Engineering p-Band Center of Oxygen Boosting H+ Intercalation in δ-MnO2 for Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries
Jianhua Zhang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wenbin Li
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJingjing Wang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaohua Pu
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorGaini Zhang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorShuai Wang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorNi Wang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xifei Li
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorJianhua Zhang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wenbin Li
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJingjing Wang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaohua Pu
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorGaini Zhang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorShuai Wang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorNi Wang
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xifei Li
Shaanxi International Joint Research Center of Surface Technology for Energy Storage Materials, Xi'an Key Laboratory of New Energy Materials and Devices, Institute of Advanced Electrochemical Energy & School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Key Laboratory of Advanced Batteries Materials for Electric Vehicles of China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an, 710048, Shaanxi China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
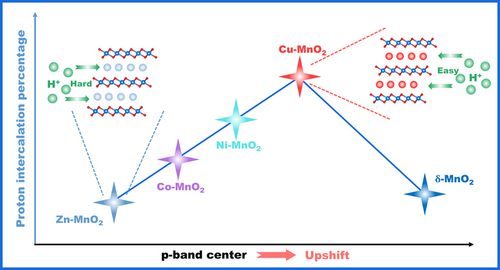
Tuning the ϵp of O in δ-MnO2 cathode can effectively increase H+ intercalation contribution with excellent rate capability for aqueous zinc ion batteries. The ϵp could be a significant descriptor for H+ intercalation contribution that describes a volcano curve as a function of ϵp, and the best cathode is optimized to be the Cu−MnO2 among Cu−, Ni−, Co−, Zn−MnO2.
Abstract
In aqueous zinc ion batteries (ZIBs), the H+ intercalation possesses superior electrochemical kinetics with excellent rate capability, however, precisely modulating H+ intercalation has been still challenging. Herein, a critical modification of pre-intercalating metal ions in the MnO2 interlayer (M−MnO2) with controllable p-band center (ϵp) of O is reported to modulate the H+ intercalation. The modulation of metal-O bond type and covalency degree on the average charge of O atom results in optimized ϵp and H+ adsorption energy for M−MnO2, thus promoting the balance between H+ adsorption and desorption, which plays a determinant role on H+ intercalation. The optimized Cu−MnO2 delivers superior rate capability with the capacity of 153 mAh g−1 at a high rate of 3 A g−1 after 1000 cycles. This work demonstrates that ϵp could be a significant descriptor for H+ intercalation, and tuning ϵp effectively increases H+ intercalation contribution with excellent rate capability in ZIBs.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202215654-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.7 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aJ. Huang, Z. Wang, M. Hou, X. Dong, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2906;
- 1bD. Yang, H. Tan, X. Rui, Y. Yu, Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2019, 2, 395–427.
- 2L. Ma, S. Chen, C. Long, X. Li, Y. Zhao, Z. Liu, Z. Huang, B. Dong, J. A. Zapien, C. Zhi, Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902446.
- 3
- 3aX. Jia, C. Liu, Z. G. Neale, J. Yang, G. Cao, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7795–7866;
- 3bH. Tang, Z. Peng, L. Wu, F. Xiong, C. Pei, Q. An, L. Mai, Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2018, 1, 169–199.
- 4H. Pan, Y. Shao, P. Yan, Y. Cheng, K. S. Han, Z. Nie, C. Wang, J. Yang, X. Li, P. Bhattacharya, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16039.
- 5D. Wang, L. Wang, G. Liang, H. Li, Z. Liu, Z. Tang, J. Liang, C. Zhi, ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10643–10652.
- 6W. Sun, F. Wang, S. Hou, C. Yang, X. Fan, Z. Ma, T. Gao, F. Han, R. Hu, M. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9775–9778.
- 7
- 7aH. Zhang, W. Wu, Q. Liu, F. Yang, X. Shi, X. Liu, M. Yu, X. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 896–903; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 909–916;
- 7bQ. Zhao, A. Song, W. Zhao, R. Qin, S. Ding, X. Chen, Y. Song, L. Yang, H. Lin, S. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 4169–4174; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 4215–4220.
- 8
- 8aX. Wang, Y. Xie, K. Tang, C. Wang, C. Yan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11569–11573; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 11743–11747;
- 8bZ. Guo, J. Huang, X. Dong, Y. Xia, L. Yan, Z. Wang, Y. Wang, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 959;
- 8cH. Jiang, W. Shin, L. Ma, J. J. Hong, Z. Wei, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, X. Wu, Y. Xu, Q. Guo, Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000968.
- 9X. Zeng, J. Liu, J. Mao, J. Hao, Z. Wang, S. Zhou, C. D. Ling, Z. Guo, Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1904163.
- 10G. Cui, Y. Zeng, J. Wu, Y. Guo, X. Gu, X. W. Lou, Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2106067.
- 11T. Sun, Q. Nian, S. Zheng, J. Shi, Z. Tao, Small 2020, 16, 2000597.
- 12B. Wu, G. Zhang, M. Yan, T. Xiong, P. He, L. He, X. Xu, L. Mai, Small 2018, 14, 1703850.
- 13C. Julien, M. Massot, R. Baddour-Hadjean, S. Franger, S. Bach, J. Pereira-Ramos, Solid State Ionics 2003, 159, 345–356.
- 14D. Barreca, A. Gasparotto, E. Tondello, Surf. Sci. Spectra 2007, 14, 41–51.
- 15C. Liu, C. Zhang, H. Fu, X. Nan, G. Cao, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601127.
- 16N. Zhang, F. Cheng, Y. Liu, Q. Zhao, K. Lei, C. Chen, X. Liu, J. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12894–12901.
- 17C. Xu, B. Li, H. Du, F. Kang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 933–935; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 957–959.
- 18N. Zhang, F. Cheng, J. Liu, L. Wang, X. Long, X. Liu, F. Li, J. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 405.
- 19W. Liu, X. Zhang, Y. Huang, B. Jiang, Z. Chang, C. Xu, F. Kang, J. Energy Chem. 2021, 56, 365–373.
- 20H. Chen, X. Zhang, L. Chen, Z. Yang, X. Zeng, J. Meng, J. Energy Storage 2020, 27, 101139.
- 21X. Zang, X. Wang, H. Liu, X. Ma, W. Wang, J. Ji, J. Chen, R. Li, M. Xue, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 9347–9354.
- 22M. Yan, P. He, Y. Chen, S. Wang, Q. Wei, K. Zhao, X. Xu, Q. An, Y. Shuang, Y. Shao, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703725.
- 23D. Kundu, B. D. Adams, V. Duffort, S. H. Vajargah, L. F. Nazar, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16119.
- 24
- 24aW. Liu, X. Li, Y. Hao, H. Maleki Kheimeh Sari, J. Qin, W. Xiao, X. Wang, H. Yang, W. Li, L. Kou, Z. Tian, L. Shao, C. Zhang, J. Zhang, ACS Appl. Energy Mater 2020, 3, 3242–3252;
- 24bJ. Wang, R. Wang, S. Wang, Li. Wang, C. Zhan, J. Electrochem. 2022, 28, 2112131.
- 25
- 25aM. Liu, Q. Zhao, H. Liu, J. Yang, X. Chen, L. Yang, Y. Cui, W. Huang, W. Zhao, A. Song, Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103942;
- 25bH. Yang, W. Zhou, D. Chen, J. Liu, Z. Yuan, M. Lu, L. Shen, V. Shulga, W. Han, D. Chao, Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 1106–1118.
- 26M. Liu, H. Chen, X. Tang, H. Liu, B. Tu, W. Guo, Y. Zheng, Y. Liu, Y. Tang, R. He, W. Zhu, Small 2022, 18, 2107444.
- 27S. Dong, W. Shin, H. Jiang, X. Wu, Z. Li, J. Holoubek, W. F. Stickle, B. Key, C. Liu, J. Lu, Chem 2019, 5, 1537–1551.
- 28
- 28aS. Chandrasekaran, N. Li, Y. Zhuang, L. Sui, Z. Xiao, D. Fan, V. Aravindan, C. Bowen, H. Lu, Y. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134073;
- 28bJ. Wang, X. Li, B. Wei, R. Sun, W. Yu, H. Y. Hoh, H. Xu, J. Li, X. Ge, Z. Chen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908708;
- 28cS. Feng, N. Miao, J. Wang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 56131–56139.