Rapid High-Specificity microRNA Detection Using a Two-stage Isotachophoresis Assay†
Giancarlo Garcia-Schwarz
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Stanford University, 440 Escondido Mall, Building 530, Room 225, Stanford, CA 94305 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Juan G. Santiago
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Stanford University, 440 Escondido Mall, Building 530, Room 225, Stanford, CA 94305 (USA)
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Stanford University, 440 Escondido Mall, Building 530, Room 225, Stanford, CA 94305 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorGiancarlo Garcia-Schwarz
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Stanford University, 440 Escondido Mall, Building 530, Room 225, Stanford, CA 94305 (USA)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Juan G. Santiago
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Stanford University, 440 Escondido Mall, Building 530, Room 225, Stanford, CA 94305 (USA)
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Stanford University, 440 Escondido Mall, Building 530, Room 225, Stanford, CA 94305 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorWe gratefully acknowledge support from the National Science Foundation under contract number CBET-1159092. G.G.-S. is supported by a Shustek Stanford Graduate Fellowship.
Graphical Abstract
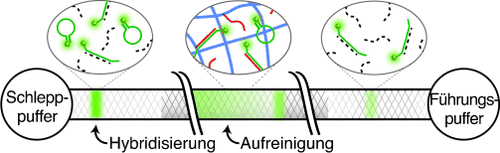
Fokus auf die Kleinen: Ein zweistufiger Assay zum Nachweis von microRNA nutzt elektrokinetische Fokussierung zur Beschleunigung der Hybridisierung und ein funktionalisiertes Hydrogel zur Affinitätsaufreinigung. Die Methode kann einzelne microRNA-Nucleotide in 15 Minuten detektieren und benötigt nur 5 ng RNA.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ange_201305875_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf1.6 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1K. A. Cissell, S. Shrestha, S. K. Deo, Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4754–4761.
- 2R. C. Lee, R. L. Feinbaum, V. Ambros, Cell 1993, 75, 843–854; H. B. Houbaviy, M. F. Murray, P. A. Sharp, Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 351–358.
- 3J. Brennecke, D. R. Hipfner, A. Stark, R. B. Russell, S. M. Cohen, Cell 2003, 113, 25–36.
- 4X. Li, R. W. Carthew, Cell 2005, 123, 1267–1277.
- 5X. Chen, Y. Ba, L. Ma, X. Cai, Y. Yin, K. Wang, J. Guo, Y. Zhang, J. Chen, X. Guo, Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006; J. V. Tricoli, J. W. Jacobson, Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4553–4555.
- 6J. Lu, G. Getz, E. A. Miska, E. Alvarez-Saavedra, J. Lamb, D. Peck, A. Sweet-Cordero, B. L. Ebert, R. H. Mak, A. A. Ferrando, Nature 2005, 435, 834–838.
- 7J. Takamizawa, H. Konishi, K. Yanagisawa, S. Tomida, H. Osada, H. Endoh, T. Harano, Y. Yatabe, M. Nagino, Y. Nimura, Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3753.
- 8S. Volinia, G. A. Calin, C.-G. Liu, S. Ambs, A. Cimmino, F. Petrocca, R. Visone, M. Iorio, C. Roldo, M. Ferracin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261.
- 9M. Baker, Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 687–692.
- 10C. Chen, D. A. Ridzon, A. J. Broomer, Z. Zhou, D. H. Lee, J. T. Nguyen, M. Barbisin, N. L. Xu, V. R. Mahuvakar, M. R. Andersen, Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e 179–e179.
- 11H. Wang, R. A. Ach, B. Curry, RNA 2007, 13, 151–159.
- 12C. C. Pritchard, H. H. Cheng, M. Tewari, Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 358–369; D. Leshkowitz, S. Horn-Saban, Y. Parmet, E. Feldmesser, RNA 2013, 19, 527; P. Chugh, D. P. Dittmer, WIREs RNA 2012, 3, 601–616.
- 13S. C. Chapin, D. C. Appleyard, D. C. Pregibon, P. S. Doyle, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 2337–2341;
10.1002/ange.201006523 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2289–2293; D. W. Wegman, S. N. Krylov, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 10519–10523;10.1002/ange.201104693 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10335–10339.
- 14H. Yang, A. Hui, G. Pampalakis, L. Soleymani, F.-F. Liu, E. H. Sargent, S. O. Kelley, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 8613–8616; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8461–8464.
- 15G. Garcia-Schwarz, J. G. Santiago, Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6366–6369.
- 16G. Garcia-Schwarz, A. Rogacs, S. S. Bahga, J. G. Santiago, J. Visualized Exp. 2012, 61, e 3890.
- 17M. Bercovici, C. M. Han, J. C. Liao, J. G. Santiago, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11127–11132.
- 18G. Bonnet, S. Tyagi, A. Libchaber, F. R. Kramer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6171–6176.
- 19N. R. Markham, M. Zuker, Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W 577–W581.
- 20H. Kaur, A. Arora, J. Wengel, S. Maiti, Biochemistry 2006, 45, 7347–7355.
- 21the LNA Oligo Tool from Exiqon is available online at www.exiqon.com/oligo-tools.
- 22N. Sugimoto, M. Nakano, S. Nakano, Biochemistry 2000, 39, 11270–11281.
Citing Literature
This is the
German version
of Angewandte Chemie.
Note for articles published since 1962:
Do not cite this version alone.
Take me to the International Edition version with citable page numbers, DOI, and citation export.
We apologize for the inconvenience.