An Updated Review on Functionalized Graphene as Sensitive Materials in Sensing of Pesticides
Anirudh Pratap Singh Raman
Department of Chemistry, Atma Ram Sanatan Dharma College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Delhi- NCR Campus, Delhi-Merrut Road, Modinagar, Ghaziabad, UP, India
Search for more papers by this authorGauri Thakur
Department of Chemistry, Atma Ram Sanatan Dharma College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, India
Search for more papers by this authorGarima Pandey
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Delhi- NCR Campus, Delhi-Merrut Road, Modinagar, Ghaziabad, UP, India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kamlesh Kumari
Department of Zoology, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prashant Singh
Department of Chemistry, Atma Ram Sanatan Dharma College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Delhi- NCR Campus, Delhi-Merrut Road, Modinagar, Ghaziabad, UP, India
Search for more papers by this authorAnirudh Pratap Singh Raman
Department of Chemistry, Atma Ram Sanatan Dharma College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Delhi- NCR Campus, Delhi-Merrut Road, Modinagar, Ghaziabad, UP, India
Search for more papers by this authorGauri Thakur
Department of Chemistry, Atma Ram Sanatan Dharma College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, India
Search for more papers by this authorGarima Pandey
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Delhi- NCR Campus, Delhi-Merrut Road, Modinagar, Ghaziabad, UP, India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kamlesh Kumari
Department of Zoology, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prashant Singh
Department of Chemistry, Atma Ram Sanatan Dharma College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering and Technology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Delhi- NCR Campus, Delhi-Merrut Road, Modinagar, Ghaziabad, UP, India
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
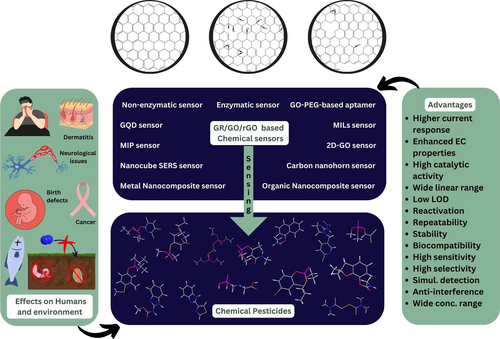
Numerous chemical pesticides were employed for a long time to manage pests, but their uncontrolled application harmed the health and the environment. Accurately quantifying pesticide residues is essential for risk evaluation and regulatory purposes. Numerous analytical methods have been developed and utilized to achieve sensitive and specific detection of pesticides in intricate sampl es like water, soil, food, and air. Electrochemical sensors based on amperometry, potentiometry, or impedance spectroscopy offer portable, rapid, and sensitive detection suitable for on-site analysis. This study examines the potential of electrochemical sensors for the accurate evaluation of various effects of pesticides. Emphasizing the use of Graphene (GR), Graphene Oxide (GO), Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO), and Graphdiyne composites, the study highlights their enhanced performance in pesticide sensing by stating the account of many actual sensors that have been made for specific pesticides. Computational studies provide valuable insights into the adsorption kinetics, binding energies, and electronic properties of pesticide-graphene complexes, guiding the design and optimization of graphene-based sensors with improved performance. Furthermore, the discussion extends to the emerging field of biopesticides. While the GR/GO/rGO based sensors hold immense future prospects, and their existing limitations have also been discussed, which need to be solved with future research.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1Pesticides use, pesticides trade and pesticides indicators, Global, regional and country trends, 1990–2020 https://www.fao.org/3/cc0918en/cc0918en.pdf.
- 2B. C. Patel, G. R. Sinha, N. Goel, in Advances in Modern Sensors, IOP Publishing, 2020.
- 3T. Ohashi, L. Dai, in Carbon Nanotechnology: Recent Developments in Chemistry, Physics, Materials Science and Device Applications (Ed. L. Dai), Elsevier, 2006, 525–575.
10.1016/B978-044451855-2/50018-8 Google Scholar
- 4H. Abdulhadi in Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering, (Ed. Md. S. H. Ador, P. Bhattacharjee, S. Kabir, Md. T. Ahmed, F. Ahmed, I. A. Choudhury) Elsevier, 2023.
- 5R. Suresh, S. Rajendran, P. S. Kumar, T. K. A. Hoang, M. Soto-Moscoso, A. A. Jalil, Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 165,113169.
- 6H. Shamkhalichenar, J.-W. Choi, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037531.
- 7G. Maduraiveeran, W. Jin, Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 13, 10–23.
- 8S. Su, W. Wu, J. Gao, J. Lu, C. Fan, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18101–18110.
- 9M. M. Sabzehmeidani, S. Mahnaee, M. Ghaedi, H. Heidari, V. A. L. Roy, Mater Adv. 2021, 2, 598–627.
- 10L. Ding, J. Guo, S. Chen, Y. Wang, Talanta 2024, 273, 125937.
- 11P. Nicolopoulou-Stamati, S. Maipas, C. Kotampasi, P. Stamatis, L. Hens, Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 148.
- 12Y. Abubakar, H. Tijjani, C. Egbuna, C. O. Adetunji, S. Kala, T. L. Kryeziu, K. C. Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, in Natural Remedies for Pest, Disease and Weed Control, (Ed: C. Egbuna, B Sawicka), Elsevier, 2019, 29–42.
- 13F. Sánchez-Santed, M. T. Colomina, E. Herrero Hernández, Cortex 2016, 74, 417–426.
- 14Y. Zheng, S. Mao, J. Zhu, L. Fu, M. Moghadam, Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136069.
- 15T. O. Ajiboye, P. O. Oladoye, C. A. Olanrewaju, G. O. Akinsola, Environ. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 100655.
- 16C. Cheng, W. Liu, K. Hou, J. Zhang, Z. Du, B. Li, L. Zhu, Appl Soil Ecol 2023, 189, 104954.
10.1016/j.apsoil.2023.104954 Google Scholar
- 17H. Fu, P. Tan, R. Wang, S. Li, H. Liu, Y. Yang, Z. Wu, J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127494.
- 18A. Ka, A. K. Mukherjee, Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 39, 90–94.
- 19S. Poomagal, R. Sujatha, P. S. Kumar, D. V. N. Vo, Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127926.
- 20B. Mohapatra, T. Dhamale, B. K. Saha, P. S. Phale, in Microbial Biodegradation and Bioremediation (Second Edition) (Eds.: S. Das, H. R. Dash), Elsevier, 2022, 365–394.
10.1016/B978-0-323-85455-9.00006-0 Google Scholar
- 21C. Zhu, X. Wang, X. Shi, F. Yang, G. Meng, Q. Xiong, Y. Ke, H. Wang, Y. Lu, N. Wu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39618–39625.
- 22N. L. Stanton, M. Allen, M. Campion, J. Appl. Ecol. 1981, 18, 417–431.
- 23M. A. Manavi, M. H. F. Nasab, S. M. Daghighi, M. Baeeri, in Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences, Elsevier, 2023, 589–591.
- 24M. L. Hladik, A. R. Main, D. Goulson, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3329–3335.
- 25D. S. Rohlman, J. R. Olson, A. A. Ismail, M. R. Bonner, G. Abdel Rasoul, O. Hendy, in Adv Neurotoxicol (Eds.: R. G. Lucchini, M. Aschner, L. G. Costa), Academic Press, 2022, 03, 203–255.
- 26R. D. Horsak, P. B. Bedient, M. C. Hamilton, F. Ben Thomas, in Environ Forensics (Eds.: R. D. Morrison, B. L. Murphy), Academic Press, Burlington, 1964, 143–165.
10.1016/B978-012507751-4/50030-6 Google Scholar
- 27A. J. Leadbeater, in Encyclopedia of Agriculture and Food Systems (Ed.: N. K. Van Alfen), Academic Press, Oxford, 2014, 408–424.
10.1016/B978-0-444-52512-3.00179-0 Google Scholar
- 28T. Gunstone, T. Cornelisse, K. Klein, A. Dubey, N. Donley, Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 643847.
- 29R. L. Mull, L. W. Hershberger, in Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology (Second Edition) (Eds.: R. I. Krieger, W. C. Krieger), Academic Press, San Diego, 2001, 1673–1699.
- 30P. K. Gupta, in Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology (Ed.: R. C. Gupta), Academic Press, San Diego, 2011, 503–521.
10.1016/B978-0-12-382032-7.10039-6 Google Scholar
- 31S. Salam, Z. Iqbal, A. A. Khan, R. Mahmood, Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 178, 104915.
- 32D. M. Janz, in Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition) (Ed.: P. Wexler), Academic Press, Oxford, 2014, 212–214.
10.1016/B978-0-12-386454-3.00139-1 Google Scholar
- 33C. Belaid, I. Sbartai, M.-R. Djebar, Studia Universitatis Vasile Goldis Arad, Seria Stiintele Vietii 2020, 29, 121–128.
- 34M. Thiruchelvam, in Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Second Edition) (Ed.: P. Wexler), Elsevier, New York, 2005, 179–182.
10.1016/B0-12-369400-0/00945-5 Google Scholar
- 35D. Abdollahdokht, G. Asadikaram, M. Abolhassani, H. Pourghadamyari, M. Abbasi-Jorjandi, S. Faramarz, M. H. Nematollahi, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 57216–57231.
- 36A. Samareh, G. Asadikaram, MojtabaAbbasi-Jorjandi, D. Abdollahdokht, M. Abolhassani, N. Khanjani, M. H. Nematollahi, Toxicol. Ind. Health 2022, 38, 455–469.
- 37F. Yousefi, G. Asadiaram, S. Karamouzian, M. Abolhassani, V. Moazed, M. H. Nematollahi, Environ. Health Eng. Manag. 2021, 8, 47–53.
- 38R. D. Damale, A. Dutta, N. Shaikh, A. Pardeshi, R. Shinde, K. D. Babu, N. N. Gaikwad, K. Banerjee, Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135179.
- 39J. Ben Attig, L. Latrous, M. Zougagh, Á. Ríos, Talanta 2021, 226, 122106.
- 40M. Liu, Z. Chen, X. Huang, H. Wang, J. Zhao, Y. Shen, L. Luo, X. Wen, B. Hammock, Z. Xu, Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122265.
- 41Q. Shao, C. Jiang, X. Chen, A. Wang, L. Lu, L. Chen, H. Lu, Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2023, 296, 122676.
- 42S. Liu, J. Zhou, X. Yuan, J. Xiong, M.-H. Zong, X. Wu, W.-Y. Lou, Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137272.
- 43L. Chen, J. Lu, M. Luo, H. Yu, X. Chen, J. Deng, X. Hou, E. Hao, J. Wei, P. Li, Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132139.
- 44Y. Pico, A. H. Alfarhan, D. Barcelo, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115720.
- 45T. B. Budak, M. F. Ayyıldız, D. S. Chormey, S. Bakırdere, Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192,– 8.
10.1007/s10661-020-8209-2 Google Scholar
- 46D. Liang, W. Liu, R. Raza, Y. Bai, H. Liu, J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 330–341.
- 47M. E. Hergueta-Castillo, R. López-Ruiz, R. Romero-González, A. Garrido Frenich, J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1685, 463588.
- 48S. Yasien, M. M. Iqbal, M. Javed, S. Iqbal, Z. Ahmad, N. Tamam, S. Nadeem, E. B. Elkaeed, R. M. Alzhrani, N. S. Awwad, H. A. Ibrahium, R. A. Hakami, Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103937.
- 49Z. Gong, Y. Huang, X. Hu, J. Zhang, Q. Chen, H. Chen, Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 140.
- 50A. J. Baeumner, G. Gauglitz, L. Mondello, M. C. M. Bondi, S. Szunerits, Q. Wang, S. A. Wise, A. T. Woolley, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 6281–6284.
- 51P. Sakdarat, J. Chongsuebsirikul, C. Thanachayanont, S. Prichanont, P. Pungetmongkol, J. Nanomater. 2021, 6623668.
- 52J. Wu, H. Liu, W. Chen, B. Ma, H. Ju, Nature Reviews Bioengineering 2023, 1, 346–360.
- 53B. Pérez-Fernández, A. Costa-García, A. D. Muñiz, Biosensors (Basel) 2020, 10, 32.
- 54S. Joo, R. Brown, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 638–651.
- 55A. Haleem, M. Javaid, R. P. Singh, R. Suman, S. Rab, Sensors International 2021, 2, 100100.
10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100100 Google Scholar
- 56J. Baranwal, B. Barse, G. Gatto, G. Broncova, A. Kumar, Chemosensors 2022, 10, 363.
- 57S. Shrivastava, T. Q. Trung, N.-E. Lee, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1812–1866.
- 58S. Kr. Jha, R. D. S. Yadava, K. Hayashi, N. Patel, Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 185, 18–31.
- 59C. La Rosa, F. Pariente, L. Hernandez, E. Lorenzo, Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 308, 129–136.
- 60Ľ. Švorc, M. Rievaj, D. Bustin, Sens. Actuators B 2013, 181, 294–300.
- 61M. G. F. Sales, M. C. V. F. Vaz, C. Delerue-Matos, S. A. A. Almeida, M. F. Barroso, H. A. O. Ferreira, Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2008, 88, 37–49.
- 62X. Zhu, J. Yang, Q. Su, J. Cai, Y. Gao, J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1092, 161–169.
- 63J. López Flores, M. L. de Córdova, A. Molina Díaz, J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 1080–1085.
- 64L. Tang, G.-M. Zeng, G.-L. Shen, Y.-P. Li, Y. Zhang, D.-L. Huang, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1207–1212.
- 65E. Llorent-Martínez, P. Ortega-Barrales, A. Molina-Díaz, Spectrosc. Lett. 2006, 39, 619–629.
- 66E. J. Llorent-Martínez, J. F. García-Reyes, P. Ortega-Barrales, A. Molina-Díaz, J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 860–865.
- 67A. H. Kamel, F. T. C. Moreira, S. A. A. Almeida, M. G. F. Sales, Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 194–202.
- 68B. Bucur, P.-M. Bucur, D. Andrei, J. Marty, Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 539, 195–201.
- 69E. Bakker, M. Telting-Diaz, Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 12781–2800.
10.1021/ac0202278 Google Scholar
- 70S. K. Choi, Nanomat. 2021, 11, 1–23.
- 71R. Umapathi, S. M. Ghoreishian, S. Sonwal, G. M. Rani, Y. S. Huh, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 453, 214305.
- 72K. Niu, J. Gao, L. Wu, X. Lu, J. Chen, Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 8656–8662.
- 73Z. Xia, Y. Zhou, Y. Gong, P. Mao, N. Zhang, C. Yuan, W. Xue, Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1513–1522.
- 74L. Yan, X. Yan, H. Li, X. Zhang, M. Wang, S. Fu, G. Zhang, C. Qian, H. Yang, J. Han, F. Xiao, Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105016.
- 75Y. Zhao, X. Zheng, Q. Wang, T. Zhe, Y. Bai, T. Bu, M. Zhang, L. Wang, Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127495.
- 76B. A. Xiao, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220672.
- 77N. Taşaltın, S. Karakuş, C. Taşaltın, G. Baytemir, Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131267.
- 78Y. Zhang, X. Liu, S. Qiu, Q. Zhang, W. Tang, H. Liu, Y. Guo, Y. Ma, X. Guo, Y. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14643–14649.
- 79W. Xu, Y. Huang, R. Zhou, Q. Wang, J. Yin, J. Kono, J. Ping, L. Xie, Y. Ying, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 44281–44287.
- 80S. Alexander, P. Baraneedharan, S. Balasubrahmanyan, S. Ramaprabhu, Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 124–129.
- 81S. Bhattacharjee, R. Joshi, A. Chughtai, C. Macintyre, Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6.
- 82T. Lazarević-Pašti, V. Anićijević, M. Baljozović, D. V. Anićijević, S. Gutić, V. Vasić, N. V. Skorodumova, I. A. Pašti, Environ. Sci.-Nano 2018, 5, 1482–1494.
- 83M. Chakraborty, M. S. J. Hashmi, in Reference Module in Mat Sci and Mat Eng, Elsevier, 2018.
- 84S. C. Ray, William Andrew Publishing, Oxford, 2015, 39–55.
- 85P. Das, S. Thomas, S. Das, Sensing of Deadly Toxic Chemical Warfare Agents, Nerve Agent Simulants, and their Toxicological Aspects, in Elsevier, 2022, 635–658.
- 86L. Kaur, J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 101019.
- 87S. M. Maliyekkal, T. S. Sreeprasad, D. Krishnan, S. Kouser, A. K. Mishra, U. V. Waghmare, T. Pradeep, Small 2013, 9, 273–283.
- 88D. F. Báez, T. P. Brito, L. C. Espinoza, A. M. Méndez-Torres, R. Sierpe, P. Sierra-Rosales, C. J. Venegas, C. Yáñez, S. Bollo, Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106303.
- 89G. Narang, D. Bansal, S. Joarder, P. Singh, L. Kumar, V. Mishra, S. Singh, K. Tumba, K. Kumari, FlatChem 2023, 40, 100517.
- 90C. Pan, C. Wang, Y. Fang, Y. Zhu, H. Deng, Y. Guo, Environ. Sci.-Nano 2021, 8, 1863–1885.
- 91D. Song, X. Xu, X. Huang, G. Li, X. Wang, Y. Zhao, F. Gao, Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1252, 341012.
- 92A. Allangawi, K. Alsayed Jalal, K. Ayub, M. Amjad Gilani, T. Mahmood, Comput. Theor. Chem. 2023, 1222, 114079.
- 93T. Liu, M. Xu, H. Yin, S. Ai, X. Qu, S. Zong, Microchim. Acta 2011, 175, 129–135.
- 94H. Borah, S. Gogoi, S. Kalita, P. Puzari, J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 828, 116–123.
- 95T. Liu, H. Su, X. Qu, P. Ju, L. Cui, S. Ai, Sens. Actuators B 2011, 160, 1255–1261.
- 96P. Hashemi, N. Karimian, H. Khoshsafar, F. Arduini, M. Mesri, A. Afkhami, H. Bagheri, Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 764–772.
- 97B. Maji, L. S. K. Achary, B. Barik, S. Jyotsna Sahoo, A. Mohanty, P. Dash, J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 909, 116115.
- 98A. Mejri, A. Mars, H. Elfil, A. H. Hamzaoui, Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 704.
- 99A. E. Parab, K. Mohanapriya, N. Jha, Mater. Today: Proc. 2021, 42, 710–717.
- 100Y. Yang, A. M. Asiri, D. Du, Y. Lin, Analyst 2014, 139, 3055–3060.
- 101P. Noyrod, O. Chailapakul, W. Wonsawat, S. Chuanuwatanakul, J. Electroanals. Chem. 2014, 719, 54–59.
- 102T. Kokulnathan, S.-M. Chen, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 16216–16226.
- 103N. G. Khare, R. A. Dar, A. K. Srivastava, Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 1915–1924.
- 104Y. Guo, S. Guo, J. Li, E. Wang, S. Dong, Talanta 2011, 84, 60–64.
- 105P. Wei, T. Gan, K. Wu, Sens. Actuators B 2018, 274, 551–559.
- 106K. Kumari, M. B. Singh, N. Tomar, A. Kumar, V. Kumar, K. L. Dabodhia, P. Singh, J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1291, 136043.
- 107J. Xiong, S. Li, Y. Li, Y. Chen, Y. Liu, J. Gan, J. Ju, Y. Xian, X. Xiong, Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2020, 36, 787–794.
- 108M. R. Mahajan, P. O. Patil, Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 144, 109883.
- 109M. R. Mahajan, P. O. Patil, Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 144, 109883.
- 110M. L. Yola, J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 50–57.
- 111L. Gao, L. Ju, H. Cui, J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7753–7758.
- 112C.-T. Hsieh, P.-Y. Sung, Y. A. Gandomi, K. S. Khoo, J.-K. Chang, Chemosphere 2023, 318, 137926.
- 113Q. Long, H. Li, Y. Zhang, S. Yao, Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 168–174.
- 114R. V. Nair, R. T. Thomas, A. P. Mohamed, S. Pillai, Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104971.
- 115M. Roushani, S. Kohzadi, S. Haghjoo, A. Azadbakht, Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 308–313.
10.1016/j.enmm.2018.08.002 Google Scholar
- 116Z. Qu, N. Li, W. Na, X. Su, Talanta 2019, 192, 61–68.
- 117V. Mariyappan, M. Keerthi, S.-M. Chen, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2679–2688.
- 118C. Tian, S. Zhang, H. Wang, C. Chen, Z. Han, M. Chen, Y. Zhu, R. Cui, G. Zhang, J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 847, 113243.
- 119A. Wicaksana, T. Rachman, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 6, 10–27.
- 120T. S. H. Pham, L. Fu, P. Mahon, G. Lai, A. Yu, Electrocatalysis 2016, 7, 411–419.
- 121C. Zhu, Q. Zhao, X. Wang, Z. Li, X. Hu, Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106090.
- 122W. Li, P. Wang, B. Chu, X. Chen, Z. Peng, J. Chu, R. Lin, Q. Gu, J. Lu, D. Wu, Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134197.
- 123S. Alagarsamy, R. Sundaresan, S.-M. Chen, R. Rasu, M. A. Mohammed, Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 673, 131830.
- 124D. Ilager, S. J. Malode, N. P. Shetti, Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134919.
- 125X. Ren, H. Zeng, Q. Zhang, H. Cai, W. Yang, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 221292.
- 126M. S. Ayilara, B. S. Adeleke, S. A. Akinola, C. A. Fayose, U. T. Adeyemi, L. A. Gbadegesin, R. K. Omole, R. M. Johnson, Q. O. Uthman, O. O. Babalola, Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1040901.
- 127G. Abdullahi, D. Obeng-Ofori, K. Afreh-Nuamah, M. K. Billah, The Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology 2020, 81, 18.
10.1186/s41936-020-00144-4 Google Scholar
- 128M. S. T. Abbas, Egypt J. Biol. Pest. Control 2022, 32, 76.
10.1186/s41938-022-00566-y Google Scholar
- 129M. S. T. Abbas, Advances in Entomology 2020, 08, 130–146.
10.4236/ae.2020.83010 Google Scholar
- 130K. C. Allen, R. G. Luttrell, T. W. Sappington, L. S. Hesler, S. K. Papiernik, J. Integr. Pest. Manag. 2018, 9, 20.
10.1093/jipm/pmy010 Google Scholar
- 131M. M. Rabelo, S. V. Paula-Moraes, E. J. G. Pereira, B. D. Siegfried, Pest Manage. Sci. 2020, 76, 4240–4247.
- 132I. Dugje, A. Menkir, N. Kamai, D. Aminu, A. Kamara, P. Odo, I. Teli, Abuja journal of agriculture and environment 2021, 1, 133–154.
- 133S. P. Pereira, S. M. A. Santos, M. A. S. Fernandes, C. M. Deus, J. D. Martins, M. C. Pedroso de Lima, J. A. F. Vicente, R. A. Videira, A. S. Jurado, Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117239.
- 134V. Kumar, S. Chandel, J. Crop. Weed. 2018, 14(2), 168–173.
- 135O. Delgado-Carrillo, S. Martén-Rodríguez, L. Ashworth, R. Aguilar, M. Lopezaraiza-Mikel, M. Quesada, Ecosphere 2018, 9, 2506.
- 136J. C. Anikwe, K. A. Kemabonta, W. A. Makanjuola, J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2014, 15, 1–5.
- 137S. Aba, Plant Pathology and Quarantine 2018, 8, 122–130.
10.5943/ppq/8/2/3 Google Scholar
- 138F. J. Scariot, A. P. L. Delamare, S. Echeverrigaray, Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 182, 105032.
- 139E. O. Imoloame, Open Agri 2021, 6, 445–455.
- 140A. A. Oso, G. O. Awe, J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2019, 41, 1–8.
10.9734/jeai/2019/v41i530415 Google Scholar
- 141S. Hassani, S. Momtaz, F. Vakhshiteh, A. S. Maghsoudi, M. R. Ganjali, P. Norouzi, M. Abdollahi, Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 109–130.
- 142S. Hassani, S. Momtaz, F. Vakhshiteh, Arch. Toxicol. n.d., 91, 109–130.
- 143X. Ye, M. Qi, H. Yang, F. S. Mediko, H. Qiang, Y. Yang, C. He, Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 247, 117017.
- 144K. Balamurugan, V. Subramanian, J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 21217–21227.
- 145Y. Zhao, X. Zheng, Q. Wang, T. Zhe, Y. Bai, T. Bu, M. Zhang, L. Wang, Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127495.
- 146M. Rouhani, Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 127, 108552.
- 147Mandeep, A. Gulati, Jogender, R. Kakkar, Struct. Chem. 2021, 32, 1541–1551.
- 148Mandeep, A. Gulati, R. Kakkar, J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 17.
- 149B. R. Shivankar, C. P. Singh, S. Krishnamurty, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 619, 156745.
- 150S. Kanagasubbulakshmi, R. Kathiresan, K. Kadirvelu, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 2018, 549, 155–163.
- 151R. Kakkar, Struct. Chem. 2021, 32 1883–1892.
- 152E. García, L. Palomino, J. Garza, A. Ramirez Torres, J. Avelar, J. Mol. Model. 2019, 25, 117.
- 153S. Yadav, A. P. Singh Raman, H. Meena, A. G. Goswami, Bhawna, V. Kumar, P. Jain, G. Kumar, M. Sagar, D. K. Rana, I. Bahadur, P. Singh, ACS Omega 2022, 7, 35387–35445.
- 154N. Deshwal, M. B. Singh, I. Bahadur, N. Kaushik, N. K. Kaushik, P. Singh, K. Kumari, Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159672.
- 155V. W. O. Wanjeri, C. J. Sheppard, A. R. E. Prinsloo, J. C. Ngila, P. G. Ndungu, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1333–1346.
- 156R. Sundaresan, V. Mariyappan, T.-W. Chen, S.-M. Chen, M. Akilarasan, X. Liu, J. Yu, J Nanostructure Chem 2023.
- 157M. L. Yola, J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 50–57.
- 158K. Halicka, J. Cabaj, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6357.
- 159S. Kogularasu, Y.-Y. Lee, G.-P. Chang-Chien, M. Govindasamy, J.-K. Sheu, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 077514.
10.1149/1945-7111/ace8c2 Google Scholar
- 160O. Moldovan, B. Iñiguez, M. J. Deen, L. F. Marsal, IET Circuits, Devices and Syst 2015, 9, 446–453.