Spherical Nucleic Acids-Directed Cryosynthesis of Manganese Nanoagents for Tumor Imaging and Therapy
Wenjing Xie
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorQiangjun Hao
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZi Ye
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
School of Environment, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, 310013 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorRui Sha
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorBei Wen
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorHailin Wang
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
School of Environment, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, 310013 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorHongquan Zhang
Division of Analytical & Environmental Toxicology, Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G2G3 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorGuohua Jia
School of Molecular and Life Sciences, Curtin University, Bentely, WA, 6102 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorX. Chris Le
Division of Analytical & Environmental Toxicology, Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G2G3 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorGuibin Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
School of Environment, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, 310013 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hanyong Peng
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorWenjing Xie
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorQiangjun Hao
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZi Ye
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
School of Environment, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, 310013 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorRui Sha
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorBei Wen
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorHailin Wang
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
School of Environment, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, 310013 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorHongquan Zhang
Division of Analytical & Environmental Toxicology, Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G2G3 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorGuohua Jia
School of Molecular and Life Sciences, Curtin University, Bentely, WA, 6102 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorX. Chris Le
Division of Analytical & Environmental Toxicology, Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G2G3 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorGuibin Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
School of Environment, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, 310013 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hanyong Peng
State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100085 China
College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
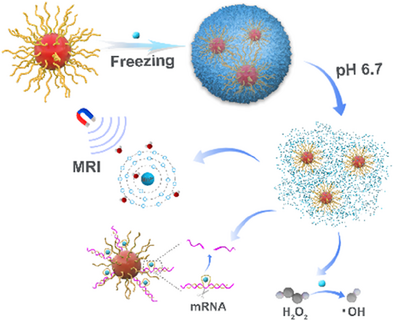
DNAzyme-based theranostic nanotechnologies that can respond to specific tumor pathophysiological parameters hold great promise for tumor diagnostics and effective treatments. However, their clinical translation is hindered by insufficient intracellular availability of essential metal cofactors required for DNAzyme activation. To overcome this limitation, we developed a temperature-controlled synthesis strategy for fabricating multifunctional DNA-templated manganese carbonate nanoparticles (DtMnP). The process involves three critical phases: (i) spherical nucleic acid hybrids, DNAzyme-functionalized AuNPs, serve as scaffolds for spatially controlled Mn2+ deposition through phosphate coordination, initiating heterogeneous nucleation of MnCO3; (ii) rapid liquid nitrogen freezing induces nanoparticle growth along DNA templates; and (iii) lyophilization-mediated structural stabilization enables convenient long-term storage. The DtMnP exhibits pH-responsive dissolution, releasing 90% of Mn2+ within 60 min under tumor microenvironment conditions (pH 5.5). The released Mn2+ ion enables dual functionality: (i) superior magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast of MCF-7 xenograft models with enhanced biosafety, and (ii) synergistic therapeutic efficacy through DNAzyme-mediated EGR-1 gene silencing (60% mRNA downregulation) combined with Mn2+-catalyzed Fenton reactions generating cytotoxic hydroxyl radicals (45% apoptosis in MCF-7 cells). The cryo-encapsulated DtMnP exemplifies a flexible and efficient approach for integrating various functional components into a single nanoparticle for tumor theranostic applications.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202503004-sup-0001-SuppMat.docx10.5 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1C. Arnold, Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 606–608.
- 2J. Wang, Y. Li, G. Nie, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 766–783.
- 3W. Xu, W. He, Z. Du, L. Zhu, K. Huang, Y. Lu, Y. Luo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 6890–6918.
- 4R. Liu, J. Li, B. J. Salena, Y. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202418725.
- 5Z. Yang, A. Farrell, S. Pradhan, K. H. Zhang, W. Guo, Y. Wu, X. Shao, A. Roy, E. S. Garcia, Y. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202413118.
- 6R. Jiang, L. Li, M. Li, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 22129–22144.
- 7F. Li, N. Song, Y. Dong, S. Li, L. Li, Y. Liu, Z. Li, D. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116569.
- 8X. Xie, H. Nan, J. Peng, K. Zeng, H.-H. Wang, Y. Huang, Z. Nie, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202410380.
- 9W. Zhou, R. Saran, J. Liu, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8272–8325.
- 10P.-J. J. Huang, D. de Rochambeau, H. F. Sleiman, J. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3573–3577.
- 11H. Peng, X.-F. Li, H. Zhang, X. C. Le, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14378.
- 12H. Fan, C. E. McGhee, R. J. Lake, Z. Yang, Z. Guo, X.-B. Zhang, Y. Lu, JACS Au 2023, 3, 1615–1622.
- 13R. Qin, S. Li, Y. Qiu, Y. Feng, Y. Liu, D. Ding, L. Xu, X. Ma, W. Sun, H. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1938.
- 14X. Zhu, R. Tang, S. Wang, X. Chen, J. Hu, C. Lei, Y. Huang, H. Wang, Z. Nie, S. Yao, ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2172–2182.
- 15Q. Cheng, Y. Chang, D. Zhang, X. Zhao, Z. Xiao, T. Chen, C. Shi, L. Luo, ACS Nano 2024, 18, 27853–27868.
- 16C. Qi, J. He, L.-H. Fu, T. He, N. T. Blum, X. Yao, J. Lin, P. Huang, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1627–1639.
- 17C. Gu, X. Liu, L. Luo, J. Chen, X. Zhou, G. Chen, X. Huang, L. Yu, Q. Chen, Y. Yang, Y. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202307020.
- 18G. Yang, L. Xu, Y. Chao, J. Xu, X. Sun, Y. Wu, R. Peng, Z. Liu, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 902.
- 19P. Zhu, Y. Pu, M. Wang, W. Wu, H. Qin, J. Shi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 5803–5815.
- 20Z. Sun, Z. Wang, T. Wang, J. Wang, H. Zhang, Z. Li, S. Wang, F. Sheng, J. Yu, Y. Hou, ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11862–11875.
- 21J. Gan, J. Lei, Y. Li, M. Lu, X. Yu, G. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 32689–32700.
- 22P. Mi, D. Kokuryo, H. Cabral, H. Wu, Y. Terada, T. Saga, I. Aoki, N. Nishiyama, K. Kataoka, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 724–730.
- 23H. Fan, Z. Zhao, G. Yan, X. Zhang, C. Yang, H. Meng, Z. Chen, H. Liu, W. Tan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4801–4805.
- 24J. Tao, Y. Tian, D. Chen, W. Lu, K. Chen, C. Xu, L. Bao, B. Xue, T. Wang, Z. Teng, L. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202216361.
- 25L.-S. Lin, J. Song, L. Song, K. Ke, Y. Liu, Z. Zhou, Z. Shen, J. Li, Z. Yang, W. Tang, G. Niu, H.-H. Yang, X. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4902–4906.
- 26Q. Yin, D. Zhao, Y. Chang, B. Liu, Y. Liu, M. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303838.
- 27Z. Zou, L. He, X. Deng, H. Wang, Z. Huang, Q. Xue, Z. Qing, Y. Lei, R. Yang, J. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22970–22976.
- 28J. Li, Z. Zhang, R. Liu, R. Amini, B. J. Salena, Y. Li, Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116886.
- 29A. Yuan, H. Hao, R. Sha, H. Xiao, F. Yang, B. Pang, J. Li, M. Jin, W. Xie, L. Zhao, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, J. Li, H. Peng, Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 20619–20629.
- 30M. U. Musheev, M. Kanoatov, S. N. Krylov, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8041–8046.
- 31T. Lu, F. Chen, J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592.
- 32S. Jia, J. Wang, M. Xie, J. Sun, H. Liu, Y. Zhang, J. Chao, J. Li, L. Wang, J. Lin, K. V. Gothelf, C. Fan, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5597.
- 33A. Yuan, R. Sha, W. Xie, G. Qu, H. Zhang, H. Wang, X. C. Le, G. Jiang, H. Peng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 26657–26666.
- 34W.-H. Lai, Y.-X. Wang, Y. Wang, M. Wu, J.-Z. Wang, H.-K. Liu, S.-L. Chou, J. Chen, S.-X. Dou, Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 695–701.
- 35X. Zhu, H. Xiong, Q. Zhou, Z. Zhao, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, S. Wang, S. Shi, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 18462–18471.
- 36R. Zhang, X. Huang, D. Wang, T. K. A. Hoang, Y. Yang, X. Duan, P. Chen, L.-C. Qin, G. Wen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705817.
- 37Y. Yuan, T. Liu, J. Xiao, Q. Yu, L. Feng, B. Niu, S. Feng, J. Zhang, N. Wang, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5708.
- 38H. Peng, A. M. Newbigging, Z. Wang, J. Tao, W. Deng, X. C. Le, H. Zhang, Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 190–207.
- 39Z. Du, X. Wang, X. Zhang, Z. Gu, X. Fu, S. Gan, T. Fu, S. Xie, W. Tan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302525.
- 40Z. Tang, Y. Liu, M. He, W. Bu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 946–956.
- 41B. Yang, Y. Chen, J. Shi, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4881–4985.