Highly Robust Microporous Metal-Organic Frameworks for Efficient Ethylene Purification under Dry and Humid Conditions
Wansheng Liu
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorShubo Geng
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorNing Li
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorSa Wang
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuping Jia
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorFazheng Jin
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorTing Wang
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorKatherine A. Forrest
Department of Chemistry, University of South Florida, 4202 East Fowler Avenue, Tampa, FL 33620 USA
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tony Pham
Department of Chemistry, University of South Florida, 4202 East Fowler Avenue, Tampa, FL 33620 USA
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Peng Cheng
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry (Ministry of Education), Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yao Chen
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Jian-Gong Ma
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry (Ministry of Education), Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhenjie Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry (Ministry of Education), Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorWansheng Liu
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorShubo Geng
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorNing Li
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorSa Wang
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuping Jia
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorFazheng Jin
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorTing Wang
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorKatherine A. Forrest
Department of Chemistry, University of South Florida, 4202 East Fowler Avenue, Tampa, FL 33620 USA
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tony Pham
Department of Chemistry, University of South Florida, 4202 East Fowler Avenue, Tampa, FL 33620 USA
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Peng Cheng
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry (Ministry of Education), Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yao Chen
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Jian-Gong Ma
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry (Ministry of Education), Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhenjie Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical biology, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry (Ministry of Education), Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage Center, Frontiers Science Center for New Organic Matter, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
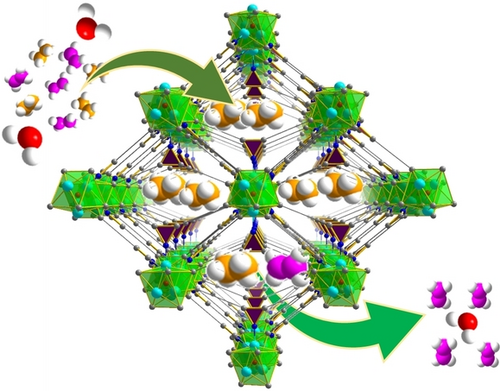
Two highly robust microporous metal–organic frameworks with high ethane uptake and selectivity, ultrahigh water stability, high chemical stability, and low ethane/ethene adsorption enthalpy were designed and synthesized, which could realize one-step C2H4 purification from binary C2H6/C2H4 mixtures under both dry and humid conditions.
Abstract
Two C2H6-selective metal-organic framework (MOF) adsorbents with ultrahigh stability, high surface areas, and suitable pore size have been designed and synthesized for one-step separation of ethane/ethylene (C2H6/C2H4) under humid conditions to produce polymer-grade pure C2H4. Experimental results reveal that these two MOFs not only adsorb a high amount of C2H6 but also display good C2H6/C2H4 selectivity verified by fixed bed column breakthrough experiments. Most importantly, the good water stability and hydrophobic pore environments make these two MOFs capable of efficiently separating C2H6/C2H4 under humid conditions, exhibiting the benchmark performance among all reported adsorbents for separation of C2H6/C2H4 under humid conditions. Moreover, the affinity sites and their static adsorption energies were successfully revealed by single crystal data and computation studies. Adsorbents described in this work can be used to address major chemical industrial challenges.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202217662-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf6.8 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. E. Bachman, Z. P. Smith, T. Li, T. Xu, J. R. Long, Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 845–849.
- 2G. Centi, E. A. Quadrelli, S. Perathoner, Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1711–1731.
- 3G. J. P. Britovsek, M. Bruce, V. C. Gibson, B. S. Kimberley, P. J. Maddox, S. Mastroianni, S. J. McTavish, C. Redshaw, G. A. Solan, S. Stromberg, A. J. P. White, D. J. Williams, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 8728–8740.
- 4L. Li, R.-B. Lin, R. Krishna, H. Li, S. Xiang, H. Wu, J. Li, W. Zhou, B. Chen, Science 2018, 362, 443–446.
- 5H. Zeng, X. J. Xie, M. Xie, Y. L. Huang, D. Luo, T. Wang, Y. Zhao, W. Lu, D. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 20390–20396.
- 6X. Zhang, J. X. Wang, L. Li, J. Pei, R. Krishna, H. Wu, W. Zhou, G. Qian, B. Chen, B. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 10304–10310; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 10392–10398.
- 7Z. Bao, J. Wang, Z. Zhang, H. Xing, Q. Yang, Y. Yang, H. Wu, R. Krishna, W. Zhou, B. Chen, Q. Ren, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16020–16025; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 16252–16257.
- 8Y. P. Li, Y. N. Zhao, S. N. Li, D. Q. Yuan, Y. C. Jiang, X. Bu, M. C. Hu, Q. G. Zhai, Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003141.
- 9A. S. Urlukov, S. I. Uskov, V. A. Sobyanin, P. V. Snytnikov, D. I. Potemkin, Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136993.
- 10J. Zhang, R. Van de Vijver, I. Amghizar, M.-F. Reyniers, K. M. Van Geem, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 3917–3927.
- 11R. B. Lin, L. Li, H. L. Zhou, H. Wu, C. He, S. Li, R. Krishna, J. Li, W. Zhou, B. Chen, Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 1128–1133.
- 12V. F. D. Martins, A. M. Ribeiro, A. Ferreira, U. H. Lee, Y. K. Hwang, J.-S. Chang, J. M. Loureiro, A. E. Rodrigues, Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 445–456.
- 13H. Wu, Y. Chen, D. Lv, R. Shi, Y. Chen, Z. Li, Q. Xia, Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 51–56.
- 14H. Park, M. Kang, D. W. Kang, C. S. Hong, J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 3579–3584.
- 15K. Su, W. Wang, S. Du, C. Ji, D. Yuan, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3703.
- 16P. M. Schoenecker, C. G. Carson, H. Jasuja, C. J. J. Flemming, K. S. Walton, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6513–6519.
- 17J. B. DeCoste, G. W. Peterson, B. J. Schindler, K. L. Killops, M. A. Browe, J. J. Mahle, J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11922–11932.
- 18Y. Zhang, B. Li, R. Krishna, Z. Wu, D. Ma, Z. Shi, T. Pham, K. Forrest, B. Space, S. Ma, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2714–2717.
- 19P. Q. Liao, W. X. Zhang, J. P. Zhang, X. M. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8697.
- 20J. R. Li, R. J. Kuppler, H. C. Zhou, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477–1504.
- 21R. B. Lin, H. Wu, L. Li, X. L. Tang, Z. Li, J. Gao, H. Cui, W. Zhou, B. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12940–12946.
- 22J. Pei, J.-X. Wang, K. Shao, Y. Yang, Y. Cui, H. Wu, W. Zhou, B. Li, G. Qian, J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 3613–3620.
- 23G. D. Wang, Y. Z. Li, W. J. Shi, L. Hou, Y. Y. Wang, Z. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205427; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202205427.
- 24S. Yang, A. J. Ramirez-Cuesta, R. Newby, V. Garcia-Sakai, P. Manuel, S. K. Callear, S. I. Campbell, C. C. Tang, M. Schroder, Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 121–129.
- 25P. Zhang, Y. Zhong, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhu, Y. Liu, Y. Su, J. Chen, S. Chen, Z. Zeng, H. Xing, S. Deng, J. Wang, Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn9231.
- 26C. Gücüyener, J. van den Bergh, J. Gascon, F. Kapteijn, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17704–17706.
- 27W. Liang, F. Xu, X. Zhou, J. Xiao, Q. Xia, Y. Li, Z. Li, Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 148, 275–281.
- 28X. W. Gu, J. Pei, K. Shao, H. M. Wen, B. Li, G. Qian, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 18792–18799.
- 29D. Luo, Y. L. Peng, M. Xie, M. Li, A. A. Bezrukov, T. Zuo, X. Z. Wang, Y. Wu, Y. Y. Li, A. R. Lowe, M. A. Chorazewski, Y. Grosu, Z. Zhang, M. J. Zaworotko, X. P. Zhou, D. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11547–11558.
- 30J. Liu, Y. Wang, A. I. Benin, P. Jakubczak, R. R. Willis, M. D. LeVan, Langmuir 2010, 26, 14301–14307.
- 31W. Zhang, Y. Hu, J. Ge, H. L. Jiang, S. H. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16978–16981.
- 32D. Ma, Y. Li, Z. Li, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7377–7379.
- 33J. Jia, X. Lin, C. Wilson, A. J. Blake, N. R. Champness, P. Hubberstey, G. Walker, E. J. Cussen, M. Schroder, Chem. Commun. 2007, 840–842.
- 34S. Yao, D. Wang, Y. Cao, G. Li, Q. Huo, Y. Liu, J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 16627–16632.
- 35Q. Zhai, Q. Lin, T. Wu, S. T. Zheng, X. Bu, P. Feng, Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 2866–2868.
- 36X. Wang, Z. Niu, A. M. Al-Enizi, A. Nafady, Y. Wu, B. Aguila, G. Verma, L. Wojtas, Y.-S. Chen, Z. Li, S. Ma, J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 13585–13590.
- 37H. Xiang, A. Ameen, P. Gorgojo, F. R. Siperstein, S. M. Holmes, X. Fan, Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 292, 109724.
- 38H. Xiang, Y. Shao, A. Ameen, H. Chen, W. Yang, P. Gorgojo, F. R. Siperstein, X. Fan, Q. Pan, Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116819.
- 39X. Zhao, C. Mao, K. T. Luong, Q. Lin, Q. G. Zhai, P. Feng, X. Bu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2768–2772; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 2818–2822.
- 40L.-Y. Feng, Y.-H. Wang, C.-W. Hu, Y.-G. Li, E.-B. Wang, J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 650, 115–122.
- 41I. Chakraborty, P. Baran, Y. Sanakis, A. Simopoulos, E. Fachini, R. G. Raptis, Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11734–11737.
- 42H. Yang, Y. Wang, R. Krishna, X. Jia, Y. Wang, A. N. Hong, C. Dang, H. E. Castillo, X. Bu, P. Feng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2222–2227.
- 43V. B. Kazansky, E. A. Pidko, J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 2103–2108.
- 44H. G. Hao, Y. F. Zhao, D. M. Chen, J. M. Yu, K. Tan, S. Ma, Y. Chabal, Z. M. Zhang, J. M. Dou, Z. H. Xiao, G. Day, H. C. Zhou, T. B. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16067–16071; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 16299–16303.
- 45J. Liu, J. Miao, S. Ullah, K. Zhou, L. Yu, H. Wang, Y. Wang, T. Thonhauser, J. Li, ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1227–1232.
- 46Y. Gong, C. Chen, R. P. Lively, K. S. Walton, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 9940–9947.
- 47T. M. McDonald, W. R. Lee, J. A. Mason, B. M. Wiers, C. S. Hong, J. R. Long, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7056–7065.
- 48L. N. Ma, G. D. Wang, L. Hou, Z. Zhu, Y. Y. Wang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 26858–26865.
- 49D. A. Hickman, L. D. Schmidt, Science 1993, 259, 343–346.
- 50B. Gould, X. Chen, J. Schwank, J. Catal. 2007, 250, 209–221.
- 51Y. Chen, H. Wu, D. Lv, R. Shi, Y. Chen, Q. Xia, Z. Li, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 4063–4069.
- 52H. Chevreau, T. Devic, F. Salles, G. Maurin, N. Stock, C. Serre, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5056–5060; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 5160–5164.
- 53Deposition numbers 2171571, 2207842, 2171572, 2171573, 2207839, 2207843, 2171574, and 2171575 contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service.