Combinatorial Chemistry with Laser Optical Encoding†
Corresponding Author
Dr. Xiao-yi Xiao
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chanfeng Zhao
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hanan Potash
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Michael P. Nova
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Xiao-yi Xiao
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chanfeng Zhao
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hanan Potash
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Michael P. Nova
IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, 11 025 N. Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037 (USA), Fax: Int. code +(619) 546-3083, e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorWe thank Prof. K. C. Nicolaou, who is an advisor to IRORI Quantum Microchemistry, and Dr. A. W. Czarnik for valuable discussions, and Mr. Bill Ewing for software development.
Graphical Abstract
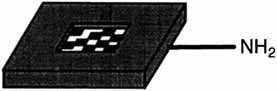
A new strategy for solid-phase combinatorial synthesis: Application of laser optical synthesis chips (shown schematically on the right; other end groups include OH, COOH, and Cl) and directed sorting allows formation and reliable characterization of libraries of small organic molecules, peptides, and oligonucleotides.
References
- 1(a) A. W. Czarnik, Chemtracts: Org. Chem. 1995, 8, 13; (b) D. J. Ecker, S. T. Crooke, Biotechnology 1995, 13, 351; (c) M. A. Gallop, R. W. Barret, W. J. Dower, S. P. A. Fodor, E. M. Gordon, J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1233; (d) E. M. Gordon, R. W. Barret, W. J. Dower, S. P. A. Fodor, M. A. Gallop, J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1385; (e) W. H. Moos, G. D. Green, M. R. Pavia, Annu. Rep. Med. Chem. 1993, 28, 315; (f) E. J. Martin, J. M. Blaney, M. A. Siani, D. C. Spellmeyer, A. K. Wong, W. H. Moos, J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 1431; (g) H. M. Geysen, R. H. Meloen, S. J. Barteling, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3998.
- 2(a)
J. S. Früchtel,
G. Jung,
Angew. Chem.
1996,
108, 19;
10.1002/ange.19961080104 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 35, 17; (b) S. Hobbs DeWitt, S. J. Kiely, C. J. Stankovic, M. C. Schroeder, D. M. Reynolds Cody, M. R. Pavia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6909; (c) B. A. Bunin, J. A. Ellman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10997; (d) C. Chen, L. A. Ahlberg Randall, R. B. Miller, A. D. Jones, M. J. Kurth, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 2661; (e) J. A. Ellman, Chemtracts: Org. Chem. 1995, 8, 1; (f) R. R. Merrifield, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2149; (g) S. J. Danishefsky, M. T. Bilodeau, Angew. Chem. 1996, 108, 1482;10.1002/ange.19961081304 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 35, 1380; (h) M. J. O'Donnel, C.-Y. Zhou, W. L. Scoot, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 6070.
- 3(a) K. S. Lam, S. E. Salmon, E. M. Hersh, V. J. Hruby, W. M. Kazmierski, R. J. Knapp, Nature 1991, 354, 82; (b) Á. Furka, F. Sevestyé, M. Asgedom, G. Dibó, Int. J. Peptide Res. 1991, 37, 487.
- 4 X.-Y. Xiao, M. P. Nova in Combinatorial Chemistry: Synthesis and Application (Eds.: S. R. Wilson, A. W. Czarnik), Wiley, New York, 1996, chap. 7.
- 5(a) H. V. Meyers, G. J. Dilley, T. L. Durgin, T. S. Powers, N. A. Winssinger, H. Zhou, M. R. Pavia, Mol. Diversity 1995, 1, 13; (b) S. H. DeWitt, A. W. Czarnik, Acc. Chem. Res. 1996, 29, 114.
- 6(a) H. M. Geysen, S. J. Rodda, T. J. Mason, G. Tribbick, P. G. Schoofs, J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 102, 259; (b) R. A. Houghten, C. Pinilla, S. E. Blondelle, J. R. Appel, C. T. Dooley, J. H. Cuervo, Nature 1991, 354, 84; (c) D. V. Patel, M. F. Gordeev, B. P. England, E. M. Gordon, J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 924.
- 7(a) J. W. Metzger, C. Kempter, K.-H. Wiesmüller, G. Jung, Anal. Biochem. 1994, 219, 261; (b) B. B. Brown, D. S. Wagner, H. M. Geysen, Mol. Diversity 1995, 1, 4; (c) R. S. Youngquist, G. R. Fuentes, M. P. Lacey, T. Keough, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 3900; (d) C. L. Brummel, I. N. W. Lee, Y. Zhou, S. J. Benkovic, N. Winograd, Science 1994, 264, 399.
- 8(a) S. Brenner, R. A. Lerner, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5381; (b) M. C. Needles, D. G. Jones, E. H. Tate, G. L. Heinkel, L. M. Kochersperger, W. J. Dower, R. W. Barret, M. A. Gallop, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10 700; (c) M. H. J. Ohlmeyer, R. N. Swanson, L. W. Dillard, J. C. Reader, G. Asouline, R. Kobayashi, M. Wigler, W. C. Still, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10 922; (d) P. Eckes, Angew. Chem. 1994, 106, 1649; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1994, 33, 1573; (e) Z. J. Ni, D. Maclean, C. P. Holmes, M. Murphy, B. Ruhland, J. W. Jacobs, E. M. Gordon, M. A. Gallop, J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 1601.
- 9
K. C. Nicolaou,
X.-Y. Xiao,
Z. Parandoosh,
A. Senyei,
M. P. Nova,
Angew. Chem.
1995,
107, 2476;
10.1002/ange.19951072036 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 2289.
- 10 H. A. J. Battaerd, G. W. Tregear, Graft Copolymers, Wiley, Interscience, New York, 1967.
- 11(a) A. R. Mitchell, S. B. H. Kent, M. Engelhard, R. B. Merrifield, J. Org. Chem. 1978, 43, 2845; (b) A. R. Mitchell, B. W. Erickson, M. N. Ryabstev, R. S. Hodges, R. B. Merrifield, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 7357.
- 12(a) A. J. Farrall, J. M. Fréchet, J. Org. Chem. 1976, 41, 3877; (b) R. B. Merrifield, Angew. Chem. 1985, 97, 801; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1985, 24, 799.
- 13 M. J. Gait, Oligonucleotide Synthesis, A Practical Approach, IRL, Oxford, 1990.
- 14 Selected 1H NMR data (500 MHz, D2O) of crude oligonucleotides: ACCT: δ = 8.47 (s, 1H, CH-adenine), 8.37 (s, 1H, CH-adenine), 8.09 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, CH-cytosine), 8.06 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, CH-cytosine), 7.68 (s, 1H, CH-thymine), 6.15–6.32 (3m, 6H, CH-cytosine and OC(N)H), 3.81–5.03 (6m, 16H, OCH2 and OCH), 2.28–2.92 (4m, 8H, CH2), 1.87 (s, 3H, CH3). ACAT: δ = 8.47 (s, 1H, CH-adenine), 8.44 (s, 1H, CH-adenine), 8.35 (s, 1H, CH-adenine), 8.34 (s, 1H, CH-adenine), 8.05 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, CH-cytosine), 7.59 (s, 1H, CH-thymine), 6.15–6.43 (3m, 5H, CH-cytosine and OC(N)H), 3.78–5.01 (7m, 16H, OCH2 and OCH), 2.17–2.87 (5m, 8H, CH2), 1.79 (s, 3 H, CH3).
- 15 Two library members with the same mass (ACGT and AGCT) were sequenced with electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. For details of this method, see (a) G. Siuzdak, Mass spectrometry for Biotechnology, Academic Press, San Diego, 1996, p. 41; (b) J. W. Metzger, C. Kempter, K.-H. Wiesmüller, G. Jung, Anal. Biochem. 1994, 219, 261; (c) J. Ni, S. C. Pomerantz, J. Rozenski, Y. Zhang, J. McCloskey, Anal. Chem. 1996 68, 1989.
- 16 A Manuscript on applications of LOSC in small molecule library synthesis is in preparation.