Photolithographic Boronate Affinity Molecular Imprinting: A General and Facile Approach for Glycoprotein Imprinting†
Correction(s) for this article
-
Berichtigung: Photolithographic Boronate Affinity Molecular Imprinting: A General and Facile Approach for Glycoprotein Imprinting
- Volume 129Issue 11Angewandte Chemie
- pages: 2871-2871
- First Published online: March 6, 2017
Li Li
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorYue Lu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorZijun Bie
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hong-Yuan Chen
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Zhen Liu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)Search for more papers by this authorLi Li
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorYue Lu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorZijun Bie
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hong-Yuan Chen
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Zhen Liu
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)
State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, 22 Hankou Road, Nanjing 210093 (China)Search for more papers by this authorWe gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant Nos. 2013CB911202 and 2008DFA01910), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21075063, 21275073, and 21121091), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. KB2011054).
Graphical Abstract
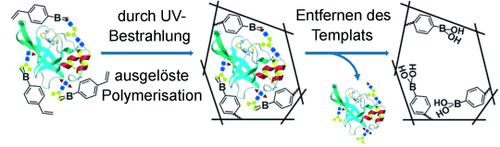
Positive Überraschung: Ein allgemeiner und einfacher Ansatz für das Glycoprotein-Prägen mit einer gewöhnlichen Boronsäure als funktionellem Monomer hat einige unerwartete Vorteile. Auf diese Weise erhaltene molekular geprägte Polymere können Spuren von Glycoproteinen in komplexen realen Proben nachweisen.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ange_201207950_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf2.9 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aG. Wulff, A. Sarhan, Angew. Chem. 1972, 84, 364–364;
10.1002/ange.19720840838 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1972, 11, 341–345;
- 1bG. Vlatakis, L. I. Andersson, R. Müller, K. Mosbach, Nature 1993, 361, 645–647;
- 1cH. Shi, W. B. Tsai, M. D. Garrison, S. Ferrari, B. D. Ratner, Nature 1999, 398, 593–597;
- 1dT. Miyata, M. Jige, T. Nakaminami, T. Uragami, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1190–1193;
- 1eJ.-L. Liao, Y. Wang, S. Hjertén, Chromatographia 1996, 42, 259–262;
- 1fY. Hoshino, H. Koide, T. Urakami, H. Kanazawa, T. Kodama, N. Oku, K. J. Shea, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6644–6645.
- 2L. X. Chen, S. F. Xu, J. H. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2922–2942.
- 3M. Kempe, M. Glad, K. Mosbach, J. Mol. Recognit. 1995, 8, 35–39.
- 4N. Nishino, C. S. Huang, K. J. Shea, Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 2452–2456;
10.1002/ange.200503760 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2392–2396.
- 5X. T. Shen, L. Ye, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10359–10361.
- 6
- 6aM. Glad, O. Norrlow, B. Sellergren, N. Siegbahn, K. Mosbach, J. Chromatogr. A 1985, 347, 11–23;
- 6bH. Q. Shi, B. D. Ratner, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 49, 1–11;
10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(200001)49:1<1::AID-JBM1>3.0.CO;2-9 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 6cA. Bossi, S. A. Piletsky, E. V. Piletska, P. G. Righetti, A. P. F. Turner, Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5281–5286;
- 6dS. A. Piletsky, E. V. Piletska, A. Bossi, K. Karim, P. Lowe, A. P. F. Turner, Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 701–707;
- 6eA. Nematollahzadeh, W. Sun, C. S. A. Aureliano, D. Lutkemeyer, J. Stute, M. J. Abdekhodaie, A. Shojaei, B. Sellergren, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 515–518;
10.1002/ange.201004774 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 495–498.
- 7T. D. James, K. R. A. S. Sandanayake, S. Shinkai, Angew. Chem. 1996, 108, 2038–2050;
10.1002/ange.19961081706 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 35, 1910–1922.
- 8
- 8aL. B. Ren, Z. Liu, Y. C. Liu, P. Dou, H. Y. Chen, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 6832–6835; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6704–6707;
- 8bY. C. Liu, L. B. Ren, Z. Liu, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5067–5069;
- 8cH. Y. Li, H. Y. Wang, Y. C. Liu, Z. Liu, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4115–4117;
- 8dL. Liang, Z. Liu, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2255–2257;
- 8eY. C. Liu, Y. Lu, Z. Liu, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1467–1471.
- 9
- 9aG. Wulff, R. Grobe-Einsler, W. Vesper, A. Sarhan, Makromol. Chem. 1977, 178, 2817–2825;
- 9bJ. Kugimiya, J. Matsui, T. Takeuchi, K. Yano, H. Muguruma, A. V. Elgersma, I. Karube, Anal. Lett. 1995, 28, 2317–2323;
- 9cA. Friggeri, H. Kobayashi, S. Shinkai, D. N. Reinhoudt, Angew. Chem. 2001, 113, 4865–4867;
10.1002/1521-3757(20011217)113:24<4865::AID-ANGE4865>3.0.CO;2-7 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 4729–4731.10.1002/1521-3773(20011217)40:24<4729::AID-ANIE4729>3.0.CO;2-M CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 10
- 10aJ. Rick, T. C. Chou, Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 26–31;
- 10bC. L. Yan, Y. Lu, S. Y. Gao, J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2007, 45, 1911–1919;
- 10cL. Li, X. He, L. Chen, Y. Zhang, Chem. Asian J. 2009, 4, 286–293;
- 10dJ. Pribyl, P. Skladal, Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 530, 75–84;
- 10eF. Bonini, S. A. Piletsky, A. P. F. Turner, A. Speghini, A. Bossi, Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2322–2328;
- 10fN. W. Turner, X. Liu, S. A. Piletsky, V. Hlady, D. W. Britt, Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2781–2787.
- 11
- 11aM. E. Byrne, E. Oral, J. Z. Hilt, N. A. Peppas, Polym. Adv. Technol. 2002, 13, 798–816;
- 11bS. Guillon, R. Lemaire, A. V. Linares, K. Haupt, C. Ayela, Lab Chip 2009, 9, 2987–2991.
- 12C. C. Lü, H. Y. Li, H. Y. Wang, Z. Liu, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2361–2369.
Citing Literature
This is the
German version
of Angewandte Chemie.
Note for articles published since 1962:
Do not cite this version alone.
Take me to the International Edition version with citable page numbers, DOI, and citation export.
We apologize for the inconvenience.