Deciphering Coulombic Efficiency of Lithium Metal Anodes by Screening Electrolyte Properties
Dr. Zhao Zheng
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xinyan Liu
Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, 611731 P.R. China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xue-Qiang Zhang
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorShu-Yu Sun
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJia-Lin Li
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYa-Nan Wang
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorNan Yao
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDong-Hao Zhan
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWen-Jun Feng
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hong-Jie Peng
Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, 611731 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJiang-Kui Hu
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
The Innovation Center for Smart Solid State Batteries, Yibin, 644002 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Jia-Qi Huang
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Qiang Zhang
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Institute for Carbon Neutrality, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zhao Zheng
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xinyan Liu
Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, 611731 P.R. China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xue-Qiang Zhang
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorShu-Yu Sun
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJia-Lin Li
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYa-Nan Wang
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorNan Yao
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDong-Hao Zhan
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWen-Jun Feng
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hong-Jie Peng
Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, 611731 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorJiang-Kui Hu
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
The Innovation Center for Smart Solid State Batteries, Yibin, 644002 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Jia-Qi Huang
Advanced Research Institute of Multidisciplinary Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Qiang Zhang
Beijing Key Laboratory of Complex Solid State Batteries & Tsinghua Center for Green Chemical Engineering Electrification, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
Institute for Carbon Neutrality, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
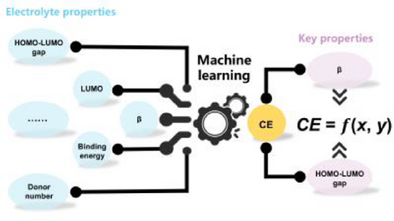
Both hydrogen-bond acceptor basicity (β) and the energy level gap between the lowest unoccupied and the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO gap) of solvents are identified as the top two parameters impacting CE by machine learning. A regression model is further proposed to estimate the CE based on β and HOMO-LUMO gap, which provides a reliable interpretable quantitative model for rational electrolyte design.
Abstract
Coulombic efficiency (CE) is a quantifiable indicator for the reversibility of lithium metal anodes in high-energy-density batteries. However, the quantitative relationship between CE and electrolyte properties has yet to be established, impeding rational electrolyte design. Herein, an interpretable model for estimating CE based on data-driven insights of electrolyte properties is proposed. Hydrogen-bond acceptor basicity (β) and the energy level gap between the lowest unoccupied and the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO-LUMO gap) of solvents are identified as the top two parameters impacting CE by machine learning. β and HOMO-LUMO gap of solvents govern anode interphase chemistry. A regression model is further proposed to estimate the CE based on β and HOMO-LUMO gap. Using the new solvent screened by above regression model, the lithium metal anode in the pouch cell with an energy density of 418 Wh kg−1 achieves the highest CE of 99.2%, which is much larger than previous CE ranging from 70%–98.5%. This work provides a reliable interpretable quantitative model for rational electrolyte design.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202507387-sup-0001-SuppMat.pdf3.4 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1D. Larcher, J. M. Tarascon, Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 19–29.
- 2J. M. Tarascon, M. Armand, Nature 2001, 414, 359–367.
- 3T. Placke, R. Kloepsch, S. Dühnen, M. Winter, J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 1939–1964.
- 4W. Cao, J. Zhang, H. Li, Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 26, 46–55.
- 5Y.-W. Song, L. Shen, X.-Y. Li, C.-X. Zhao, J. Zhou, B.-Q. Li, J.-Q. Huang, Q. Zhang, Nat. Chem. Eng. 2024, 1, 588–596.
10.1038/s44286-024-00115-4 Google Scholar
- 6M. He, L. G. Hector, F. Dai, F. Xu, S. Kolluri, N. Hardin, M. Cai, Nat. Energy 2024, 9, 1199–1205.
- 7C. Niu, D. Liu, J. A. Lochala, C. S. Anderson, X. Cao, M. E. Gross, W. Xu, J.-G. Zhang, M. S. Whittingham, J. Xiao, J. Liu, Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 723–732.
- 8J. Xiao, Q. Li, Y. Bi, M. Cai, B. Dunn, T. Glossmann, J. Liu, T. Osaka, R. Sugiura, B. Wu, J. Yang, J.-G. Zhang, M. S. Whittingham, Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 561–568.
- 9S.-Y. Sun, X.-Q. Zhang, X.-Y. Yan, Z. Zheng, Q.-K. Zhang, J.-Q. Huang, EES Batteries 2025. https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EB00034J.
10.1039/D4EB00034J Google Scholar
- 10C. Fang, X. Wang, Y. S. Meng, Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 152–158.
- 11Y. Jiang, B. Wang, P. Liu, B. Wang, Y. Zhou, D. Wang, H. Liu, S. Dou, Nano Energy 2020, 77, 105308.
- 12B. Jagger, M. Pasta, Joule 2023, 7, 2228–2244.
- 13X.-B. Cheng, R. Zhang, C.-Z. Zhao, F. Wei, J.-G. Zhang, Q. Zhang, Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1500213.
- 14S.-Y. Sun, X.-Q. Zhang, Y.-N. Wang, J.-L. Li, Z. Zheng, J.-Q. Huang, Mater. Today 2024, 77, 39–65.
- 15P. Xu, X. Lin, Z. Sun, K. Li, W. Dou, Q. Hou, Z. Zhou, J. Yan, M. Zheng, R. Yuan, Q. Dong, J. Energy Chem. 2022, 72, 186–194.
- 16Y.-X. Yao, X. Chen, C. Yan, X.-Q. Zhang, W.-L. Cai, J.-Q. Huang, Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4090–4097; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 4136–4143.
- 17N. Yao, X. Chen, X. Shen, R. Zhang, Z.-H. Fu, X.-X. Ma, X.-Q. Zhang, B.-Q. Li, Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21473–21478; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 24643–21648.
- 18T. D. Pham, K.-K. Lee, Small 2021, 17, 2100133.
- 19K. Chen, X. Shen, L. Luo, H. Chen, R. Cao, X. Feng, W. Chen, Y. Fang, Y. Cao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202312373; Angew. Chem. 2023, 135, e202312373.
- 20J. Xu, J. Zhang, T. P. Pollard, Q. Li, S. Tan, S. Hou, H. Wan, F. Chen, H. He, E. Hu, K. Xu, X.-Q. Yang, O. Borodin, C. Wang, Nature 2023, 614, 694–700.
- 21Z. Zhu, J. Ji, X. Qi, Y. Ji, Z. Liu, W. Du, Y. Pan, D. Yang, J. Ma, L. Qie, Y. Huang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2300936.
- 22P. Zhou, Y. Xiang, K. Liu, Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 8057–8077.
- 23J. Chen, Y. Zhang, H. Lu, J. Ding, X. Wang, Y. Huang, H. Ma, J. Wang, eScience 2023, 3, 100135.
- 24Q. Wang, Z. Yao, C. Zhao, T. Verhallen, D. P. Tabor, M. Liu, F. Ooms, F. Kang, A. Aspuru-Guzik, Y.-S. Hu, M. Wagemaker, B. Li, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4188.
- 25Y. Meng, J. Li, S. Gu, Y. Fu, Z. Wang, J. Liu, X. Gong, Electrochim. Acta. 2023, 449, 142262.
- 26S. Perez Beltran, P. B. Balbuena, J. Power Sources 2022, 551, 232203.
- 27H. Cheng, Q. Sun, L. Li, Y. Zou, Y. Wang, T. Cai, F. Zhao, G. Liu, Z. Ma, W. Wahyudi, Q. Li, J. Ming, ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 490–513.
- 28C.-C. Su, M. He, R. Amine, Z. Chen, K. Amine, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12033–12036; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 12209–12212.
- 29C.-C. Su, M. He, R. Amine, T. Rojas, L. Cheng, A. T. Ngo, K. Amine, Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1249–1254.
- 30S. C. Kim, X. Kong, R. A. Vilá, W. Huang, Y. Chen, D. T. Boyle, Z. Yu, H. Wang, Z. Bao, J. Qin, Y. Cui, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 10301–10308.
- 31N. Leifer, D. Aurbach, S. G. Greenbaum, Prog. Nucl. Mag. Res. Sp. 2024, 142–143, 1–54.
- 32P. Zhou, W. Hou, Y. Xia, Y. Ou, H.-Y. Zhou, W. Zhang, Y. Lu, X. Song, F. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Liu, S. Yan, K. Liu, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 17169–17179.
- 33R. W. Taft, M. J. Kamlet, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 2886–2894.
- 34Y. Zhao, T. Zhou, M. Mensi, J. W. Choi, A. Coskun, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 299.
- 35F. Pedregosa, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, V. Michel, B. Thirion, O. Grisel, M. Blondel, G. Louppe, P. Prettenhofer, R. Weiss, R. J. Weiss, J. Vanderplas, A. Passos, D. Cournapeau, M. Brucher, M. Perrot, E. Duchesnay, J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830.
- 36M. J. Kamlet, R. W. Taft, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 377–383.
- 37B. Cui, J. Xu, J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 8223–8245.
- 38X. Chen, X. Q. Zhang, H. R. Li, Q. Zhang, Batteries Supercaps 2019, 2, 128–131.
- 39Y.-C. Gao, N. Yao, X. Chen, L. Yu, R. Zhang, Q. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 23764–23770.
- 40Y. Yamada, M. Yaegashi, T. Abe, A. Yamada, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11194.
- 41L. Suo, D. Oh, Y. Lin, Z. Zhuo, O. Borodin, T. Gao, F. Wang, A. Kushima, Z. Wang, H.-C. Kim, Y. Qi, W. Yang, F. Pan, J. Li, K. Xu, C. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18670–18680.
- 42D. N. Reshef, Y. A. Reshef, H. K. Finucane, S. R. Grossman, G. McVean, P. J. Turnbaugh, E. S. Lander, M. Mitzenmacher, P. C. Sabeti, Science 2011, 334, 1518–1524.
- 43R. Guo, K.-H. Kim, B. M. Gallant, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 100523.
- 44T. Li, X.-Q. Zhang, P. Shi, Q. Zhang, Joule 2019, 3, 2647–2661.
- 45L. Suo, Y.-S. Hu, H. Li, M. Armand, L. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1481.
- 46H. Wan, J. Xu, C. Wang, Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 30–44.
- 47Y. Chen, Z. Yu, P. Rudnicki, H. Gong, Z. Huang, S. C. Kim, J.-C. Lai, X. Kong, J. Qin, Y. Cui, Z. Bao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 18703–18713.
- 48Z. Wu, R. Li, S. Zhang, L. lv, T. Deng, H. Zhang, R. Zhang, J. Liu, S. Ding, L. Fan, L. Chen, X. Fan, Chem 2023, 9, 650–664.