Mechanism of TMB Discoloration Catalyzed by Layered CoNi@CN Nanozymes: Application Based on Smart Phone for Resorcinol Detection
Qingyong Guo
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorRongsheng Xiao
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaifeng Chen
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeishuo Bao
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorJingwen Qi
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qian-qian Jia
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
E-mail: [email protected] (Qian-qian Jia); [email protected] (Wuxiang Zhang)Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wuxiang Zhang
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
E-mail: [email protected] (Qian-qian Jia); [email protected] (Wuxiang Zhang)Search for more papers by this authorQingyong Guo
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorRongsheng Xiao
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaifeng Chen
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeishuo Bao
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorJingwen Qi
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qian-qian Jia
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
E-mail: [email protected] (Qian-qian Jia); [email protected] (Wuxiang Zhang)Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wuxiang Zhang
School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212003 China
E-mail: [email protected] (Qian-qian Jia); [email protected] (Wuxiang Zhang)Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
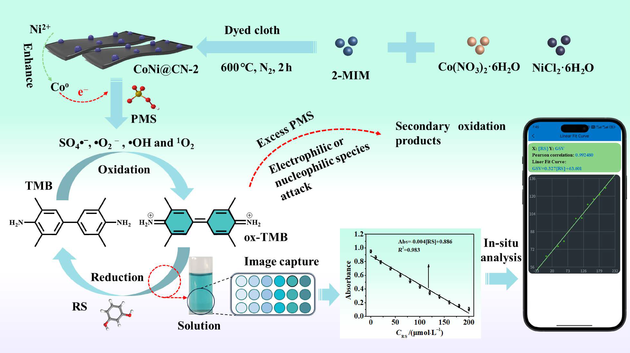
Real-time on-site monitoring of resorcinol (RS) concentrations is crucial for detecting hazardous levels, enabling prompt response measures to mitigate potential environmental and health risks. In this study, we developed an innovative method using CoNi@CN-2 nanozymes to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for oxidizing 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). Our results show that the formation of Ni2+ through the oxidation of Ni0 on the CoNi@CN-2 surface significantly enhances the electron-donating capacity of Co0. The catalytic reaction of TMB is mediated by redox active species (SO4•−, •O2−, •OH and 1O2). RS drives colorimetry by transferring electrons to the benzene ring and specific nitrogen atoms in ox-TMB, reducing ox-TMB to TMB. Furthermore, the colorimetric assay shows a robust linear correlation between RS concentration and absorbance (Abs), described by Abs = –0.44[RS] + 0.886 (0—200 μmol/L, R2 = 0.983). Also, we introduce a novel smartphone-integrated autonomous detection software that can analyze RS concentration and grayscale values (GSV), yielding GSV = 0.327[RS] + 63.601 (0—200 μmol/L, R2 = 0.990) with a detection limit of 5.29 μmol/L. Additionally, excess PMS leads to ROS attacking specific sites in ox-TMB, forming secondary oxidation products. This study has enabled rapid and accurate detection of RS, making a significant contribution to environmental safety and protection.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| CJOC202400841-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.6 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Mo, Z.; Jiquan, Z.; Caiyun, S. Occurrence, ecological and human health risks, and seasonal variations of phenolic compounds in surface water and sediment of a potential polluted river basin in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1140.
- 2 Saeed, M. A.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Arshad, M. Y.; Skrinsky, J.; Andrews, G. E.; Phylaktou, H. N. Combustion and explosion characteristics of pulverised wood, valorized with mild pyrolysis in pilot scale installation, using the modified ISO 1 m3 dust explosion vessel. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12928.
- 3 Robert-Peillard, F.; Chottier, C.; Coulomb, B.; Boudenne, J.-L. Simple and ultrasensitive microplate method for spectrofluorimetric determination of trace resorcinol. Microchem. J. 2015, 122, 5–9.
- 4 Zargar, B.; Hatamie, A. Colorimetric determination of resorcinol based on localized surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles. Analyst 2012, 137, 5334.
- 5 Yin, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhu, L.; Ai, S. Electrochemical behavior of catechol, resorcinol and hydroquinone at graphene- chitosan composite film modified glassy carbon electrode and their simultaneous determination in water samples. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2748–2753.
- 6 Pistonesi, M. F.; Di Nezio, M. S.; Centurión, M. E.; Palomeque, M. E.; Lista, A. G.; Fernández Band, B. S. Determination of phenol, resorcinol and hydroquinone in air samples by synchronous fluorescence using partial least-squares (PLS). Talanta 2006, 69, 1265–1268.
- 7 Wu, H.-W.; Chen, M.-L.; Shou, D.; Zhu, Y. Determination of resorcinol and phloroglucinol in environmental water samples using ion chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 1747–1751.
- 8 Cui, H.; Zhou, J.; Xu, F.; Lai, C.-Z.; Wan, G.-H. Determination of phenolic compounds using high-performance liquid chromatography with Ce4+-Tween 20 chemiluminescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 511, 273–279.
- 9 Valiev, R. Materials science: Nanomaterial advantage. Nature 2002, 419, 887–889.
- 10 Grigorenko, A. N.; Roberts, N. W.; Dickinson, M. R.; Zhang, Y. Nanometric optical tweezers based on nanostructured substrates. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 365–370.
- 11 Banin, U. Tiny seeds make a big difference - A seeded-growth approach provides shape-controlled bimetallic nanocrystals and opens the way for a rich selection of new nanoscale building blocks. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 625–626.
- 12 Ma, L.; Zheng, J.-J.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, R.; Fang, L.; Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, C.; Yan, X.; Fan, K. A natural biogenic nanozyme for scavenging superoxide radicals. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–17.
- 13 Breslow, R. Artificial enzymes. Science 1982, 218, 532–537.
- 14 Murakami, Y.; Kikuchi, J.-i.; Hisaeda, Y.; Hayashida, O. Artificial enzymes. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 721–758.
- 15 Nanda, V.; Koder, R. L. Designing artificial enzymes by intuition and computation. Nat. Chem. 2009, 2, 15–24.
- 16
Zhang, R.; Jiang, B.; Fan, K.; Gao, L.; Yan, X. Designing nanozymes for in vivo applications. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222–024–00205–1
10.1038/s44222-024-00205-1 Google Scholar
- 17 Bao, M.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, R.; Wang, X.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. A novel colorimetric sensor through peroxymonosulfate activated by CoFe@CN nanozymes for on-site resorcinol detection. Microchem. J. 2024, 206, 111419.
- 18 Xiao, R.; Dai, H.; Liu, X.; Qi, J.; Bao, M.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Yan, D. Enhancing colorimetric efficiency: nanozyme-activated peroxymonosulfate for in situ 3-aminophenol detection. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 582.
- 19 Meng, X.; Fan, H.; Chen, L.; He, J.; Hong, C.; Xie, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, K.; Gao, X.; Gao, L.; Yan, X.; Fan, K. Ultrasmall metal alloy nanozymes mimicking neutrophil enzymatic cascades for tumor catalytic therapy. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1626.
- 20 Cao, X.; Yang, H.; Wei, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X. Fast colorimetric sensing of H2O2 and glutathione based on Pt deposited on NiCo layered double hydroxide with double peroxidase-/oxidase- like activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 123, 108331.
- 21 Lu, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Z.; Su, L.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, Y. Cu-MOF derived CuO@g-C3N4 nanozyme for cascade catalytic colorimetric sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 5949–5960.
- 22 Macias, E.; Suarez, A.; Lloret, J. Mobile sensing systems. Sensors 2013, 13, 17292–17321.
- 23 Lee, D.-S.; Jeon, B. G.; Ihm, C.; Park, J.-K.; Jung, M. Y. A simple and smart telemedicine device for developing regions: a pocket-sized colorimetric reader. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 120–126.
- 24 Yang, X.; Jin, C.; Zheng, J.; Chai, F.; Tian, M. Portable intelligent paper-based sensors for rapid colorimetric and smartphone-assisted analysis of hydrogen peroxide for food, environmental and medical detection applications. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 2023, 394, 134417.
- 25 Zhang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Yang, W.; Xie, C.; Jiang, H. L. Rational fabrication of low-coordinate single-atom Ni electrocatalysts by MOFs for highly selective CO2 reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 7607–7611.
- 26 Han, X.; Ling, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhong, C.; Hu, W.; Deng, Y. Generation of nanoparticle, atomic-cluster, and single-atom cobalt catalysts from zeolitic imidazole frameworks by spatial isolation and their use in zinc-air batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5359–5364.
- 27 Niu, W.; Pakhira, S.; Marcus, K.; Li, Z.; Mendoza-Cortes, J. L.; Yang, Y. Apically dominant mechanism for improving catalytic activities of N-doped carbon nanotube arrays in rechargeable Zinc-Air battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800480.
- 28 Gao, S.; Yang, S.-H.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, G.-S.; Yin, P.-G.; Zhang, X.-J. CoNi alloy with tunable magnetism encapsulated by N-doped carbon nanosheets toward high-performance microwave attenuation. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 215, 108781.
- 29 Xia, S.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, M.; Pang, H.; Xu, L.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y. In-situ immobilization of CoNi nanoparticles into N-doped carbon nanotubes/nanowire-coupled superstructures as an efficient Mott-Schottky electrocatalyst toward electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 54, 278–289.
- 30 Zhu, L. P.; Xiao, H. M.; Fu, S. Y. Surfactant-assisted synthesis and characterization of novel chain-Like CoNi alloy assemblies. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 3947–3951.
- 31 Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y.; Indrawirawan, S.; Wang, S. Insights into heterogeneous catalysis of persulfate activation on dimensional-structured nanocarbons. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4629–4636.
- 32 Cheng, C.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, C.; Du, C.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W. High-efficiency bifunctional electrocatalyst based on 3D freestanding Cu foam in situ armored CoNi alloy nanosheet arrays for overall water splitting. J. Power Sources 2019, 427, 184–193.
- 33 Li, K.; Sun, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Three-dimensional architectures assembled with branched metal nanoparticle-encapsulated nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays for absorption of electromagnetic wave. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 821, 153267.
- 34 Li, Q; Zhu, H.; Zheng, L. R.; Fan, L. L.; Wang, N.; Rong, Y.; Ren, Y.; Chen, J.; Deng, J.; Xing, X. Local chemical ordering and negative thermal expansion in PtNi alloy nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7892–7896.
- 35 Zhu, Z.; Ji, C.; Zhong, L.; Liu, S.; Cui, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, W. Magnetic Fe-Co crystal doped hierarchical porous carbon fibers for removal of organic pollutants. J. Mater. Chem., A 2017, 5, 18071–18080.
- 36 Chattopadhyay, K.; Mazumdar, S. Structural and conformational stability of horseradish peroxidase: Effect of temperature and pH. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 263–270.
- 37 Kang, J.; Zhang, H.; Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Tan, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, S. Magnetic Ni-Co alloy encapsulated N-doped carbon nanotubes for catalytic membrane degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 251–261.
- 38
Zheng, Z.; Wang, C.; Mao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Ran, R.; Zhou, W.; Liao, K.; Shao, Z. In situ formation of self-antistacking FeCoOx on N-doped graphene: A 3D-on-2D nanoarchitecture for long-life Zn-air batteries. Carbon Energy 2022, 5, e274.
10.1002/cey2.274 Google Scholar
- 39 Deng, W.; Wu, T.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, G.; Yang, M.; Zou, X.; Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jing, M.; Wang, X. Single atomic Fe-pyridine N catalyst with dense active sites improve bifunctional electrocatalyst activity for rechargeable and flexible Zn-air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 20993–21003.
- 40 Xing, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, B.; Tong, M.; Tian, C.; Wang, L.; Fu, H. Strengthening oxygen reduction activity based on the cooperation of pyridinic-N and graphitic-N for atomically dispersed Fe sites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 9493–9503.
- 41 Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xing, H.; Feng, W.; Feng, J.; Shi, Z.; Zong, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Fe3C nanocrystals encapsulated in N-doped carbon nanofibers as highefficient microwave absorbers with superior oxidationcorrosion. Carbon 2021, 178, 515–527.
- 42 Ma, M.; Liao, Z.; Su, X.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wan, F. Magnetic CoNi alloy particles embedded N-doped carbon fibers with polypyrrole for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2022, 608, 2203–2212.
- 43 He, X.; Yin, F.; Li, G.; Chen, B.; Wang, S.; Gu, M. CoNi alloys with slight oxidation@N,O Co-doped carbon: enhanced collective contributions of cores and shells to multifunctional electrocatalytic activity and Zn-air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 25805–25823.
- 44 Josephy, P. D.; Elin, T.; Mason, R. P. The horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of 3,5,3',5'-tetramethylbenzidine. Free radical and charge-transfer complex intermediates. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 3669–3675.
- 45 Han, S.; Xiao, P.; An, L.; Wu, D. Oxidative degradation of tetracycline using peroxymonosulfate activated by cobalt-doped pomelo peel carbon composite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2021, 29, 21656–21669.
- 46 Yao, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, C.; Qi, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Duan, X.; Li, J. Rational regulation of Co-N-C coordination for high-efficiency generation of 1O2 toward nearly 100% selective degradation of organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8833–8843.
- 47 Liu, F.; Cao, J.; Yang, Z.; Xiong, W.; Xu, Z.; Song, P.; Jia, M.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X. Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by cobalt-doped MIL-53(Al) for efficient tetracycline degradation in water: Coexistence of radical and non-radical reactions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 195–204.
- 48 Jia, Q.-Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.-Z. Reductive dehalogenation in groundwater by Si-Fe(II) co-precipitates enhanced by internal electric field and low vacancy concentrations. Water Res. 2023, 228, 119386.
- 49 Zhang, G.; Qin, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, H.; Meng, F. Catalytic performance for CO methanation over Ni/MCM-41 catalyst in a slurry-bed reactor. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1–13.
- 50 Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Sun, Z. CoNi alloy anchored onto N-doped porous carbon for the removal of sulfamethoxazole: Catalyst, mechanism, toxicity analysis, and application. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136291.
- 51 Akçay, H. T.; Demir, A.; Özçifçi, Z.; Yumak, T.; Keleş, T. Treatment of wastewater containing organic pollutants in the presence of N-doped graphitic carbon and Co3O4/peroxymonosulfate. Carbon Lett. 2023, 33, 1445–1460.
- 52 Lin, Y.; Zhao, A.; Tao, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Ionic Liquid as an Efficient Modulator on Artificial Enzyme System: Toward the Realization of High-Temperature Catalytic Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4207–4210.
- 53 Gao, L.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Perrett, S.; Yan, X. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577–583.
- 54 Guo, Y.; Long, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Can the commonly used quenching method really evaluate the role of reactive oxygen species in pollutant abatement during catalytic ozonation? Water Res. 2022, 215, 118275.
- 55 Gao, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhan, J.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Assessment of the validity of the quenching method for evaluating the role of reactive species in pollutant abatement during the persulfate-based process. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118730.
- 56 Si, Q.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, H.; Ren, N.; Yu, T. Spin-states-assistance peroxymonosulfate absorption via Mn doped catalyst with/without light for BPA oxidation: The negative contribution of electrons transfer by light. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136399.
- 57 Zhang, X.; Jia, Q.; Deng, J.; Li, L.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, L.; Huang, L.-Z. Intervention timing of H* and •OH determines the catalytical degradation of tribromophenol by palladium(II) doped green rust in redox-alternating environments. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2024, 343, 123510.
- 58 Chen, F.; Jiang, Y.; Sui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H.; Han, Y.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W.; Geng, Y. Donor-acceptor conjugated polymers based on bisisoindigo: Energy level modulation toward unipolar n-type semiconductors. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 8652–8661.
- 59 Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Lang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wu, P. Rationale of 3,3’,5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine as the chromogenic substrate in colorimetric analysis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 12400–12406.
- 60 Zhang, D.; Qi, J.; Ji, H.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Huang, T.; Xu, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, W. Photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin by perovskite-type NaNbO3 nanorods modified g-C3N4 heterojunction under simulated solar light: Theoretical calculation, ofloxacin degradation pathways and toxicity evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125918.
- 61 Chen, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Lv, W.; Liu, G. Degradation of propranolol by UV-activated persulfate oxidation: Reaction kinetics, mechanisms, reactive sites, transformation pathways and Gaussian calculation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 878–890.
- 62 Vleeschouwer, F. D.; Speybroeck, V. V.; Waroquier, M.; Geerlings, P.; De Proft, F. Electrophilicity and nucleophilicity index for radicals. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 2721–2724.
- 63 Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, D.; Liang, J. Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac by carbon quantum dots modified porous g-C3N4: Mechanisms, degradation pathway and DFT calculation. Water Res. 2019, 151, 8–19.
- 64 Gao, X.; Chen, J.; Che, H.; Ao, Y.; Wang, P. Rationally constructing of a novel composite photocatalyst with multi charge transfer channels for highly efficient sulfamethoxazole elimination: Mechanism, degradation pathway and DFT calculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131585.
- 65 Oña, O. B.; De Clercq, O.; Alcoba, D. R.; Torre, A.; Lain, L.; Van Neck, D.; Bultinck, P. Atom and bond fukui functions and matrices: A hirshfeld-I atoms-in-molecule approach. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2016, 17, 2881–2889.
- 66 Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J. A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710.
- 67 Li, R.; Jiao, L.; Jia, X.; Yan, L.; Li, X.; Yan, D.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, C.; Lu, X. Bioinspired FeN5 Sites with Enhanced Peroxidase-like Activity Enable Colorimetric Sensing of Uranyl Ions in Seawater. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 3124–3130.
- 68 Han, S.; Zou, M.; Pu, X.; Lu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, F.; Huang, N.; Shen, M.; Song, E.; Wang, D. Smart MXene-based bioelectronic devices as wearable health monitor for sensing human physiological signals. View 2023, 4, 1–10.
- 69 Abood, E. S. Metals Concentrations in Blood and Urine Measured Using a New Nano Metals Oxide Electrode. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2022, 14, 107–113.




