Cover Image
Graphical Abstract
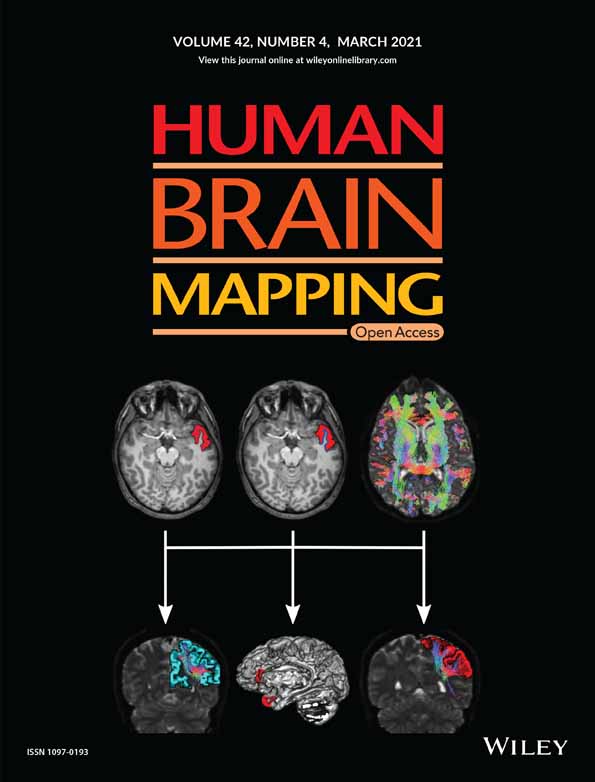
COVER ILLUSTRATION Migraine is a primary headache disorder characterized by attacks of moderate to severe intensity. To represent gray matter structure, the cortical curvature, cortical thickness (top left), surface area (top center) and gray matter volume were used as morphometry parameters. Structural connectivity was obtained with tractography (top right) and represented by the number of streamlines. Simultaneous changes of gray matter morphometry and structural connectivity were analyzed using multimodal Canonical Correlation Analysis followed by joint Independent Component Analysis. Higher curvature values in migraine patients in the frontal pole and the cingulate gyrus (bottom center) were associated with connectivity alterations. Lower number of streamlines, possibly representing debilitated connectivity (blue, bottom left), and also higher streamline count, possibly representing strengthened connectivity (red, bottom right), were identified in migraine.