Electrochemical Amination of Aryl Halides with NH3
Yaowen Liu
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, 94 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorYanfei Sun
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, 94 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuan Deng
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, 94 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Youai Qiu
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, 94 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300071 China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorYaowen Liu
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, 94 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorYanfei Sun
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, 94 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuan Deng
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, 94 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Youai Qiu
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, 94 Weijin Road, Tianjin, 300071 China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorHomepage: https://www.x-mol.com/groups/qiu_youai
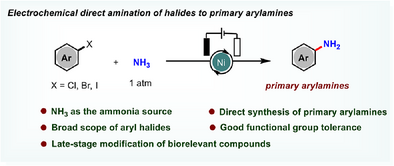
Graphical Abstract
A General and Efficient Method for the Direct Synthesis of Primary Arylamines Through Electrochemical Amination of Aryl Halides With NH3 Has Been Developed. The Weak Nucleophilic Reagent NH3 Acted as an Ammonia Surrogate. This Approach Shows Good Functional Group Tolerance and a Broad Scope of Functionalized Primary Arylamines That Can be Further Late-stage Modification of Drug Molecules and Gram-scale Reaction Demonstrate Its Synthetic Utility.
Abstract
Primary arylamines are the most pivotal class of organic motifs in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, ligands and natural products. Ammonia (NH3) is an ideal nitrogen source in terms of reactivity, atom economy, and environmental compatibility. Despite significant progress in the synthesis of primary arylamines, the development of a general method for rapid access to diversely functionalized primary arylamines is still urgent and necessary. Herein, we developed a method for the direct synthesis of primary arylamines through electrochemical amination of aryl halides with NH3. Notably, the weak nucleophilic reagent NH3 was directly used as an ammonia surrogate, allowing for efficient conversion of carbon-halogen bonds to diverse primary arylamines with good functional group tolerance. A broad scope of functionalized primary arylamines has been achieved in moderate to excellent yields.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
Materials and methods, optimization studies, experimental procedures, mechanistic studies, 1H NMR, 13C NMR spectra, and high-resolution mass spectrometry data are available in the Supplementary Information.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202504459-sup-0001-SuppMat.pdf10.9 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1H. N. C. Wong, M. Y. Hon, C. W. Tse, Y. C. Yip, J. Tanko, T. Hudlicky, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3388–3432.
- 2P. Ruiz-Castillo, S. L. Buchwald, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12564–12649.
- 3J. A. Smith, B. C. Johnson, J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 6543–6572.
- 4L. Wang, X. Zhang, Cancer Res. Rev. 2019, 45, 234–250.
- 5R. T. Brown, M. L. Davis, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 1–15.
- 6C. Lamberth, S. Jeanmart, T. Luksch, A. Plant, Science 2013, 341, 742–746.
- 7W. Zhang, J. Jiang, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4085–4098.
- 8P. Jeschke, Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1053–1066.
- 9A. Bafana, S. Devi, T. Chakrabarti, Environ. Rev. 2011, 19, 350–371.
- 10S. K. Shorey, V. K. Gupta, J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2012, 4, 508–514.
- 11R. M. Christie, Color. Technol. 2001, 117, 1–8.
10.1111/j.1478-4408.2001.tb00327.x Google Scholar
- 12R. C. Gupta, Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2018, 131, 1–22.
- 13M. A. Ibrahim, J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 902–918.
- 14S. Kumar, J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 12–27.
- 15P. Zhang, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 96, 1–27.
- 16J. F. Hartwig, Nature, 455, 314–322.
- 17P. Ruiz-Castillo, S. L. Buchwald, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12564–12649.
- 18J. Bariwal, E. Eycken, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9283.
- 19C. L. Allen, J. M. Williams, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3405.
- 20J. L. Klinkenberg, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 11830–11833.
- 21R. J. Lundgren, B. D. Peters, P. G. Alsabeh, M. A. Stradiotto, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4071–4074.
- 22A. Borzenko, N. L. Rotta-Loria, P. M. Macqueen, C. M. Lavoie, R. McDonald, M. Stradiotto, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3773–3777.
- 23R. Green, J. F. Hartwig, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3768–3772.
- 24P. Ruiz-Castillo, S. L. Buchwald, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12564–12649.
- 25K. Choi, J. N. Brunn, K. Borate, R. Kaduskar, C. L. Pueyo, H. Shinde, R. Goetz, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 19414–19424.
- 26E. R. Raguram, J. C. Dahl, K. F. Jensen, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 33035–33047.
- 27K. Feng, E. R. Raguram, J. R. Howard, E. Peters, C. Liu, M. S. Sigman, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 26609–26615.
- 28J. Kim, S. Chang, Chem. Commun. 2008, 3052.
- 29N. Xia, M. Taillefer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 337–339.
- 30L. Jiang, X. Lu, H. Zhang, Y. Jiang, D. Ma, J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 4542–4546.
- 31H. Xu, C. Wolf, Chem. Commun. 2009, 3035–3037.
- 32M. K. Elmkaddem, C. Fischmeister, C. M. Thomas, J. L. Renaud, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 925–927.
- 33M. Fan, W. Zhou, Y. Jiang, D. Ma, Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5934–5937.
- 34S. Bhunia, G. Goroba Pawar, S. VijayKumar, Y. Jiang, D. Ma, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16136–16179.
- 35C. Sambiagio, S. P. Marsden, A. J. Blacker, P. C. McGowan, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3525–3550.
- 36Y. Zhang, J. Wang, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 876–894.
- 37X. Guo, M. Rueping, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4567–4580.
- 38G. Song, Q. Li, J. Song, D. Nong, J. Dong, G. Li, J. Fan, C. Wang, D. Xue, ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 4968–4974.
- 39M. R. Lasky, E. Liu, M. S. Remy, M. S. Sanford, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10080–10083.
- 40G. Song, J. Song, Q. Li, D. Nong, J. Dong, G. Li, J. Fan, C. Wang, J. Xiao, D. Xue, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202314355.
- 41R. Kancherla, K. Muralirajan, S. Dutta, K. Pal, B. Li, B. Maity, L. Cavallo, M. Rueping, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202314508.
- 42B. D. Akana-Schneider, D. J. Weix, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 16150–16159.
- 43G. Song, L. Yang, J. Li, W. Tang, W. Zhang, R. Cao, C. Wang, J. Xiao, D. Xue, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21536–21542.
- 44G. Li, L. Yang, J. Liu, W. Zhang, R. Cao, C. Wang, Z. Zhang, J. Xiao, D. Xue, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5230–5234.
- 45J. Wang, S. Li, C. Yang, H. Gao, L. Zuo, Z. Gao, P. Yang, Y. Jiang, J. Li, L-Z, W.u, Z. Tang, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6907.
- 46W. S. Ham, J. Hillenbrand, J. Jacq, C. Genicot, T. Ritter, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 532–536.
- 47Y. Zheng, B. Chen, P. Ye, K. Feng, W. Wang, Q. Meng, L-Z. Wu, C.-H. Tung, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10080–10083.
- 48N. A. Romero, K. A. Margrey, N. E. Tay, D. A. Nicewicz, Science 2015, 349, 1326–1330.
- 49V. A. Pistritto, M. E. Schutzbach-Horton, D. A. Nicewicz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 17187–17194.
- 50L. Zhang, L. Liardet, J. Luo, D. Ren, M. Grätzel, X. Hu, Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 366–373.
- 51R. Y. Liu, J. M. Dennis, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4500–4507.
- 52J. Li, P. Wang, B. Bai, Y. Xiao, Y. Wan, Y. Yan, F. Li, G. Song, G. Li, C. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Dong, T. Kang, D. Xue, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 5851–5859.
- 53G. Song, J. Song, Q. Li, T. Kang, J. Dong, G. Li, J. Fan, C. Wang, D. Xue, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 26936–26946.
- 54F. Li, H. Lu, H. Liao, W. Xiong, J. Dong, G. Li, D. Xue, Org. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 6089–6095.
- 55H. Ai, S. Kim, C. Liu, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 25949–25955.
- 56M. J. Strauss, K. X. Liu, M. E. Greaves, J. C. Dahl, S. Kim, Y. Wu, M. A. Schmidt, P. M. Scola, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 18616–18625.
- 57S. Kim, M. J. Strauss, A. Cabré, S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 6966–6975.
- 58S. M. Papidocha, H. R. Wilke, K. J. Patej, M. Isomura, T. J. Stucky, L. Rothenbühler, E. M. Carreira, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 11675-11681.
- 59M. Yan, Y. Kawamata, P. S. Baran, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13230–13319.
- 60P. Xiong, H.-C. Xu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 3339–3350.
- 61C. W. Anson, S. S. Stahl, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3749–3786.
- 62L. F. T. Novaes, J.-J. Liu, Y.-F. Shen, L.-X. Lu, J. M. Meinhardt, S. Lin, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 7941–8002.
- 63C. Zhu, N. W. J. Ang, T. H. Meyer, Y. Qiu, L. Ackermann, ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 415–431.
- 64J. C. Siu, N. Fu, S. Lin, Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 547–560.
- 65Y. Qiu, C. Zhu, M. Stangier, J. Struwe, L. Ackermann, CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 1529–1552.
- 66C.-Y. Cai, H.-C. Xu, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3551.
- 67L.-X. Lu, J. C. Siu, Y. Lai, S. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21272–21278.
- 68S.-Z. Li, S.-C. Wang, P.-J. Wang, Z.-L. Huan, T. Wan, A. Lei, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 443.
- 69C.-Y. Cai, Y.-T. Zheng, J.-F. Li, H.-C. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11980–11985.
- 70K. Liang, Q. Zhang, C. Guo, Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd7134.
- 71N. Fu, G. S. Sauer, A. Saha, A. Loo, S. Lin, Science 2017, 357, 575–579.
- 72P. Zhou, K. Niu, H. Song, Y. Liu, Q. Wang, Green Chem. 2022, 24, 5760–5763.
- 73E. J. Horn, B. R. Rosen, Y. Chen, J. Tang, K. Chen, M. D. Eastgate, P. S. Baran, Nature 2016, 533, 77–81.
- 74Y. Liang, S.-H. Shi, R. Jin, X. Qiu, J. Wei, H. Tan, X. Jiang, X. Shi, S. Song, N. Jiao, Nat. Catal 2021, 4, 116–123.
- 75K.-J. Jiao, Y.-K. Xing, Q.-L. Yang, H. Qiu, T.-S. Me, Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 300–310.
- 76Q.-L. Yang, Y.-Q. Li, C. Ma, P. Fang, X.-J. Zhang, T.-S. Mei, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3293–3298.
- 77N. Sauermann, T.-H. Meyer, C. Tian, L. Ackermann, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 18452–18455.
- 78G.-Q. Sun, P. Yu, W. Zhang, W. Zhang, Y. Wang, L.-L. Liao, Z. Zhang, L. Li, Z. Lu, D.-G. Yu, S. Lin, Nature 2023, 615, 67–72.
- 79W. Zhang, L.-L. Liao, L. Li, Y. Liu, L.-F. Dai, G.-Q. Sun, C.-K. Ran, J.-H. Ye, Y. Lan, D.-G. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301892.
- 80D. S. Chung, S. H. Park, S. G. Lee, H. Kim, Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5892–5897.
- 81S. H. Park, G. Bae, A. Choi, S. Shin, K. Shin, C. H. Choi, H. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 15360–15369.
- 82Y.-M. Jiang, Y.-Y. Lin, L. Zhu, Y. Yu, Y. Li, Y. Lin, K.-Y. Ye, CCS Chem. 2024, 6, 2021–2030.
- 83F. Bu, Y. Deng, J. Xu, D. Yang, Y. Li, W. Li, A. Lei, Nature 2024, 634, 592–599.
- 84Z. Su, R. Deng, S. S. Stahl, Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 2036–2043.
- 85S.-S. Xu, H. Qiu, P.-P. Xie, Z. H. Wang, X. Wang, C. Zheng, S.-L. You, T.-S. Mei, CCS Chem 2025, 7, 245–255.
- 86P. Li, Y. Wang, H. Zhao, Y. Qiu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2025, 58, 113–129.
- 87Q. Wang, X. Zhang, P. Wang, X. Gao, H. Zhang, A. Lei, Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 143–148.
- 88M. Chen, Z.-J. Wu, J. Song, H.-C. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115954.
- 89C. Huang, W. Ma, X. Zheng, M. Xu, X. Qi, Q. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1389–1395.
- 90Z. Zhao, Y. Liu, S. Wang, S. Tang, D. Ma, Z. Zhu, C. Guo, Y. Qiu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214710.
- 91M. J. Kim, D. J. Wang, K. Targos, U. A. Garcia, A. F. Harris, I. A. Guzei, Z. K. Wickens, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 135, e202303032.
- 92X. Zhang, X. Cheng, Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 8645–8650.
- 93L.-B. Li, X.-Y. Wang, N.-K. Fu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202403475.
- 94S.-L. Fang, K.-H. Zhong, S.-G. Zeng, X.-W. Hu, P.-H. Sun, Z.-X. Ruan, Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 11425–11428.
- 95H.-T. Tang, H.-Y. Zhou, Y.-M. Pan, J.-L. Zhang, F.-H. Cui, W.-H. Li, D. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 136, e202315032.
- 96T. Wang, F. He, W. Jiang, J. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202316140.
- 97S.-Z. Sun, Y.-M. Cai, D.-L. Zhang, J.-B. Wang, H.-Q. Yao, X.-Y. Rui, R. Martin, M. Shang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1130–1137.
- 98S. P. Blum, T. Karakaya, D. Schollmeyer, A. Klapars, S. R. Waldvogel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5056–5062.
- 99J. Liu, A. Guðmundsson, J. E. Bäckvall, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 15686–15704.
- 100J. Zhang, B. Das, O. Verho, J. E. Bäckvall, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212131.
- 101X.-Y. Wang, Y.-Z. Pan, J. Yang, W.-H. Li, T. Gan, Y.-M. Pan, H.-T. Tang, D. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 22, e202404295.
- 102H.-T. Tang, H.-Y. Zhou, Y.-M. Pan, J.-L. Zhang, F.-H. Cui, W.-H. Li, D.-S. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202315032.
- 103T. J. DeLano, S. E. Reisman, ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6751–6754.
- 104J. L. Hofstra, A. H. Cherney, C. M. Ordner, S. E. Reisman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 139–142.
- 105W. Yi, P. C. Xu, T. He, S. Shi, S. Huang, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9645.
- 106G. Kou, P. Li, G. Yang, Y. Qiu, CCS Chem. 2024, https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.024.202404697.
- 107A. Shi, Y. Liu, R. Zhang, Z. Zhu, Y. Qiu, eScience 2024, 4, 100255.
- 108Y. Zhong, H. Xiong, J. Low, R. Long, Y. Xiong, eScience 2023, 3, 100086.
- 109X. Peng, L. Zeng, D. Wang, Z. Liu, Y. Li, Z. Li, B. Yang, L. Lei, L. Dai, Y. Hou, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 2193–2237.
- 110Y. Wang, D. Chen, C. Chen, S. Wang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 247–256.
- 111T. Morofuji, A. Shimizu, J. Yoshida, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4496–4499.
- 112B. Zhang, S. L. Homölle, T. Bauch, J. C. A. Oliveira, S. Warratz, B. Yuan, X. Gou, L. Ackermann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202407384.
- 113S.-K Zhang, R. C. Samanta, N. Sauermann, L. Ackermann, Chem. - Eur. J. 2018, 24, 19166–19170.
- 114T. Morofuji, A. Shimizu, J. Yoshida, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5000–5003.
- 115H. Huang, T. H. Lambert, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11163–11167.
- 116H. Huang, K. A. Steiniger, T. H. Lambert, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 12567–12583.
- 117L. Qian, M. Shi, Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 3487–3506.
- 118H. Zhao, P. Xu, J. Song, H. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15153–15156.
- 119H. Zhao, Z. Liu, J. Song, H. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12732–12735.
- 120C. Guan, J. Yin, J. Ji, J. Liu, X. Wu, T. Zhu, Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 5383–5388.
- 121J. Xu, Y. Liu, Q. Wang, X. Tao, S. Ni, W. Zhang, L. Yu, Y. Pan, Y. Wang, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6116.
- 122N. Sauermann, R. Mei, L. Ackermann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5090–5094.
- 123Z. Zhu, P. Li, Y. Qiu, Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 44, 871.
- 124C. Li, Y. Kawamata, H. Nakamura, J. C. Vantourout, Z. Liu, Q. Hou, D. Bao, J. T. Starr, J. Chen, M. Yan, P. S. Baran, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13088–13093.
- 125Y. Kawamata, J. C. Vantourout, D. P. Hickey, P. Bai, L. Chen, Q. Hou, W. Qiao, K. Barman, M. A. Edwards, A. F. Garrido-Castro, J. N. Gruyter, H. Nakamura, K. Knouse, C. Qin, K. J. Clay, D. Bao, C. Li, J. T. Starr, C. Garcia-Irizarry, N. Sach, H. S. White, M. Neurock, S. D. Minteer, P. S. Baran, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6392–6402.
- 126D. Liu, Z. Liu, C. Ma, K. Jiao, B. Sun, L. Wei, J. Lefranc, S. Herbert, T.-S. Mei, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9444–9449.
- 127Z. Liu, S. Herbert, H. Schirok, C. Ma, T.-S. Mei, Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 9034–9039.
- 128J. Luo, M. T. Davenport, C. Callister, S. D. Minteer, D. H. Ess, T. L. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 16130–16141.
- 129J. Morvan, K. P. L. Kuijpers, D. Fanfair, B. Tang, K. Bartkowiak, L. Eynde, E. Renders, J. Alcazar, P. J. J. A. Buijnsters, M. Carvalho, A. X. Jones, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202413383.
- 130C. Zhu, A. P. Kale, H. Yue, M. Rueping, JACS Au 2021, 1, 1057–1065.
- 131S. Sengmany, F. Daili, I. Kribii, E. Léonel, J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 675–683.
- 132S. Liu, X. Cheng, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 425.
- 133S. Liu, W. Zhao, J. Li, N. Wu, C. Liu, X. Wang, S. Li, Y. Zhu, Y. Liang, X. Cheng, CCS Chem 2022, 4, 693–703.
- 134X. Zhang, R. Jiang, X. Cheng, J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 16016–16025.
- 135Y.-W. Wang, Q. Wang, L. Wu, K.-P. Jia, M.-Y. Wang, Y. Qiu, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2780.
- 136M. Liu, T. Feng, Y.-W. Wang, G.-S. Kou, Q. Wang, Q.-Y. Wang, Y. Qiu, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6467.
- 137P.-F. Li, G.-S. Kou, T. Feng, M.-Y. Wang, Y. Qiu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202311941.
- 138K.-M. Yang, T. Feng, Y. Qiu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202312803.
- 139M. Liu, Y.-W. Wang, C. Gao, J. Jia, Z. Zhu, Y. Qiu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, e202425634.
- 140R. Zhang, M. Liu, Z. Zhao, Y. Qiu, Green Chem. 2025, 27, 1658–1666.
- 141Z. Zhao, R. Zhang, Y. Liu, Z. Zhu, Q. Wang, Y. Qiu, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3832.
- 142X. Liu, R. Liu, J. Qiu, X. Cheng, G. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13962–13967.
- 143P. Li, Y. Wang, H. Zhao, Y. Qiu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2025, 58, 113–129.
- 144Y. Liu, P. Li, Y. Wang, Y. Qiu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306679.
- 145W. Zeng, Y. Wang, C. Peng, Y. Qiu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1039/d4cs01142b.
- 146W. Zeng, C. Peng, Y. Qiu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c00259.
- 147L. Cardinale, G. L. Beutner, C. Y. Bemis, D. J. Weix, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 32249–32254.
- 148M. Wang, C. Zhang, C. Ci, H. Jiang, P. H. Dixneuf, M. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 10967–10973.
- 149M. Wang, C. Zhang, H. Zhao, H. Jiang, P. H. Dixneuf, M. Zhang, CCS Chem 2024, 6, 342–352.
- 150J. Schranck, A. Tlili, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 405–418.
- 151G. Song, D. Nong, Q. Li, Y. Yan, G. Li, J. Fan, W. Zhang, R. Cao, C. Wang, J. Xiao, D. Xue, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 15590–15599.