Near-Infrared Light-Mediated Photoactivation of a Platinum Antitumor Prodrug and Simultaneous Cellular Apoptosis Imaging by Upconversion-Luminescent Nanoparticles†
Yuanzeng Min
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorJinming Li
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorFang Liu
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Edwin K. L. Yeow
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Bengang Xing
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorYuanzeng Min
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorJinming Li
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorFang Liu
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Edwin K. L. Yeow
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Bengang Xing
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical & Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 637371 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported by a Start-Up Grant, A*Star (grant number SERC1121202008), MOE, Tier 1 (grant number RG 64/10), and a COS research collaboration award to the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
Graphical Abstract
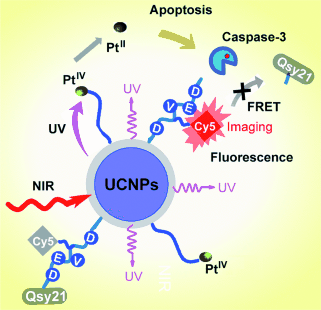
Platinum-based drugs: Near-infrared (NIR) light illumination of conjugates made of photoactive platinum(IV) prodrugs and upconversion-luminescent nanoparticles (UCNPs) is used for the remotely controlled activation of antitumor effects and for simultaneous initiation of apoptosis in the targeted tumor cells. The apoptosis-dependent caspase-3 enzyme offers the promising possibility of imaging apoptosis in real time.
Abstract
Platinum-based drugs are among the most active antitumor reagents in clinical practice; their application is limited by side effects and drug resistance. A novel and personalized near-infrared (NIR) light-activated nanoplatform is obtained by combining a photoactivatable platinum(IV) prodrug and a caspase imaging peptide conjugated with silica-coated upconversion-luminescent nanoparticles (UCNPs) for the remote control of antitumor platinum prodrug activation, and simultaneously for real-time imaging of apoptosis induced by activated cytotoxicity. Upon NIR light illumination, the PtIV prodrug complex is activated at the surface of the nanoparticle and active components are selectively released which display cytotoxicity against human ovarian carcinoma A2780 cells and its cisplatin-resistant variant A2780cis cells. More importantly, the caspases enzymes triggered by cytotoxicity would effectively cleave the probe peptide, thereby allowing the direct imaging of apoptosis in living cells.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201308834_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf5.7 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1S. J. Berners-Price, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 830; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 804.
- 2
- 2aL. Kelland, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573;
- 2bM. D. Hall, M. Okabe, D. Shen, X. Liang, M. M. Gottesman, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 495.
- 3
- 3aU. Kalinowska-Lis, J. Ochocki, K. Matlawska-Wasowska, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 1328;
- 3bN. J. Wheate, S. Walker, G. E. Craig, R. Oun, Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 8113;
- 3cX. Wang, Z. Guo, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 202.
- 4
- 4aJ. S. Butler, P. J. Sadler, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 175;
- 4bN. Graf, S. J. Lippard, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2012, 64, 993;
- 4cM. D. Hall, T. W. Hambley, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 232, 49.
- 5
- 5aN. A. Kratochwil, M. Zabel, K. J. Range, P. J. Bednarski, J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 2499;
- 5bF. S. Mackay, J. A. Woods, P. Heringova, J. Kasparkova, A. M. Pizarro, S. A. Moggach, S. Parsons, V. Brabec, P. J. Sadler, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20743;
- 5cN. J. Farrer, J. A. Woods, L. Salassa, Y. Zhao, K. S. Robinson, G. Clarkson, F. S. Mackay, P. J. Sadler, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 9089;
10.1002/ange.201003399 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8905.
- 6K. Szaciłowski, W. Macyk, A. Drzewiecka-Matuszek, M. Brindell, G. Stochel, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2647.
- 7Y. Zhao, G. M. Roberts, S. E. Greenough, N. J. Farrer, M. J. Paterson, W. H. Powell, V. G. Stavros, P. J. Sadler, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 11425; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11263.
- 8
- 8aF. Wang, X. Liu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 976;
- 8bM. Haase, H. Schäfer, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 5928;
10.1002/ange.201005159 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5808;
- 8cH. H. Gorris, O. S. Wolfbeis, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 3668;
10.1002/ange.201208196 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3584;
- 8dB. Yan, J. C. Boyer, D. Habault, N. R. Branda, Y. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16558;
- 8eC. J. Carling, F. Nourmohammadian, J. C. Boyer, N. R. Branda, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 3870;
10.1002/ange.201000611 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3782;
- 8fW. Feng, L. Sun, Y. Zhang, C. Yan, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 1038;
- 8gY. Liu, D. Tu, H. Zhu, X. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6924;
- 8hZ. Gu, L. Yan, G. Tian, S. Li, Z. Chai, Y. Zhao, Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3758;
- 8iF. Wang, D. Banerjee, Y. Liu, X. Chen, X. Liu, Analyst 2010, 135, 1839.
- 9
- 9aZ. Zhao, Y. Han, C. Lin, D. Hu, F. Wang, X. Chen, Z. Chen, N. Zheng, Chem. Asian J. 2012, 7, 830;
- 9bN. M. Idris, M. K. Gnanasammandhan, J. Zhang, P. Ho, R. Mahendran, Y. Zhang, Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1580.
- 10
- 10aL. Cheng, K. Yang, Y. Li, J. Chen, C. Wang, M. Shao, S. T. Lee, Z. Liu, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 7523; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7385;
- 10bQ. Xiao, X. Zheng, W. Bu, W. Ge, S. Zhang, F. Chen, H. Xing, Q. Ren, W. Fan, K. Zhao, Y. Hua, J. Shi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13041;
- 10cL. Cheng, K. Yang, Y. Li, X. Zeng, M. Shao, S. T. Lee, Z. Liu, Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2215.
- 11
- 11aY. Yang, Q. Shao, R. Deng, C. Wang, X. Teng, K. Cheng, Z. Cheng, L. Huang, Z. Liu, X. Liu, B. Xing, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 3179; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3125;
- 11bQ. Shao, B. Xing, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2835;
- 11cW. Zheng, S. Zhou, Z. Chen, P. Hu, Y. Liu, D. Tu, H. Zhu, R. Li, M. Huang, X. Chen, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 6803; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6671;
- 11dW. Feng, C. Han, F. Li, Adv. Mater. 2013, DOI: ;
- 11eY. Yang, Q. Zhao, W. Feng, F. Li, Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 192.
- 12Y. Zhang, F. Zheng, T. Yang, W. Zhou, Y. Liu, N. Man, L. Zhang, N. Jin, Q. Dou, Z. Li, L. Wen, Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 817.
- 13
- 13aJ. Shen, L. Zhao, G. Han, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2013, 65, 744;
- 13bJ. Liu, W. Bu, L. Pan, J. Shi, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 4471; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4375;
- 13cY. Yang, B. Velmurugan, X. Liu, B. Xing, Small 2013, 9, 2937;
- 13dF. Zhang, G. B. Braun, A. Pallaoro, Y. Zhang, Y. Shi, D. Cui, M. Moskovits, D. Zhao, G. D. Stucky, Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 61;
- 13eL. Li, P. Wu, K. Hwang, Y. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2411.
- 14
- 14aS. Lee, K. Park, K. Kim, K. Choi, I. C. Kwon, Chem. Commun. 2008, 4250;
- 14bX. Huang, M. Swierczewska, K. Y. Choi, L. Zhu, A. Ghirde, J. Park, K. Kim, J. Xie, G. Niu, K. Lee, S. Lee, X. Chen, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 1657; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1625;
- 14cE. M. Barnett, X. Zhang, D. Maxwell, Q. Chang, D. Piwnica-Worms, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9391;
- 14dJ. Lovell, T. Liu, J. Chen, G. Zheng, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2839.
- 15
- 15aR. P. Feazell, N. N. Ratchford, H. Dai, S. J. Lippard, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8438;
- 15bS. Dhar, N. Kolishetti, S. J. Lippard, O. C. Farokhzad, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1850;
- 15cK. M. Taylor-Pashow, J. Della Rocca, Z. Xie, S. Tran, W. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14261;
- 15dP. Ma, H. Xiao, X. Li, C. Li, Y. Dai, Z. Cheng, X. Jing, J. Lin, Adv. Mater. 2013, DOI: ;
- 15eY. Min, C. Mao, S. Chen, G. Ma, J. Wang, Y. Liu, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 6846; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6742.
- 16
- 16aJ. Reedijk, Platinum Met. Rev. 2008, 52, 2;
- 16bJ. Della Rocca, R. C. Huxford, E. Comstock-Duggan, W. Lin, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 10514;
10.1002/ange.201104510 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10330.