Enzyme-Initiated Free-Radical Polymerization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanogels on a Solid Phase with an Immobilized Radical Source
Graphical Abstract
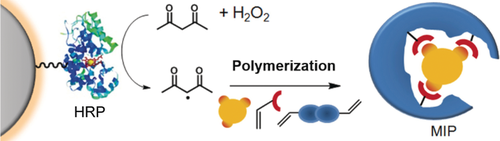
Mighty Immobilized Peroxidase: The radical polymerization of methacrylate or vinyl monomers and cross-linkers was initiated by immobilized horseradish peroxidase (HRP) to prepare molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) nanogels in aqueous media (see scheme). MIP nanoparticles with sizes between 50 and 300 nm were obtained with good binding properties and high selectivity for the target molecule, the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid.
Abstract
An enzyme-mediated synthetic approach is described for the preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles (MIP-NPs) in aqueous media. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was used to initiate the polymerization of methacrylate or vinyl monomers and cross-linkers by catalyzing the generation of free radicals. To prevent entrapment of the enzyme in the cross-linked polymer, and to enable it to be reused, HRP was immobilized on a solid support. MIPs based on 4-vinylpyridine and 1,4-bis(acryloyl)piperazine for the recognition of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and salicylic acid were synthesized in an aqueous medium. MIPs for the protein trypsin were also synthesized. MIP nanoparticles with sizes between 50 and 300 nm were obtained with good binding properties, a good imprinting effect, and high selectivity for the target molecule. The reusability of immobilized HRP for MIP synthesis was shown for several batches.