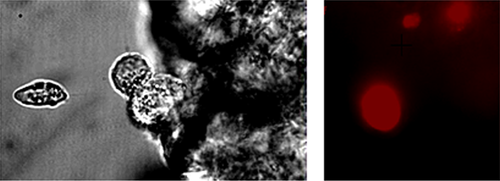
The use of optical trap and microbeam to investigate the mechanical and transport characteristics of tunneling nanotubes in tumor spheroids
Corresponding Author
Pooja Patheja
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Corresponding authors: e-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Raktim Dasgupta
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Department of Theory and Bio-systems, Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces, 14476 Potsdam, Germany
Corresponding authors: e-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAlok Dube
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Search for more papers by this authorSunita Ahlawat
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Search for more papers by this authorRavi Shanker Verma
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Search for more papers by this authorPradeep Kumar Gupta
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Pooja Patheja
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Corresponding authors: e-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Raktim Dasgupta
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Department of Theory and Bio-systems, Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces, 14476 Potsdam, Germany
Corresponding authors: e-mail: [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAlok Dube
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Search for more papers by this authorSunita Ahlawat
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Search for more papers by this authorRavi Shanker Verma
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Search for more papers by this authorPradeep Kumar Gupta
Laser Biomedical Applications and Instrumentation Division, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology, Indore, 452013 India
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
The use of optical trap and microbeam for investigating mechanical and transport properties of inter cellular tunneling nanotubes (TnTs) in tumor spheroids has been demonstrated. TnTs in tumor spheroids have been visualized by manipulating TnT connected cells using optical tweezers. Functionality of the TnTs for transferring cytoplasmic vesicles and injected dye molecules by optoporation method has been studied. Further, the TnTs could be longitudinally stretched by manipulating the connected cells and their elastic response was studied.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201400039-sup-0001-author-biographies.pdfPDF document, 181 KB | Author biographies |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1K. Francisand B. O. Palsson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 12258–12262 (1997).
- 2N. M. Kumarand N. B. Gilula, Cell 84, 381–388 (1996).
- 3S. K. Bromley, W. R. Burack, K. G. Johnson, K. Somersalo, T. N. Sims, C. Sumen, M. M. Davis, A. S. Shaw, P. M. Allen, and M. L. Dustin, Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 375–396 (2001).
- 4A. Rustom, R. Saffrich, I. Markovic, P. Walther, and H. H. Gerdes, Science 303, 1007–1010 (2004).
- 5D. M. Davisand S. Sowinski, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.9, 431–436 (2008).
- 6J. Pasquier, L. Galas, C. Boulangé-Lecomte, D. Rioult, F. Bultelle, P. Magal, G. Webb, and F. Le Foll, J. Biol. Chem. 287, 7374–7387 (2012).
- 7H. R. Chinnery, E. Pearlman, and P. G. McMenamin, J. Immunol. 180, 5779–5783 (2008).
- 8R. D. Salterand S. C. Watkins, Immunol. Res. 36, 211–220 (2006).
- 9B. Onfelt, S. Nedvetzki, K. Yanagi, and D. M. Davis, J. Immunol. 173, 1511–1513 (2004).
- 10P. D. Arkwright, F. Luchetti, J. Tour, C. Roberts, R. Ayub, A. P. Morales, J. J. Rodríguez, A. Gilmore, B. Canonico, S. Papa, and M. D. Esposti, Cell Res. 20, 72–88 (2010).
- 11S. C. Watkinsand R. D. Salter, Immunity 23, 309–318 (2005).
- 12I. F. Smith, J. Shuai, and I. Parker, Biophys. J. 100, 37–39 (2011).
- 13S. Gurke, J. F. Barroso, E. Hodneland, N. V. Bukoreshtliev, O. Schlicker, and H. H. Gerdes, Exp. Cell. Res. 314, 3669–3683 (2008).
- 14M. Koyanagi, R. P. Brandes, J. Haendeler, A. M. Zeiher, and S. Dimmeler, Circ. Res. 96, 1039–1041 (2005).
- 15J. L. Spees, S. D. Olson, M. J. Whitney, and D. J. Prockop, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, USA 103, 1283–1288 (2006).
- 16J. Pasquier, B. S. Guerrouahen, H. Al Thawadi, P. Ghiabi, M. Maleki, N. Abu-Kaoud, A. Jacob, M. Mirshahi, L. Galas, S. Rafii, F. Le Foll, and A. Rafii, J. Transl. Med. 11, 94 (2013).
- 17K. Yasuda, A. Khandare, L. Burianovskyy, S. Maruyama, F. Zhang, A. Nasjletti, and M. S. Goligorsky, Aging 3, 597–608 (2011).
- 18E. Lou, S. Fujisawa, A. Morozov, A. Barlas, Y. Romin, Y. Dogan, S. Gholami, A. L. Moreira, K. Manova-Todorova, and M. A. Moore, PLoS One 7, e33093 (2012).
- 19B. B. Tysnesand R. Bjerkvig, Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1775, 283–297 (2007).
- 20V. Thayanithy, E. L. Dickson, C. Steer, S. Subramanian, and E. Lou, Transl. Res. (2014) DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2014.05.011
- 21E. Lou, S. Fujisawa, A. Barlas, Y. Romin, K. Manova-Todorova, M. A. Moore, and S. Subramanian, Commun. Integr. Biol. 5, 399–403 (2012).
- 22M. A. Castro, V. A. Grieneisen, and R. M. de Almeida, Cell Biol. Int. 29, 929–931 (2005).
- 23I. Dufau, C. Frongia, F. Sicard, L. Dedieu, P. Cordelier, F. Ausseil, B. Ducommun, and A. Valette, BMC Cancer 12, 15 (2012).
- 24L. A. Kunz-Schughart, J. P. Freyer, F. Hofstaedter, and R. Ebner, J. Biomol. Screen. 9, 273–285 (2004).
- 25B. Pontes, N. B. Viana, L. Campanati, M. Farina, V. M. Neto, and H. M. Nussenzveig, Eur. Biophys. J. 37, 121–129 (2008).
- 26J. M. Kelm, N. E. Timmins, C. J. Brown, M. Fussenegger, and L. K. Nielsen, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 83, 173–180 (2003).
- 27J. M. Kelmand M. Fussenegger, Trends Biotechnol. 22, 195–202 (2004).
- 28K. Alessandri, B. R. Sarangi, V. V. Gurchenkov, B. Sinha, T. R. Kießling, L. Fetler, F. Rico, S. Scheuring, C. Lamaze, A. Simon, S. Geraldo, D. Vignjevic, H. Doméjean, L. Rolland, A. Funfak, J. Bibette, N. Bremond, and P. Nassoy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 14843–14848 (2013).
- 29S. Sowinski, C. Jolly, O. Berninghausen, M. A. Purbhoo, A. Chauveau, K. Köhler, S. Oddos, P. Eissmann, F. M. Brodsky, C. Hopkins, B. Onfelt, Q. Sattentau, and D. M. Davis, Nat. Cell. Biol. 10, 211–219 (2008).
- 30J. Rakand A. Guha, Bioessays 34, 489–497 (2012).
- 31C. Campillo, P. Sens, D. Köster, L. L. Pontani, D. Lévy, P. Bassereau, P. Nassoy, and C. Sykes, Biophys. J. 104, 1248–1256 (2013).
- 32Z. Li, B. Anvari, M. Takashima, P. Brecht, J. H. Torres, and W. E. Brownell, Biophys. J. 82, 1386–1395 (2002).
- 33H. Kojima, A. Ishijima, and T. Yanagida, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 12962–12966 (1994).
- 34T. Bornschlögl, S. Romero, C. L. Vestergaard, J. F. Joanny, G. T. Van Nhieu, and P. Bassereau, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 18928–18933 (2013).
- 35M. P. Sheetz, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 392–396 (2001).
- 36D. Raucher, T. Stauffer, W. Chen, K. Shen, S. Guo, J. D. York, M. P. Sheetz, and T. Meyer, Cell 100, 221–228 (2000).
- 37S. K. Mohanty, A. Rapp, S. Monajembashi, P. K. Gupta, and K. O. Greulich, Radiat. Res. 157, 378–385 (2002).
- 38S. K. Mohanty, M. Sharma, and P. K. Gupta, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 5, 134–139 (2006).
- 39H. Zhang,
A. Kay,
N. R. Forsyth,
K. K. Liu, and
A. J. El Haj,
J. Tissue Eng.
3,
2041731412451988
(2012).
10.1177/2041731412451988 Google Scholar