Polarity Sensitive and H2O2/Lipid Droplets Sequence-Activated Asymmetric Cyanine Probe Achieves Multi-marker Imaging of Atherosclerosis
Weihua Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHan Zhu
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Biosensing and Molecular Recognition, Research Center for Analytical Sciences, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorBo Gu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongze Xie
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorXinlei Xu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shu-Lin Liu
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Biosensing and Molecular Recognition, Research Center for Analytical Sciences, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Heng Song
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Wuhan University Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518000 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorWeihua Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHan Zhu
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Biosensing and Molecular Recognition, Research Center for Analytical Sciences, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorBo Gu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongze Xie
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorXinlei Xu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shu-Lin Liu
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Biosensing and Molecular Recognition, Research Center for Analytical Sciences, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Heng Song
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Wuhan University Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518000 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
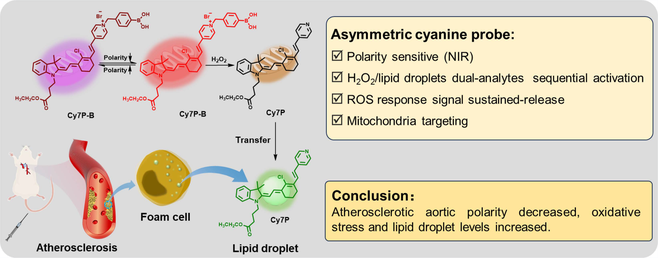
Atherosclerosis is a lipoprotein-driven disease. In-depth understanding of pathology and accurate identification are particularly important in clinical assessment and treatment due to the irreversibility of atherosclerotic plaque formation. Atherosclerosis is not only accompanied by lipid droplets accumulation but also closely related to inflammation, which is accompanied by excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) and changes in microenvironment. However, there is still a lack of a simple and rapid detection platform to simultaneously evaluate multiple indicators of atherosclerosis in multiple channels. In this study, we propose a multicolor imaging probe Cy7P-B for polarity, H2O2 and lipid droplets to evaluate atherosclerotic plaques in vivo. Cy7P-B is sensitive to environmental polarity and can monitor polarity changes by near-infrared ratio. Moreover, Cy7P-B has H2O2/lipid droplets dual-analyte sequential activation characteristics. Based on the multifunctional properties of Cy7P-B, the classical biomarkers of atherosclerotic plaque, lipid accumulation and up-regulation of oxidative stress are effectively detected in atherosclerotic plaques, and more importantly, the change of aortic polarity in atherosclerosis was detected for the first time. This work provides a general molecular design approach for multi-species imaging of AS, which is helpful for effective cardiovascular disease stewardship.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202401274-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 3.4 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Saigusa, R.; Winkels, H.; Ley, K. T cell subsets and functions in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 387–401.
- 2 Su, Y.; Guan, P.; Li, D.; Hang, Y.; Ye, X.; Han, L.; Lu, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhang, P.; Hu, W. Intermedin attenuates macrophage phagocytosis via regulation of the long noncoding RNA Dnm3os/miR-27b-3p/SLAMF7 axis in a mouse model of atherosclerosis in diabetes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 583, 35–42.
- 3 Steinl, D.; Kaufmann, B. Ultrasound imaging for risk assessment in atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9749–9769.
- 4 Björkegren, J. L. M.; Lusis, A. J. Atherosclerosis: recent developments. Cell 2022, 185, 1630–1645.
- 5 Wada, T.; Kodaira, K.; Fujishiro, K.; Okamura, T. Correlation of common carotid flow volume measured by ultrasonic quantitative flowmeter with pathological findings. Stroke 1991, 22, 319–323.
- 6 Roy, P.; Orecchioni, M.; Ley, K. How the immune system shapes atherosclerosis: roles of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 22, 251–265.
- 7 Shah, P. K. Mechanisms of plaque vulnerability and rupture. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, S15–S22.
- 8 Libby, P.; Ridker, P. M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143.
- 9 Budoff, M. J.; Achenbach, S.; Duerinckx, A. Clinical utility of computed tomography and magnetic resonance techniques for noninvasive coronary angiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 1867–1878.
- 10 Ruud B. van Heeswijk; Pellegrin, M.; Flögel, U.; Gonzales, C.; Aubert, J.-F.; Mazzolai, L.; Schwitter, J.; Stuber, M. Fluorine MR imaging of inflammation in atherosclerotic plaque in vivo. Radiology 2015, 275, 421–429.
- 11 Jaffer, F. A.; Albaghdadi, M. S. Clinical OCT-based polarization assessment of coronary artery disease: bending light to reveal atherosclerosis pathology. ACC: Cardiovasc. Imag. 2020, 13, 802–803.
- 12 Tian, X.; Murfin, L. C.; Wu, L.; Lewis, S. E.; James, T. D. Fluorescent small organic probes for biosensing. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3406–3426.
- 13 Kolanowski, J. L.; Liu, F.; New, E. J. Fluorescent probes for the simultaneous detection of multiple analytes in biology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 195–208.
- 14 Usama, S. M.; Inagaki, F.; Kobayashi, H.; Schnermann, M. J. Norcyanine-carbamates are versatile near-infrared fluorogenic probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 5674–5679.
- 15 Wang, S.; Ren, W. X.; Hou, J.-T.; Won, M.; An, J.; Chen, X.; Shu, J.; Kim, J. S. Fluorescence imaging of pathophysiological microenvironments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8887–8902.
- 16 Xiao, H.; Li, P.; Tang, B. Recent progresses in fluorescent probes for detection of polarity. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213582.
- 17 Yang, Z.; Cao, J.; He, Y.; Yang, J. H.; Kim, T.; Peng, X.; Kim, J. S. Macro-/micro-environment-sensitive chemosensing and biological imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4563–4601.
- 18 Yin, J.; Huang, L.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; James, T. D.; Lin, W. Small molecule based fluorescent chemosensors for imaging the microenvironment within specific cellular regions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12098–12150.
- 19 Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Tang, B.; Li, P. Recent advances in small molecule fluorescent probes for simultaneous imaging of two bioactive molecules in live cells and in vivo. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 4–33.
- 20 Ge, X.; Long, Y.; Wang, J.; Gu, B.; Yang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.; Song, H. Regulation of P450 TleB catalytic flow for the synthesis of sulfur-containing indole alkaloids by substrate structure- directed strategy and protein engineering. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 3232–3241.
- 21 Lei, L.; Yang, F.; Meng, X.; Xu, L.; Liang, P.; Ma, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. B.; Song, G. Noninvasive Imaging of Tumor Glycolysis and Chemotherapeutic Resistance via De Novo Design of Molecular Afterglow Scaffold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 24386–24400.
- 22 Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Liao, S.; Yin, B.; Yue, R.; Guan, G.; Chen, B.; Song, G. Enhancing Fractionated Cancer Therapy: A Triple-Anthracene Photosensitizer Unleashes Long-Persistent Photodynamic and Luminous Efficacy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 6252–6265.
- 23 Xu, J.; Guan, G.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, C.; Lei, L.; Zhang, X. B.; Song, G. Enhancing lipid peroxidation via radical chain transfer reaction for MRI guided and effective cancer therapy in mice. Sci. Bull. (Beijing) 2024, 69, 636–647.
- 24 Poznyak, A. V.; Kashirskikh, D. A.; Sukhorukov, V. N.; Kalmykov, V.; Omelchenko, A. V.; Orekhov, A. N. Cholesterol transport dysfunction and its involvement in atherogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1332.
- 25 Xu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, R. Exercise ameliorates atherosclerosis via up-regulating serum β-hydroxybutyrate levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3788.
- 26 Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Hua, Z.; Xue, X.; Wang, X.; Pang, M.; Wang, T.; Lyu, A.; Liu, Y. Apolipoproteins as potential communicators play an essential role in the pathogenesis and treatment of early atherosclerosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 4493–4510.
- 27 Wu, G.; Wei, W.; Zhang, J.; Nie, W.; Yuan, L.; Huang, Y.; Zuo, L.; Huang, L.; Xi, X.; Xie, H.-Y. A self-driven bioinspired nanovehicle by leukocyte membrane-hitchhiking for early detection and treatment of atherosclerosis. Biomaterials 2020, 250, 119963.
- 28 Zheng, J.; Qin, S.; Gui, L.; Li, H.; Fan, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Yuan, Z. Light-up lipid droplets for the visualization of lipophagy and atherosclerosis by coumarin-derived bioprobe. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2385–2389.
- 29 Sang, M.; Cai, B.; Qin, S.; Zhao, S.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Zheng, J. Lipid droplet-specific probe for rapidly locating atherosclerotic plaques and intraoperative imaging via in situ spraying. ACS Appl. Mater. 2021, 13, 58369–58381.
- 30 Azad, M. B.; Chen, Y.; Gibson, S. B. Regulation of autophagy by reactive oxygen species (ROS): implications for cancer progression and treatment. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2009, 11, 777–790.
- 31 He, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Xu, F.; Zou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, H.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive size-reducible nanoassemblies for deeper atherosclerotic plaque penetration and enhanced macrophage-targeted drug delivery. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 115–126.
- 32 Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Yin, H.; Sun, L.; Su, C.; Zhang, K.; Xu, H. Reactive oxygen species scavenging and inflammation mitigation enabled by biomimetic prussian blue analogues boycott atherosclerosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 161.
- 33 Reddy, V. P. Oxidative stress in health and disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2925.
- 34 Reuter, S.; Gupta, S. C.; Chaturvedi, M. M.; Aggarwal, B. B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radical Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616.
- 35 Ma, Y.; Shang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Xu, X.; Cao, H.; Xu, L.; Sun, W.; Song, G.; Zhang, X. B. Rational Design of a Double-Locked Photoacoustic Probe for Precise In Vivo Imaging of Cathepsin B in Atherosclerotic Plaques. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 17881–17891.
- 36 Ye, Z.; Ji, M.; Wu, K.; Yang, J.; Liu, A. A.; Sun, W.; Ding, D.; Liu, D. In-sequence high-specificity dual-reporter unlocking of fluorescent probe enables the precise identification of atherosclerotic plaques. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202204518.
- 37 Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Huang, F.; Xiu, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Tang, B. Prediction of early atherosclerotic plaques using a sequence-activated fluorescence probe for the simultaneous detection of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase and hypobromous acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 63, e202315861.
- 38 Sang, M.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Dai, C.; Zheng, J. Peroxynitrite/lipid droplet sequence-activated dual-lock fluorescent probes enable precise intraoperative imaging of atherosclerotic plaques. ACS Sensors 2023, 8, 893–903.
- 39 Bhat, M. A.; Izaddoost, S.; Lu, Y.; Cho, K.-O.; Choi, K.-W.; Bellen, H. J. Discs lost, a novel multi-PDZ domain protein, establishes and maintains epithelial polarity. Cell 1999, 96, 833–845.
- 40 Wodarz, A.; Näthke, I. Cell polarity in development and cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1016–1024.
- 41 Teshome, A.; Bhuiyan, M. D. H.; Gainsford, G. J.; Ashraf, M.; Asselberghs, I.; Williams, G. V. M.; Kay, A. J.; Clays, K. Synthesis, linear and quadratic nonlinear optical properties of ionic indoline and N,N-dimethylaniline based chromophores. Opt. Mater. 2011, 33, 336–345.
- 42 Shindy, H. A. Fundamentals in the chemistry of cyanine dyes: A review. Dyes Pigm. 2017, 145, 505–513.
- 43 Deng, Y.; Feng, G. Visualization of ONOO– and viscosity in Drug-induced hepatotoxicity with different fluorescence signals by a sensitive fluorescent probe. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14667–14675.
- 44 Ren, M.; Deng, B.; Zhou, K.; Kong, X.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lin, W. Single fluorescent probe for dual-imaging viscosity and H2O2 in mitochondria with different fluorescence signals in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2016, 89, 552–555.
- 45 Li, R.; Guo, J.; Duan, Y.; Liu, X.; Gui, L.; Xu, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Z. Monitoring inflammation-cancer progression by cell viscosity, polarity and leucine aminopeptidase using multicolor fluorescent probe. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 135043.
- 46 Li, S.-J.; Li, Y.-F.; Liu, H.-W.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Jiang, W.-L.; Ou-Yang, J.; Li, C.-Y. A dual-response fluorescent probe for the detection of viscosity and H2S and its application in studying their cross-talk influence in mitochondria. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9418–9425.
- 47 Ma, Y.; Guo, B.; Ge, J.-Y.; Chen, L.; Lv, N.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z. Rational design of a near-infrared ratiometric probe with a large stokes shift: visualization of polarity abnormalities in non-alcoholic fatty liver model mice. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 12383–12390.
- 48 Oushiki, D.; Kojima, H.; Terai, T.; Arita, M.; Hanaoka, K.; Urano, Y.; Nagano, T. Development and application of a near-infrared fluorescence probe for oxidative stress based on differential reactivity of linked cyanine dyes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2795–2801.
- 49 Zhang, S.; Zheng, H.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Yu, M. NIR mitochondrial fluorescent probe for visualizing SO2/Polarity in drug induced inflammatory mice. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 5377–5383.
- 50 Ma, Y.; Yu, Z.-Q.; Wang, M.; Guan, Y.; Ding, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, M. Ratiometric NIR cell membrane-targeted probe for monitoring cell membrane polarity and tumor application. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2024, 405, 135331.
- 51 Trivedi, E. R.; Harney, A. S.; Olive, M. B.; Podgorski, I.; Moin, K.; Sloane, B. F.; Barrett, A. G. M.; Meade, T. J.; Hoffman, B. M. Chiral porphyrazine near-IR optical imaging agent exhibiting preferential tumor accumulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 1284–1288.
- 52 Yang, X.; Shi, C.; Tong, R.; Qian, W.; Zhau, H. E.; Wang, R.; Zhu, G.; Cheng, J.; Yang, V. W.; Cheng, T.; Henary, M.; Strekowski, L.; Chung, L. W. K. Near IR heptamethine cyanine dye-mediated cancer imaging. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2010, 16, 2833–2844.
- 53 Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Su, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, X.; Fan, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, T.; Shi, C. A near-infrared fluorescent heptamethine indocyanine dye with preferential tumor accumulation for in vivo imaging. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6612–6617.
- 54 Shi, C.; Zhang, C.; Su, Y.; Cheng, T. Cyanine dyes in optical imaging of tumours. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 815–816.