Regioselective Electrochemical Hydroalkylations of [60]Fullerene-Fused Furochromenone
Zheng-Chun Yin
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorChuang Niu
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorMingjie Li
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorWen-Rui Liu
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guan-Wu Wang
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu, 730000 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorZheng-Chun Yin
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorChuang Niu
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorMingjie Li
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorWen-Rui Liu
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guan-Wu Wang
Hefei National Research Center for Physical Sciences at the Microscale and Department of Chemistry, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, 230026 China
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu, 730000 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this author† Dedicated to the Special Issue of Recent Advances in Fullerene Chemistry.
Comprehensive Summary
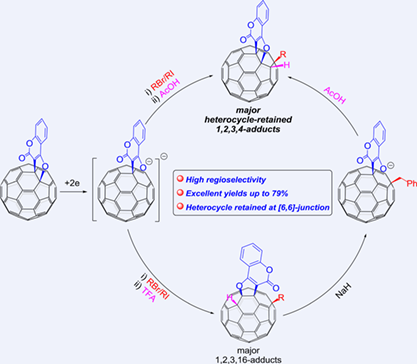
Regioselective electrochemical hydroalkylations of [60]fullerene-fused furochromenone with alky halides under different acidic conditions unexpectedly afford three types of tetra-functionalized [60]fullerene derivatives in high yields. When acetic acid is used as the proton source, two 1,2,3,4-adducts with retained or rearranged five-membered heterocycle are obtained as major and minor products, respectively. While trifluoroacetic acid is employed as the proton source, 1,2,3,16-adducts and 1,2,3,4-adducts, both with the five-membered heterocycle rearranged from [6,6]-junction to [5,6]-junction, are generated. Intriguingly, the obtained 1,2,3,16-adducts can be transformed into 1,2,3,4-adducts accompanied by rearrangement of the fused five-membered heterocycle from [5,6]-junction to [6,6]-junction. These products have been characterized by spectroscopic data and single-crystal X-ray analysis. Moreover, the two 1,2,3,4-adducts with the heterocycle fused to [5,6]-junction or [6,6]-junction show diagnostic UV-vis spectra, which may be useful for the identification of these two types of 1,2,3,4-adducts in the future. A plausible reaction mechanism has been proposed to elucidate the formation of hydroalkylation products in the presence of different acids.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202200669-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 10.6 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For selected recent reviews, see: (a) Harano, K.; Nakamura, E. Interfacial Chemistry of Conical Fullerene Amphiphiles in Water. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2090–2100; (b) Umeyama, T.; Imahori, H. Isomer Effects of Fullerene Derivatives on Organic Photovoltaics and Perovskite Solar Cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2046–2055; (c) Jia, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, S. Functionalization of fullerene materials toward applications in perovskite solar cells. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 2256–2282; (d) Wang, G.-W. Fullerene Mechanochemistry: Serendipitous Discovery of Dumb-Bell-Shaped C120 and Beyond. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1797–1803; (e) Shen, W.; Bao, L.; Lu, X. Endohedral Metallofullerenes: An Ideal Platform of Sub-Nano Chemistry. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 275–284.
- 2For selected reviews, see: (a) Matsuo, Y.; Nakamura, E. Selective Multiaddition of Organocopper Reagents to Fullerenes. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3016–3028; (b) Zhu, S.-E; Li, F.; Wang, G.-W. Mechanochemistry of fullerenes and related materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7535–7570; (c) Gan, L. Molecular Containers Derived from [60]Fullerene through Peroxide Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1793–1801.
- 3For examples on tetra-functionalizations of C60, see: (a) Hirsch, A.; Lamparth, I.; Karfunkel, H. R. Fullerene Chemistry in Three Dimensions: Isolation of Seven Regioisomeric Bisadducts and Chiral Trisadducts of C60 and Di(ethoxycarbonyl)methylene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1994, 33, 437–438; (b) Schick, G.; Hirsch, A.; Mauser, H.; Clark, T. Opening and Closure of the Fullerene Cage in cis-1-Bisimino Adducts of C60: The Influence of the Addition Pattern and the Addend. Chem. - Eur. J. 1996, 2, 935–943; (c) Lu, Q.; Schuster, D. I.; Wilson, S. R. Preparation and Characterization of Six Bis(N-methylpyrrolidine)- C60 Isomers: Magnetic Deshielding in Isomeric Bisadducts of C60. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 4764–4768; (d) Djojo, F.; Herzog, A.; Lamparth, I.; Hampel, F.; Hirsch, A. Regiochemistry of Twofold Additions to [6,6] Bonds in C60: Influence of the Addend-Independent Cage Distortion in 1,2-Monoadducts. Chem. - Eur. J. 1996, 2, 1537–1547; (e) Nakamura, Y.; Takano, N.; Nishimura, T.; Yashima, E.; Sato, M.; Kudo, T.; Nishimura, J. First Isolation and Characterization of Eight Regioisomers for [60]Fullerene−Benzyne Bisadducts. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 1193–1196; (f) Kordatos, K.; Bosi, S.; Da Ros, T.; Zambon, A.; Lucchini, V.; Prato, M. Isolation and Characterization of All Eight Bisadducts of Fulleropyrrolidine Derivatives. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 2802–2808.
- 4(a) Diederich, F.; Kessinger, R. Templated Regioselective and Stereoselective Synthesis in Fullerene Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 1999, 32, 537–545; (b) Nakamura, Y.; O-kawa, K.; Nishimura, J. Biscycloaddition to [60]Fullerene: Regioselectivity and Its Control with Templates. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 76, 865–882.
- 5 Niu, C.; Wang, G. Progress in Electrochemical Reactions of [60]Fullerene-Fused Heterocycles. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 3633–3645.
- 6(a) Yang, W.-W.; Li, Z.-J.; Li, F.-F.; Gao, X. Electrochemical and H/D-Labeling Study of Oxazolino[60]Fullerene Rearrangement. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 1384–1389; (b) Hou, H.-L.; Li, Z.-J.; Gao, X. Reductive Benzylation of C60 Imidazoline with a Bulky Addend. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 712–715; (c) Xiao, Y.; Zhu, S.-E; Liu, D.-J.; Suzuki, M.; Lu, X.; Wang, G.-W. Regioselective Electrosynthesis of Rare 1,2,3,16-Functionalized [60]Fullerene Derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3006–3010; (d) Xiao, Y.; Wang, G. A 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydrofullerene Derivative Generated from a [60]Fulleroindoline: Regioselective Electrosynthesis and Computational Study. Chin. J. Chem. 2014, 32, 699–702; (e) Lin, H.-S.; Matsuo, Y.; Wang, J.-J.; Wang, G.-W. Regioselective acylation and carboxylation of [60]fulleroindoline via electrochemical synthesis. Org. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 603–607; (f) Li, F.; Wang, J.-J.; Wang, G.-W. Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of [60]fullerenefused benzofurans via heteroannulation of phenols. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 1852–1855; (g) Hussain, M.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, G.-W. Palladium-Catalyzed Heteroannulation of Indole-1-carboxamides with [60]Fullerene and Subsequent Electrochemical Transformations. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8568–8571; (h) Liu, K.-Q.; Wang, J.-J.; Yan, X.-X.; Niu, C.; Wang, G.-W. Regioselective electrosynthesis of tetra- and hexafunctionalized [60]fullerene derivatives with unprecedented addition patterns. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 384–388; (i) Yan, X.-X.; Li, B.; Lin, H.-S.; Jin, F.; Niu, C.; Liu, K.-Q.; Wang, G.-W.; Yang, S. Successively Regioselective Electrosynthesis and Electron Transport Property of Stable Multiply Functionalized [60]Fullerene Derivatives. Research 2020, 2020, 2059190; (j) Hussain, M.; Niu, C.; Wang, G.-W. Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of [60]fullerene-fused furochromenones and further electrochemical functionalization. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 1249–1254; (k) Yang, Y.; Niu, C.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, G.-W. Electrochemical regioselective alkylations of a [60]fulleroindoline with bulky alkyl bromides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 4783–4787; (l) Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Z.-C.; Wang, G.-W. Synthesis of [60]fullerene- fused dihydrobenzooxazepines via the palladiumcatalyzed oxime- directed C–H bond activation and subsequent electrochemical functionalization. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 2518–2525; (m) Liu, Z.; Yin, Z.-C.; Lu, W.-Q.; Niu, C.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, G.-W. Cu(I)-Catalyzed Synthesis of [60]Fullerene-Fused Lactams and Further Electrochemical Functionalization. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 4051–4056.
- 7 Niu, C.; Zhou, D.-B.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Z.-C.; Wang, G.-W. A retro Baeyer–Villiger reaction: electrochemical reduction of [60]fullerene-fused lactones to [60] fullerene-fused ketones. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 3012–3017.
- 8 Smith III, A. B.; Strongin, R. M.; Brard, L.; Furst, G. T.; Romanow, W. J.; Owens, K. G.; Goldschmidt, R. J.; King, R. C. Synthesis of Prototypical Fullerene Cyclopropanes and Annulenes. Isomer Differentiation via NMR and UV Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5492–5502.
- 9(a) Bordwell, F. G. Equilibrium Acidities in Dimethyl Sulfoxide Solution. Acc. Chem. Res. 1988, 21, 456–463; (b) Fagan, P. J.; Krusic, P. J.; Evans, D. H.; Lerke, S. A.; Johnston, E. Synthesis, Chemistry, and Properties of a Monoalkylated Buckminsterfullerene Derivative, t-BuC60 Anion. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 9697–9701; (c) Kaliszan, R.; Wiczling, P.; Markuszewski, M. J. pH gradient high-performance liquid chromatography: theory and applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1060, 165–175. The reported pKa values of t-BuC60H and AcOH in DMSO were 5.7 and 12.3, respectively. The reported pKa values of warfarine and AcOH in water were 5.1 and 4.75, respectively.
- 10(a) Izquierdo, M.; Osuna, S.; Filippone, S.; Martín-Domenech, A.; Solà, M.; Martín, N. H-Bond-Assisted Regioselective (cis-1) Intramolecular Nucleophilic Addition of the Hydroxyl Group to [60]Fullerene. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 1480–1487; (b) Izquierdo, M.; Osuna, S.; Filippone, S.; Martín-Domenech, A.; Solà, M.; Martín, N. Regioselective Intramolecular Nucleophilic Addition of Alcohols to C60: One-Step Formation of a cis-1 Bicyclic-Fused Fullerene. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 6253–6259.




