Stabilizing the Quinoidal Form of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by O─B←N Units to Give a > 1000 nm Redshift in the Absorption Wavelength
Canyun Mao
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P.R. China
School of Applied Chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xingxin Shao
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jun Liu
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P.R. China
School of Applied Chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Lixiang Wang
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P.R. China
School of Applied Chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCanyun Mao
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P.R. China
School of Applied Chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xingxin Shao
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jun Liu
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P.R. China
School of Applied Chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Lixiang Wang
State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun, 130022 P.R. China
School of Applied Chemistry and Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
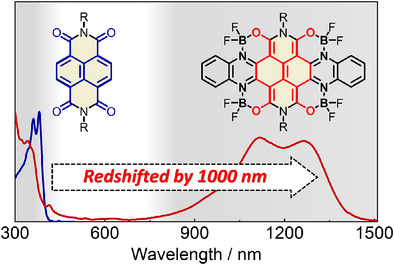
By incorporating four O─B←N units into naphthalene diimide, the core is transformed from an aromatic form to a quinoidal form, significantly enhancing π-electron delocalization. This results in a reduced bandgap from 3.10 to 0.88 eV and a redshift in absorption from 400 to 1410 nm. The synthesized polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exhibits strong SWIR absorption and high transparency in the visible region, developing a colorless anti-counterfeiting application.
Abstract
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) have distinct chemical structures and excellent optoelectronic properties. Although PAHs with ultra-large π-conjugated skeletons have been successfully synthesized, ultrasmall bandgap (Eg < 1.2 eV) or short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) light absorption (λ > 1000 nm) is seldom reported for PAHs. In this work, we design and synthesize a PAH by incorporating four O─B←N units into naphthalene diimide (NDI) as the core. The incorporation of four O─B←N units changes the NDI core from an aromatic form to a quinoidal form, leading to significantly enhanced π-electron delocalization. As a result, the optical bandgap of the molecule decreases from 3.10 to 0.88 eV, and the onset absorption wavelength is redshifted from 400 to 1410 nm. The resulting molecule exhibits strong light absorption in the infrared region and high transparency in the visible region. It can be used to develop colorless infrared anti-counterfeiting technology. This work provides a novel molecular design strategy to tune optoelectronic properties of PAHs.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supporting information of this article.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202505353-supp-0001-SupMat.docx23.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1M. Stępień, E. Gońka, M. Żyła, N. Sprutta, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3479–3716.
- 2B. Pigulski, K. Shoyama, M.-J. Sun, F. Würthner, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5718–5722.
- 3J. D. Zimmerman, V. V. Diev, K. Hanson, R. R. Lunt, E. K. Yu, M. E. Thompson, S. R. Forrest, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2780–2783.
- 4Z. Zhou, A. Wakamiya, T. Kushida, S. Yamaguchi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4529–4532.
- 5K. Schickedanz, J. Radtke, M. Bolte, H.-W. Lerner, M. Wagner, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2842–2851.
- 6K. Liu, Z. Jiang, R. A. Lalancette, X. Tang, F. Jäkle, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 18908–18917.
- 7M. Vanga, A. Sahoo, R. A. Lalancette, F. Jäkle, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113075.
- 8X. Yao, H. Zhang, F. Kong, A. Hinaut, R. Pawlak, M. Okuno, R. Graf, P. N. Horton, S. J. Coles, E. Meyer, L. Bogani, M. Bonn, H. I. Wang, K. Müllen, A. Narita, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202312610.
- 9C. Zhu, X. Ji, D. You, T. L. Chen, A. U. Mu, K. P. Barker, L. M. Klivansky, Y. Liu, L. Fang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 18173–18182.
- 10Y. Min, C. Dou, D. Liu, H. Dong, J. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17015–17021.
- 11S. Dong, T. Y. Gopalakrishna, Y. Han, H. Phan, T. Tao, Y. Ni, G. Liu, C. Chi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 62–66.
- 12Y. Kondo, K. Yoshiura, S. Kitera, H. Nishi, S. Oda, H. Gotoh, Y. Sasada, M. Yanai, T. Hatakeyama, Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 678–682.
- 13S. Pascal, S. David, C. Andraud, O. Maury, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6613–6658.
- 14R. S. Rao, S. P. S. Suman, Chem. - Eur. J. 2020, 26, 16582–16593.
- 15A. Tsuda, A. Osuka, Science 2001, 293, 79–82.
- 16W. Zeng, H. Phan, T. S. Herng, T. Y. Gopalakrishna, N. Aratani, Z. Zeng, H. Yamada, J. Ding, J. Wu, Chem 2017, 2, 81–92.
- 17X. Cui, C. Xiao, T. Winands, T. Koch, Y. Li, L. Zhang, N. L. Doltsinis, Z. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12175–12180.
- 18Z. Yuan, S.-L. Lee, L. Chen, C. Li, K. S. Mali, S. De Feyter, K. Müllen, Chem. - Eur. J. 2013, 19, 11842–11846.
- 19Y. Jiang, Y. Zhang, Y. Deng, S. Dong, B. Li, Y. Yi, Z. Zeng, H. Chen, H. Luo, Y. Geng, CCS Chem 2022, 4, 3497–3504.
- 20A. Patra, L. J. Patalag, P. G. Jones, D. B. Werz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 747–752.
- 21G. Liu, Y. Liu, C. Zhao, Y. Li, Z. Wang, H. Tian, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214769.
- 22L. Yang, J. Ma, W. Zheng, S. Osella, J. Droste, H. Komber, K. Liu, S. Böckmann, D. Beljonne, M. R. Hansen, M. Bonn, H. I. Wang, J. Liu, X. Feng, Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200708.
- 23F. Hernández-Culebras, M. Melle-Franco, A. Mateo-Alonso, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205018.
- 24R. K. Dubey, M. Melle-Franco, A. Mateo-Alonso, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6593–6600.
- 25L. Dou, Y. Liu, Z. Hong, G. Li, Y. Yang, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12633–12665.
- 26Z. Wu, Y. Zhai, H. Kim, J. D. Azoulay, T. N. Ng, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3144–3153.
- 27N. Li, X. Hu, X. Sui, Q. Chen, T. N. Ng, ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 21–33.
- 28T. Mikie, I. Osaka, J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 14262–14288.
- 29X. Ji, L. Fang, Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 1347–1361.
- 30M. Murai, T. Enoki, S. Yamaguchi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202311445.
- 31X.-X. Chen, J.-T. Li, Y.-H. Fang, X.-Y. Deng, X.-Q. Wang, G. Liu, Y. Wang, X. Gu, S.-D. Jiang, T. Lei, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2258.
- 32G. M. Fischer, E. Daltrozzo, A. Zumbusch, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1406–1409.
- 33Q. Ye, J. Chang, K.-W. Huang, C. Chi, Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5960–5963.
- 34Y. Min, X. Cao, H. Tian, J. Liu, L. Wang, Chem. - Eur. J. 2021, 27, 2065–2071.
- 35P. M. Burrezo, J. L. Zafra, J. T. López Navarrete, J. Casado, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2250–2259.
- 36C. Chen, Y. Zhang, X.-Y. Wang, J.-Y. Wang, J. Pei, Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 10277–10294.
- 37M. Hirai, N. Tanaka, M. Sakai, S. Yamaguchi, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 8291–8331.
- 38L. Ji, S. Griesbeck, T. B. Marder, Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 846–863.
- 39M. Metzler, A. Virovets, H.-W. Lerner, M. Wagner, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 23824–23831.
- 40B. Kohl, F. Rominger, M. Mastalerz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6051–6056.
- 41S.-L. Suraru, F. Würthner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7428–7448.
- 42X. Guo, M. D. Watson, Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5333–5336.
- 43H. Yan, Z. Chen, Y. Zheng, C. Newman, J. R. Quinn, F. Dötz, M. Kastler, A. Facchetti, Nature 2009, 457, 679–686.
- 44R. Steyrleuthner, R. Di Pietro, B. A. Collins, F. Polzer, S. Himmelberger, M. Schubert, Z. Chen, S. Zhang, A. Salleo, H. Ade, A. Facchetti, D. Neher, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4245–4256.
- 45W. Jiang, Z. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14976–14991.
- 46K. Cai, J. Xie, D. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 28–31.
- 47T. Nakazato, H. Takekoshi, T. Sakurai, H. Shinokubo, Y. Miyake, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13877–13881.
- 48S. Qiu, L. Zhang, X. Jin, C. Zhao, J. Liu, D.-H. Qu, W. Jiang, Z. Wang, CCS Chem 2025, 7, 307–315.
- 49T. Lu, F. Chen, J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592.
- 50T. Lu, J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 161, 082503.
- 51K. Zhao, Z.-F. Yao, Z.-Y. Wang, J.-C. Zeng, L. Ding, M. Xiong, J.-Y. Wang, J. Pei, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3091–3098.
- 52Z. Chen, C. S. Wannere, C. Corminboeuf, R. Puchta, P. v. R. Schleyer, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3842–3888.
- 53X. Gao, W. Qiu, X. Yang, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, H. Zhang, T. Qi, Y. Liu, K. Lu, C. Du, Z. Shuai, G. Yu, D. Zhu, Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 3917–3920.
- 54C. Röger, F. Würthner, J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 8070–8075.
- 55K. Cai, Q. Yan, D. Zhao, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 3175–3182.
- 56K. Cai, J. Xie, X. Yang, D. Zhao, Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1852–1855.
- 57S. Guo, W. Wu, H. Guo, J. Zhao, J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 3933–3943.
- 58K. Mandal, D. Bansal, Y. Kumar, J. S. Rustam, P. Mukhopadhyay, Chem. - Eur. J. 2020, 26, 10607–10619.
- 59Z. Zeng, S. Lee, J. L. Zafra, M. Ishida, X. Zhu, Z. Sun, Y. Ni, R. D. Webster, R.-W. Li, J. T. López Navarrete, C. Chi, J. Ding, J. Casado, D. Kim, J. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8561–8565.
- 60Y. Huang, K. Wu, Y. Sun, Y. Hu, Z. Wang, L. Yuan, S. Wang, D. Ji, X. Zhang, H. Dong, Z. Gong, Z. Li, X. Weng, R. Huang, Y. Cui, X. Chen, L. Li, W. Hu, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 626.
- 61S. J. Choi, E. J. Seo, H. E. Bae, H. C. Jung, S. H. Lee, J. C. Kim, Y. J. Jung, J. S. Park, J.-E. Jeong, Y. I. Park, RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 3560–3566.
- 62J. Xu, J. Liu, L. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303870.