppendixS2.docxWord 2007 document , 426.3 KB | Appendix S2. Author biography. |
| jbio201700385-sup-0003-VideoS1.avivideo/avi, 615 KB | Video S1. Changes in size of probing structure which is used to probe a numerically synthesised object presented in Fig. 2A. |
| jbio201700385-sup-0004-VideoS2.avivideo/avi, 724.6 KB | Video S2. Changes in sSESF image of the numerically synthesized object as a result of probing with numerically synthesized structure (Video S1). |
| jbio201700385-sup-0005-VideoS3.avivideo/avi, 697.4 KB | Video S3. Changes in sSESF image of 400 nm spheres aggregates as a result of probing with numerically synthesized structure. |
| jbio201700385-sup-0006-VideoS4.avivideo/avi, 539.6 KB | Video S4. Changes in sSESF image of 520 nm spheres aggregates as a result of probing with numerically synthesized structure. |
| jbio201700385-sup-0007-VideoS5.avivideo/avi, 514.2 KB | Video S5. Changes in sSESF image of 620 nm spheres aggregates as a result of probing with numerically synthesized structure. |
| jbio201700385-sup-0008-VideoS6.avivideo/avi, 593.1 KB | Video S6. Changes in sSESF image of the collagen scaffold at 3 days of culture as a result of probing with numerically synthesized structure. |
| jbio201700385-sup-0009-VideoS7.avivideo/avi, 583.5 KB | Video S7. Changes in sSESF image of the collagen scaffold at 7 days of culture as a result of probing with numerically synthesized structure. |
| jbio201700385-sup-0010-VideoS8.avivideo/avi, 802.1 KB | Video S8. Changes in sSESF image of the collagen scaffold at 21 days of culture as a result of probing with numerically synthesized structure. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1S. A. Alexandrov, T. R. Hillman, T. Gutzler, D. D. Sampson, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 168102.
- 2J. Marrison, L. Raty, P. Marriott, P. O'Toole, Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2369.
- 3V. Mico, Z. Zalevsky, C. Ferreira, J. Garcia, Opt. Express 2008, 16, 19260.
- 4T. R. Hillman, T. Gutzler, S. A. Alexandrov, D. D. Sampson, Opt. Express 2009, 17, 7873.
- 5L. Li, W. Guo, Y. Z. Yan, S. Lee, T. Wang, Light-Sci. Appl. 2013, 2, e104.
- 6I. Pita, N. Hendaoui, N. Liu, M. Kumbham, S. A. M. Tofail, A. Peremans, C. Silien, Opt. Express 2013, 21, 25632. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.21.025632.
- 7E. G. van Putten, D. Akbulut, J. Bertolotti, W. L. Vos, A. Lagendijk, A. P. Mosk, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 193905.
- 8P. Wang, M. N. Slipchenko, J. Mitchell, C. Yang, E. O. Potma, X. F. Xu, J. X. Cheng, Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 450.
- 9P. von Olshausen, A. Rohrbach, Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 4066.
- 10L. Cherkezyan, I. Capoglu, H. Subramanian, J. D. Rogers, D. Damania, A. Taflove, V. Backman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 033903.
- 11I. Itzkan, L. Qiu, H. Fang, M. M. Zaman, E. Vitkin, L. C. Ghiran, S. Salahuddin, M. Modell, C. Andersson, L. M. Kimerer, P. B. Cipolloni, K. H. Lim, S. D. Freedman, I. Bigio, B. P. Sachs, E. B. Hanlon, L. T. Perelman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 17255.
- 12J. E. Chandler, L. Cherkezyan, H. Subramanian, V. Backman, Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 883.
- 13R. K. Bista, S. Uttam, P. Wang, K. Staton, S. Choi, C. J. Bakkenist, D. J. Hartman, R. E. Brand, Y. Liu, J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 070503.
- 14S. Uttam, R. K. Bista, K. Staton, S. Alexandrov, S. Choi, C. J. Bakkenist, D. J. Hartman, R. E. Brand, Y. Liu, Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 2491.
- 15A. K. Ellerbee, T. L. Creazzo, J. A. Izatt, Opt. Express 2007, 15, 8115.
- 16M. G. Shan, M. E. Kandel, G. Popescu, Opt. Express 2017, 25, 1573.
- 17S. A. Alexandrov, S. Uttam, R. K. Bista, Y. Liu, Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 3323.
- 18S. A. Alexandrov, S. Uttam, R. K. Bista, C. Q. Zhao, Y. Liu, Opt. Express 2012, 20, 9203.
- 19S. A. Alexandrov, S. Uttam, R. K. Bista, K. Staton, Y. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 033702.
- 20S. Uttam, S. A. Alexandrov, R. K. Bista, Y. Liu, Opt. Express 2013, 21, 7488.
- 21S. A. Alexandrov, H. M. Subhash, A. Zam, M. Leahy, Nanoscale 2014, 6, 3545.
- 22S. A. Alexandrov, J. McGrath, H. Subhash, F. Boccafoschi, C. Giannini, M. Leahy, Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13274.
- 23W. Lukosz, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1967, 57, 932.
- 24G. Toraldo di Francia, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1969, 59, 799.
- 25I. J. Cox, C. J. R. Sheppard, J. Opt, Soc. Am. A-Optics Image Sci. Vis. 1986, 3, 1152.
- 26A. L. Kartashov, Opt. Spectrosc. 1960, 9, 204.
- 27S. A. Basinger, E. Michielssen, D. J. Brady, J. Opt, Soc. Am. A-Optics Image Sci. Vis. 1995, 12, 704.
- 28A. M. van Oijen, J. Kohler, J. Schmidt, M. Muller, G. J. Brakenhoff, Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 292, 183.
- 29M. Davidson, K. Kaufman, I. Mazor, F. Cohen, Proc. SPIE 1987, 775, 233.
10.1117/12.940433 Google Scholar
- 30G. Hausler, M. W. Lindner, J. Biomed. Opt. 1998, 3, 21.
- 31C. J. R. Sheppard, K. G. Larkin, Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 4731.
- 32T. S. Ralston, D. L. Marks, P. S. Carney, S. A. Boppart, Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 129.
- 33C. J. R. Sheppard, S. S. Kou, C. Depeursinge, J. Opt, Soc. Am. A-Optics Image Sci. Vis. 2012, 29, 244.
- 34M. Born, E. Wolf, Principles of Optics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1999, p. 695.
- 35N. Rajan, J. Habermehl, M. F. Cote, C. J. Doillon, D. Mantovani, Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2753.
- 36F. Boccafoschi, M. Ramella, T. Sibillano, L. De Caro, C. Giannini, R. Comparelli, A. Bandiera, M. Cannas, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 1218.
- 37D. Altamura, R. Lassandro, F. A. Vittoria, L. De Caro, D. Siliqi, M. Ladisa, C. Giannini, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 869.
- 38T. Sibillano, L. De Caro, D. Altamura, D. Siliqi, M. Ramella, F. Boccafoschi, G. Ciasca, G. Campi, L. Tirinato, E. Di Fabrizio, C. Giannini, Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6985.
- 39J. F. de Boer, B. Cense, B. H. Park, M. C. Pierce, G. J. Tearney, B. E. Bouma, Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 2067.
- 40R. Leitgeb, C. K. Hitzenberger, A. F. Fercher, Opt. Express 2003, 11, 889.