Nickel-Catalyzed LiCl-Controlled Switchable Carboxylation of Aryl C—F Bonds with One or Two Molecules of CO2
Chunzhe Pei
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Hebei Key Laboratory of Heterocyclic Compounds, College of Chemical Engineering & Material, Handan University, Handan, Hebei, 056005 China
Search for more papers by this authorShanglin Han
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorHanxuan Wu
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorBin Li
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Baiquan Wang
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 200032 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorChunzhe Pei
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Hebei Key Laboratory of Heterocyclic Compounds, College of Chemical Engineering & Material, Handan University, Handan, Hebei, 056005 China
Search for more papers by this authorShanglin Han
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorHanxuan Wu
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorBin Li
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Baiquan Wang
State Key Laboratory of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 200032 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
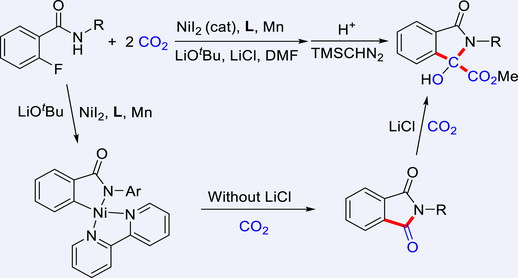
The use of CO2 as a renewable C1 source for the synthesis of value-added chemicals can contribute to a more sustainable chemistry. In this work, a nickel-catalyzed amide-directed carboxylation of aryl C−F bonds with CO2 has been developed. The reaction is switchable controlled by LiCl to react with one or two molecules of CO2 to afford valuable phthalimides or α-hydroxycarboxylic acid derivatives. Further study shows that the reaction is a step-by-step process. The first step is a nickel-catalyzed carboxylation of aryl C−F bonds with CO2 and tandem cyclization to afford phthalimides. The second step is a nickel-catalyzed C−N bond carboxylation of phthalimides with CO2, and intramolecular nucleophilic addition of amide anion to the carbonyl. The carboxylation of phthalimides with CO2 is also developed based on this reaction. The work features inert C−F bond functionalization, amide C−N bond activation, and multiple CO2 incorporation. Mechanistic studies indicate that the azanickelacycle intermediates play an important role, and LiCl facilitates the reduction of Ni(II) to Ni(I) and promotes the carboxylation with the second molecule of CO2. This protocol provides an efficient route for C−F bond functionalization under mild conditions via the chemical fixation of one or two molecules of CO2.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202401208-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 2.9 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Aresta, M. Carbon Dioxide as Chemical Feedstock, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2010;
10.1002/9783527629916 Google Scholar(b) Centi, G.; Perathoner, S. Green Carbon Dioxide, Wiley-VCH, New Jersey, 2014;10.1002/9781118831922 Google Scholar(c) Das, S. CO2 as a Building Block in Organic Synthesis, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2020.10.1002/9783527821952 Google Scholar
- 2For recent selected reviews, see: (a) Tortajada, A.; Juliá-Hernández, F.; Börjesson, M.; Moragas, T.; Martin, R. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Carboxylation Reactions with Carbon Dioxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15948–15982; (b) Yan, S.-S.; Fu, Q.; Liao, L.-L.; Sun, G.-Q.; Ye, J.-H.; Gong, L.; Bo-Xue, Y.-Z.; Yu, D.-G. Transition metal-catalyzed carboxylation of unsaturated substrates with CO2. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 374, 439–463; (c) Hong, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, B.; Mo, F. C−H Bond Carboxylation with Carbon Dioxide. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 6–39; (d) Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Takimoto, M.; Hou, Z. Carboxylation Reactions with Carbon Dioxide Using N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Copper Catalysts. Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 494–512; (e) Tortajada, A.; Börjesson, M.; Martin, R. Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Carboxylation and Amidation Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3941–3952; (f) Cauwenbergh, R.; Goyal, V.; Maiti, R.; Natte, K.; Das, S. Challenges and recent advancements in the transformation of CO2 into carboxylic acids: straightforward assembly with homogeneous 3d metals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 9371–9423; (g) Rawat, A.; Dhakla, S.; Lama, P.; Pal, T. K. Fixation of carbon dioxide to aryl/aromatic carboxylic acids. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 59, 101939; (h) Zhang, L.; Gao, E.-Q. Catalytic C(sp)-H carboxylation with CO2. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 486, 215138; (i) Pradhan, S.; Das, S. Recent Advances on the Carboxylations of C(sp3)–H Bonds Using CO2 as the Carbon Source. Synlett 2023, 34, 1327–1342; (j) Song, L.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Z.; Gui, Y.-Y.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Yu, D.-G. CO2 = CO + [O]: recent advances in carbonylation of C–H bonds with CO2. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8355–8367; (k) Bertuzzi, G.; Cerveri, A.; Lombardi, L.; Bandini, M. Tandem Functionalization-Carboxylation Reactions of π-Systems with CO2. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 3116–3126; (l) Ye, J.-H.; Ju, T.; Huang, H.; Liao, L.-L.; Yu, D.-G. Radical Carboxylative Cyclizations and Carboxylations with CO2. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 2518–2531; (m) Sun, G.-Q.; Liao, L.-L.; Ran, C.-K.; Ye, J.-H. Yu, D.-G. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Carboxylation with CO2. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 2728–2745.
- 3For selected reviews, see: (a) Ran, C.-K.; Xiao, H.-Z.; Liao, L.-L.; Ju, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, D.-G. Progress and challenges in dicarboxylation with CO2. Nat. Sci. Open 2023, 2, 20220024;
10.1360/nso/20220024 Google Scholar(b) Wang, S.; Xu, P.; Zhu, X. CO2 Radical Anion in Photochemical Dicarboxylation of Alkenes. ChemCatChem 2023, 15, e202300695.
- 4(a) Takimoto, M.; Kawamura, M.; Mori, M.; Sato, Y. Nickel-Catalyzed Regio- and Stereoselective Double Carboxylation of Trimethylsilylallene under an Atmosphere of Carbon Dioxide and Its Application to the Synthesis of Chaetomellic Acid A Anhydride. Synlett 2005, 13, 2019–2022; (b) Fujihara, T.; Horimoto, Y.; Mizoe, T.; Sayyed, F. B.; Tani, Y.; Terao, J.; Sakaki, S.; Tsuji, Y. Nickel-Catalyzed Double Carboxylation of Alkynes Employing Carbon Dioxide. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 4960–4963; (c) Zhang, W.-Z.; Yang, M.-W.; Yang, X.-T.; Shi, L.-L.; Wang, H.-B.; Lu, X.-B. Double carboxylation of o-alkynyl acetophenone with carbon dioxide. Org. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 217–221; (d) Tortajada, A.; Ninokata, R.; Martin, R. Ni-Catalyzed Site-Selective Dicarboxylation of 1,3-Dienes with CO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2050–2053; (e) Mita, T.; Ishii, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Sato, Y. Pd-Catalyzed Dearomative Carboxylation of Indolylmethanol Derivatives. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 7603–7606; (f) Mita, T.; Masutani, H.; Ishii, S.; Sato, Y. Catalytic Carboxylation of Heteroaromatic Compounds: Double and Single Carboxylation with CO2. Synlett 2019, 30, 841–844; (g) Nie, W.; Shao, Y.; Ahlquist, M. S. G.; Yu, H.; Fu, Y. Mechanistic study on the regioselective Ni-catalyzed dicarboxylation of 1,3-dienes with CO2. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 4080–4088; (h) Ju, T.; Zhou, Y.-Q.; Cao, K.-G.; Fu, Q.; Ye, J.-H.; Sun, G.-Q.; Liu, X.-F.; Chen, L.; Liao, L.-L.; Yu, D.-G. Dicarboxylation of alkenes, allenes and (hetero) arenes with CO2 via visible-light photoredox catalysis. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 304–311; (i) Takahashi, K.; Sakurazawa, Y.; Iwai, A.; Iwasawa, N. Catalytic Synthesis of a Methylmalonate Salt from Ethylene and Carbon Dioxide through Photoinduced Activation and Photoredox-Catalyzed Reduction of Nickelalactones. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 3776–3781; (j) Liao, L.-L.; Wang, Z.-H.; Cao, K.-G.; Sun, G.-Q.; Zhang, W.; Ran, C.-K.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Cao, G.-M.; Yu, D.-G. Electrochemical Ring-Opening Dicarboxylation of Strained Carbon−Carbon Single Bonds with CO2: Facile Synthesis of Diacids and Derivatization into Polyesters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2062–2068; (k) You, Y.; Kanna, W.; Takano, H.; Hayashi, H.; Maeda, S.; Mita, T. Electrochemical Dearomative Dicarboxylation of Heterocycles with Highly Negative Reduction Potentials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3685–3695; (l) Song, L.; Wang, W.; Yue, J.-P.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Wei, M.-K.; Zhang, H.-P.; Yan, S.-S.; Liao, L.-L.; Yu, D.-G. Visible-light photocatalytic di- and hydrocarboxylation of unactivated alkenes with CO2. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 832–838; (m) Zhang, W.; Liao, L.-L.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Dai, L.-F.; Sun, G.-Q.; Ran, C.-K.; Ye, J.-H.; Lan, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electroreductive Dicarboxylation of Unactivated Skipped Dienes with CO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301892; (n) Xiao, H.-Z.; Yu, B.; Yan, S.-S.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.-X.; Bao, Y.; Luo, S.-P.; Ye, J.-H.; Yu, D.-G. Photocatalytic 1,3-dicarboxylation of unactivated alkenes with CO2. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 50, 222–228; (o) Zhang, F.; Wu, X.-Y.; Gao, P.-P.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Ai, S.; Li, G. Visible- light-driven alkene dicarboxylation with formate and CO2 under mild conditions. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 6178–6183.
- 5(a) Rovner, E. S. Trospium Chloride in the Management of Overactive Bladder. Drugs 2004, 64, 2433–2446; (b) Jang, J.-H.; Kanoh, K.; Adachi, K.; Shizuri, Y. Awajanomycin, a Cytotoxic ϒ-Lactone-δ-lactam Metabolite from Marine-Derived Acremonium sp. AWA16–1. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1358–1360; (c) Reddy, D. S.; Shibata, N.; Nagai, J.; Nakamura, S.; Toru, T. A Dynamic Kinetic Asymmetric Transformation in the α-Hydroxylation of Racemic Malonates and Its Application to Biologically Active Molecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 803–806; (d) Yamashita, Y.; Tanaka, K.-I.; Asano, T.; Yamakawa, N.; Kobayashi, D.; Ishihara, T.; Hanaya, K.; Shoji, M.; Sugai, T.; Wada, M.; Mashimo, T.; Fukunishi, Y.; Mizushima, T. Synthesis and biological comparison of enantiomers of mepenzolate bromide, a muscarinic receptor antagonist with bronchodilatory and anti-inflammatory activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 3488–3497; (e) Xiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Wen, X. Discovery of Novel Potent Muscarinic M3 Receptor Antagonists with Proper Plasma Stability by Structural Recombination of Marketed M3 Antagonists. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1173–1182.
- 6
Coppola, G. M.; Schuster, H. F. α-Hydroxy Acids in Enantioselective Syntheses, Wiley-VCH, 1997.
10.1002/352760085X Google Scholar
- 7For selected examples, see: (a) Yoshikazu, I.; Eiichiro, M. Syntheses of Benzilic Acids through Electrochemical Reductive Carboxylation of Benzophenones in the Presence of Carbon Dioxide. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1985, 58, 1723–1726;
10.1246/bcsj.58.1723 Google Scholar(b) Hou, Z.; Takamine, K.; Aoki, O.; Shiraishi, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Taniguchi, H. Nucleophilic Addition of Lanthanoid Metal Umpoled Diaryl Ketones to Electrophiles. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 6077–6084; (c) Chan, A. S. C.; Huang, T. T.; Wagenknecht, J. H.; Miller, R. E. A Novel Synthesis of 2-Aryllactic Acids via Electrocarboxylation of Methyl Aryl Ketones. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 742–744; (d) Yuan, G.; Li, Z.; Jiang, H. Electrosyntheses of α-Hydroxycarboxylic Acids from Carbon Dioxide and Aromatic Ketones Using Nickel as the Cathode. Chin. J. Chem. 2009, 27, 1464–1470; (e) Liu, R.; Yuan, G.; Joe, C. L.; Lightburn, T. E.; Tan, K. L.; Wang, D. Silicon Nanowires as Photoelectrodes for Carbon Dioxide Fixation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6709–6712; (f) Amaya, T.; Kurata, I.; Hirao, T. Synthesis of oxindoles via reductive CO2 fixation. Org. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 929–933; (g) Masada, K.; Kusumoto, S.; Nozaki, K. Reductive Coupling of Carbon Dioxide and an Aldehyde Mediated by a Copper(I) Complex toward the Synthesis of α-Hydroxycarboxylic Acids. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 4922–4926; (h) Cao, G.-M.; Hu, X.-L.; Liao, L.-L.; Yan, S.-S.; Song, L.; Chruma, J. J.; Gong, L.; Yu, D.-G. Visible-light photoredox-catalyzed umpolung carboxylation of carbonyl compounds with CO2. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3306; (i) Okumura, S.; Uozumi, Y. Photocatalytic Carbinol Cation/Anion Umpolung: Direct Addition of Aromatic Aldehydes and Ketones to Carbon Dioxide. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 7194–7198.
- 8(a) Amii, H.; Uneyama, K. C−F Bond Activation in Organic Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2119−2183; (b) Ahrens, T.; Kohlmann, J.; Ahrens, M.; Braun, T. Functionalization of Fluorinated Molecules by Transition-Metal-Mediated C−F Bond Activation to Access Fluorinated Building Blocks. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 931−972; (c) Das, A.; Chatani, N. The Directing Group: A Tool for Efficient and Selective C−F Bond Activation. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12915−12930; (d) Fu, L.; Chen, Q.; Nishihara, Y. Recent Advances in Transition-metalcatalyzed C−C Bond Formation via C(sp2)−F Bond Cleavage. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 3394–3410; (e) Ma, R.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Mao, G.; Song, Y.; Xin, S. Advances in Catalytic C–F Bond Activation and Transformation of Aromatic Fluorides. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1665; (f) Wang, K.; Kong, W. Synthesis of Fluorinated Compounds by Nickel-Catalyzed Defluorinative Cross-Coupling Reactions. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 12238−12268.
- 9(a) Tobisu, M.; Xu, T.; Shimasaki, T.; Chatani, N. Nickel-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Reaction of Aryl Fluorides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19505–19511; (b) Sun, A. D.; Love, J. A. Nickel-Catalyzed Selective Defluorination to Generate Partially Fluorinated Biaryls. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2750–2753; (c) He, Y.; Chen, Z.; He, C.-Y.; Zhang, X. Nickel- Catalyzed ortho-Selective Hydrodefluorination of N-Containing Heterocycle-Polyfluoroarenes. Chin. J. Chem. 2013, 31, 873–877; (d) Yang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, X. Nickel-catalyzed C-F bond activation and alkylation of polyfluoroaryl imines. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 723, 36–42; (e) Sun, A. D.; Leung, K.; Restivo, A. D.; LaBerge, N. A.; Takasaki, H.; Love, J. A. Nickel-Catalyzed Csp2-Csp3 Bond Formation by Carbon-Fluorine Activation. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 3162–3168; (f) Yu, D.; Wang, C.-S.; Yao, C.; Shen, Q.; Lu, L. Nickel-Catalyzed α-Arylation of Zinc Enolates with Polyfluoroarenes via C−F Bond Activation under Neutral Conditions. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5544−5547; (g) Capdevila, L.; Meyer, T. H.; Roldán-Gómez, S.; Luis, J. M.; Ackermann, L.; Ribas, X. Chemodivergent Nickel(0)-Catalyzed Arene C−F Activation with Alkynes: Unprecedented C−F/C−H Double Insertion. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 11074−11081; (h) Matsuura, A.; Chatani, N. Nickel- catalyzed C-F/O-H [4+2] Annulation of ortho-Fluoro Aromatic Carboxylic Acids with Alkynes. Chem. Lett. 2021, 50, 1990–1992; (i) Kawakami, H.; Nohira, I.; Chatani, N. Nickel-Catalyzed C–F/N–H Annulation of 2-(2-Fluoroaryl) N-Heteroaromatic Compounds with Alkynes: Activation of C–F Bonds. Synthesis 2021, 53, 3075–3080; (j) Kawakami, H.; Chatani, N. Nickel-catalyzed C-F/N-H Alkyne Annulation of Anilines: The Synthesis of Indole Derivatives via C-F Bond Activation. Chem. Lett. 2022, 51, 546–548; (k) Xi, L.; Du, L.; Shi, Z. Nickel-catalyzed reductive cross-coupling of polyfluoroarenes with alkyl electrophiles by site-selective C–F bond activation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4287–4292.
- 10(a) Nohira, I.; Liu, S.; Bai, R.; Lan, Y.; Chatani, N. Nickel-Catalyzed C−F/N−H Annulation of Aromatic Amides with Alkynes: Activation of C−F Bonds under Mild Reaction Conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 17306−17311; (b) Nohira, I.; Chatani, N. Nickel-Catalyzed Cross-Electrophile Coupling between C(sp2)−F and C(sp2)−Cl Bonds by the Reaction of ortho-Fluoro-Aromatic Amides with Aryl Chlorides. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4644−4649; (c) Zhang, T.; Nohira, I.; Chatani, N. Nickel-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling of C–F bonds. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 3783–3787; (d) Parker, B. F.; Chatani, N. Selective Nickel-Catalyzed Hydrodefluorination of Amides Using Sodium Borohydride. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 9969−9976; (e) Morishige, A.; Matsuura, A.; Chatani, N. Nickel-catalyzed Hydrodefluorination of ortho-Fluoro Aromatic Amides with 2-Propanol. Chem. Lett. 2023, 52, 63–66.
- 11(a) Pei, C.; Zong, J.; Han, S.; Li, B.; Wang, B. Ni-Catalyzed Direct Carboxylation of an Unactivated C−H Bond with CO2. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 6897–6902; (b) Pei, C.; Zong, J.; Li, B.; Wang, B. Ni-Catalyzed Direct Carboxylation of Aryl C-H Bonds in Benzamides with CO2. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 493–499; (c) Pei, C.; Wang, B. Nickel-Catalyzed Carboxylation of Aryl C–F Bonds with CO2. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 1245–1250.
- 12(a) Fu, L.; Li, S.; Cai, Z.; Ding, Y.; Guo, X.-Q.; Zhou, L.-P.; Yuan, D.; Sun, Q.-F.; Li, G. Ligand-enabled site-selectivity in a versatile rhodium(II)- catalysed aryl C–H carboxylation with CO2. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 469−478; (b) Song, L.; Cao, G.-M.; Zhou, W.-J.; Ye, J.-H.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, X.-Y.; Li, J.; Yu, D.-G. Pd-catalyzed carbonylation of aryl C–H bonds in benzamides with CO2. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 2086−2090; (c) Gao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Li, G. Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed Aryl C−H Carboxylation of 2-Arylanilines with CO2. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3663−3669.
- 13 Liu, Y.-Y.; Sun, S.-H.; Min, X.-T.; Wan, B.; Chen, Q.-A. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Decarbonylative Functionalization of Phthalimides. Synthesis 2022, 54, 2561–2573.
- 14(a) Malapit, C. A.; Bour, J. R.; Brigham, C. E.; Sanford, M. S. Base-free nickel-catalysed decarbonylative Suzuki–Miyaura coupling of acid fluorides. Nature 2018, 563, 100–104; (b) Jacobs, E.; Keaveney, S. T. Experimental and Computational Studies towards Chemoselective C−F over C−Cl Functionalisation: Reversible Oxidative Addition is the Key. ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 637–645; (c) Bo, Z.-Y.; Yan, S.-S.; Gao, T.-Y.; Song, L.; Ran, C.-K.; He, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cao, G.-M.; Yu, D.-G. Visible-light photoredox-catalyzed selective carboxylation of C(sp2)−F bonds in polyfluoroarenes with CO2. Chin. J. Catal. 2022, 43, 2388–2394; (d) Min, S.-Y.; Song, H.-X.; Yan, S.-S.; Yuan, R.; Ye, J.-H.; Wang, B.-Q.; Gui, Y.-Y.; Yu, D.-G. Photocatalytic defluorocarboxylation using formate salts as both a reductant and a carbon dioxide source. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 6194–6199; (e) Yan, S.-S.; Liu, S.-H.; Chen, L.; Bo, Z.-Y.; Jing, K.; Gao, T.-Y.; Yu, B.; Lan, Y. Luo S.-P.; Yu, D.-G. Visible-light photoredox-catalyzed selective carboxylation of C(sp3)−F bonds with CO2. Chem 2021, 7, 3099–3113.
- 15 Su, Z.-M.; Deng, R.; Stahl, S. S. Zinc and manganese redox potentials in organic solvents and their influence on nickel-catalysed cross-electrophile coupling. Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 2036−2043.
- 16 Coyle, E. E.; Doonan, B. J.; Holohan, A. J.; Walsh, K. A.; Lavigne, F.; Krenske, E. H.; O'Brien, C. J. Catalytic Wittig Reactions of Semi- and Nonstabilized Ylides Enabled by Ylide Tuning. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12907−12911.