Catalyzed Dehydrogenative Coupling of Primary Alcohols with Water, Methanol, or Amines†
Theo Zweifel Dipl.-Chem.
Department of Chemistry and Applied Biology, ETH-Hönggerberg, CH-8093 Zurich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorJean-Valère Naubron Dr.
Department of Chemistry and Applied Biology, ETH-Hönggerberg, CH-8093 Zurich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorHansjörg Grützmacher Prof. Dr.
Department of Chemistry and Applied Biology, ETH-Hönggerberg, CH-8093 Zurich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorTheo Zweifel Dipl.-Chem.
Department of Chemistry and Applied Biology, ETH-Hönggerberg, CH-8093 Zurich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorJean-Valère Naubron Dr.
Department of Chemistry and Applied Biology, ETH-Hönggerberg, CH-8093 Zurich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorHansjörg Grützmacher Prof. Dr.
Department of Chemistry and Applied Biology, ETH-Hönggerberg, CH-8093 Zurich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNF) and the ETH Zurich
Graphical Abstract
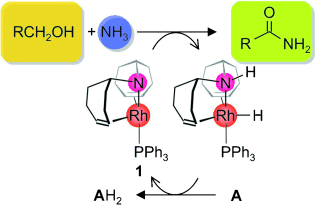
A working partnership: Metal–ligand cooperativity is responsible for the high activity of the rhodium amido complex 1 in the dehydrogenative coupling of primary alcohols with water, methanol, or amines, including ammonia (see scheme), to give carboxylic acids, methyl carboxylates, or amides, respectively. The catalysis proceeds under mild reaction conditions in the presence of a recyclable hydrogen acceptor A. The multistep mechanism was elucidated by computational methods.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_200804757_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf53.4 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1K. Weissermel, H.-J. Arpe, Industrial Organic Chemistry, 4th compl. rev.ed., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003.
10.1002/9783527619191 Google Scholar
- 2See for example: M. Beller, C. Bolm, Transition metals for Organic Syntheses, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004.
- 3N. Armaroli, V. Balzani, Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 52;
10.1002/ange.200602373 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 52.
- 4
- 4aJ. Zhang, M. Gandelman, L. J. W. Shimon, H. Rozenberg, D. Milstein, Organometallics 2004, 23, 4026;
- 4bJ. Zhang, G. Leitus, Y. Ben-David, D. Milstein, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10840; for catalytic systems capable of dehydrogenating alcohols to symmetrical esters in the presence of a suitable hydrogen acceptor, see:
- 4cY. Blum, Y. Shvo, J. Organomet. Chem. 1985, 282, C 7;
- 4dY. Blum, Y. Shvo, J. Organomet. Chem. 1984, 263, 93;
- 4eS. I. Murahashi, T. Naota, K. Ito, Y. Maeda, H. Taki, J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 4319;
- 4fT. Suzuki, K. Morita, M. Tsuchida, K. Hiroi, Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 2361;
- 4gR. H. Meijer, G. Ligthart, J. Meuldijk, J. Vekemans, L. A. Hulshof, A. M. Mills, H. Kooijman, A. L. Spek, Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 1065;
- 4hT. Suzuki, T. Yamada, T. Matsuo, K. Watanabe, T. Katoh, Synlett 2005, 1450; for a recent example with oxygen as the hydrogen acceptor, see
- 4iS. Arita, T. Koike, Y. Kayaki, T. Ikariya, Chem. Asian. J. 2008, 3, 1479.
- 5C. Gunanathan, Y. Ben-David, D. Milstein, Science 2007, 317, 790.
- 6H. Grützmacher, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 1838; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1814.
- 7P. Maire, T. Büttner, F. Breher, P. Le Floch, H. Grützmacher, Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 6477;
10.1002/ange.200500773 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6318.
- 8T. Zweifel, J. Naubron, T. Büttner, T. Ott, H. Grützmacher, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 3289;
10.1002/ange.200704685 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3245.
- 9Oxidation potentials of aldehydes and ketones:
- 9aH. Adkins, R. M. Elofson, A. G. Rossow, C. C. Robinson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1949, 71, 3622; for other successful applications of cyclohexanone as hydrogen acceptor, see:
- 9bG. R. A. Adair, J. M. J. Williams, Chem. Commun. 2005, 5578;
- 9cN. J. Wise, J. M. J. Williams, Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 3639.
- 10We refined the protocol given by H. Rohit Ingle, N. K. Kala Raj, P. Manikandan, J. Mol. Catal. A 2007, 262, 52 and obtained excellent yields (see the Supporting Information for details).
- 11The dehydrogenation of primary alcohols to methyl esters under harsh reaction conditions using crotonitrile was described: N. A. Owston, A. J. Parker, J. M. J. Williams, Chem. Commun. 2008, 624.
- 12R. W. Hoffmann, Synthesis 2006, 3531.
- 13This coupling reaction proceeds with high efficiency because catalyst 2 converts methanol very slowly into methylformate. The initial step, the dehydrogenation of MeOH into formaldehyde, is significantly thermodynamically less favorable than the dehydrogenation of higher alcohols (RCH2OH), to their corresponding aldehydes (see also reference [7]).
- 14R. D. Gaussian 03, M. J. Frisch et al., see the Supporting Information.
- 15R. Noyori, M. Yamakawa, S. Hashiguchi, J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 7931.
- 16The mechanism of the reaction between the amino hydride e and hydrogen acceptor A is simply given by the counter-clockwise reading of the catalytic cycle, that is, e→d→c→b→a in Scheme 3.
- 17The reaction: 2 PhCHO+MeOH→PhCO(OMe)+PhCH2OH is catalyzed by 0.001 mol % 1 in the presence of a small amount K2CO3 (1 mol %) and is complete in 10 minutes at room temperature. Benzaldehyde (3 M) in MeOH was used. One equivalent of benzaldehyde served as the hydrogen acceptor.