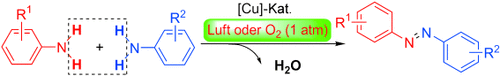
Copper-Catalyzed Aerobic Oxidative Dehydrogenative Coupling of Anilines Leading to Aromatic Azo Compounds using Dioxygen as an Oxidant†
Chun Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China), Fax: (+86) 10-8280-5297
Search for more papers by this authorNing Jiao Dr.
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China), Fax: (+86) 10-8280-5297
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry and Chemical Processes, Department of Chemistry, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorChun Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China), Fax: (+86) 10-8280-5297
Search for more papers by this authorNing Jiao Dr.
State Key Laboratory of Natural and Biomimetic Drugs, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Xue Yuan Rd. 38, Beijing 100191 (China), Fax: (+86) 10-8280-5297
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry and Chemical Processes, Department of Chemistry, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062 (China)
Search for more papers by this authorFinancial support from Peking University, the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 20702002, 20872003), and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program; Grant No. 2009CB825300) are greatly appreciated. We thank Chong Qin in this group for reproducing the results of 2 ii, 2 ah, and 2 lb.
Graphical Abstract
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ange_201001651_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf924.1 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For some reviews, see:
- 1aK. Hunger, Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, properties, Applications; Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003;
- 1bR. G. Anderson, G. Nickless, Analyst 1967, 92, 207;
- 1cP. N. D. Ashutosh, J. K. Mehrotra, Colourage 1979, 26, 25;
- 1dR. D. Athey, Jr., Eur. Coatings J. 1998, 3, 146;
- 1eC. S. Sheppard, Encycl. Polym. Sci. Eng. 1985, 2, 143;
- 1fJ. R. S. Hoult, Drugs 1986, 32, 18;
- 1gW. J. Sandborn, Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2939;
- 1hS. C. Cation, E. Farris, Concise encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, Wiley, 1985.
- 2There are few reported catalytic approaches for azo compounds from nitroaromatics, anilines, or aryl hydrazides:
- 2aA. Grirrane, A. Corma, H. García, Science 2008, 322, 1661;
- 2bA. Corma, P. Concepción, P. Serna, Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 7404;
10.1002/ange.200700823 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7266;
- 2cZ. Zhu, J. H. Espenson, J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 1326;
- 2dW. Lu, C. Xi, Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 4011;
- 2eY.-K. Lim, K.-S. Lee, C.-G. Cho, Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 979;
- 2fE. Drug, M. Gozin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13784.
- 3aH. E. Baumgarten, A. Staklis, E. M. Miller, J. Org. Chem. 1965, 30, 1203;
- 3bH. Firouzabadi, Z. Mostafavippor, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1983, 56, 914;
- 3cJ. M. Birchall, R. N. Haszeldine, J. E. G. Kemp, Chem. Commun. 1970, 449;
- 3dK. Wenkert, B. Wickberg, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 4914;
- 3eS. Farhadi, P. Zaringhadam, R. Z. Sahamieh, Acta Chim. Slov. 2007, 54, 647;
- 3fS. L. Goldstein, E. McNelis, J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 183;
- 3gH. Huang, D. Sommerfeld, B. C. Dunn, C. R. Lloyd, E. M. Eyring, J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2001, 1301.
- 4
- 4aH. A. Dabbagh, A. Teimouri, A. N. Chermahini, Dyes Pigm. 2007, 73, 239;
- 4bM. Barbero, S. Cadamuro, S. Dughera, C. Giaveno, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 4884;
- 4cM. Barbero, I. Degani, S. Dughera, R. Fochi, P. Perracino, Synthesis 1998, 1235.
- 5
- 5aW. H. Nutting, R. A. Jewell, H. Rapoport, J. Org. Chem. 1970, 35, 505;
- 5bK. Krageloh, G. H. Anderson, P. J. Stang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 6015;
- 5cZ. Liu, M. Jiang, J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 4249.
- 6For some reviews, see:
- 6aS. S. Stahl, Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 3480;
10.1002/ange.200300630 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3400;
- 6bT. Punniyamurthy, S. Velusamy, J. Iqbal, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2329. For some recent copper-catalyzed reactions using dioxygen as oxidant, see:
- 6cA. E. King, T. C. Brunold, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5044;
- 6dH.-Q. Do, O. Daugulis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17052;
- 6eY. Gao, G. Wang, L. Chen, P. Xu, Y. Zhao, Y. Zhou, L.-B. Han, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7956;
- 6fO. Baslé, C.-J. Li, Chem. Commun. 2009, 4124;
- 6gD. Monguchi, T. Fujiwara, H. Furukawa, A. Mori, Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1607;
- 6hT. Hamada, X. Ye, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 833;
- 6iG. Brasche, S. L. Buchwald, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 1958;
10.1002/ange.200705420 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1932;
- 6jS. Ueda, H. Nagasawa, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 6511; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6411;
- 6kY. Wei, H. Zhao, J. Kan, W. Su, M. Hong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2522.
- 7For some of our recent work using dioxygen as an oxidant:
- 7aZ. Shi, S. Ding, Y. Cui, N. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 8035; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7895;
- 7bZ. Shi, C. Zhang, S. Li, D. Pan, S. Ding, Y. Cui, N. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4642; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4572;
- 7cA. Chen, R. Lin, Q. Liu, N. Jiao, Chem. Commun. 2009, 6842.
- 8C. Zhang, N. Jiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 28.
- 9For some reviews, see:
- 9aC.-J. Li, Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 335;
- 9bL. Ackermann, R. Vicente, A. R. Kapdi, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 9976; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9792. For some recent examples, see:
- 9cY.-Z. Li, B.-J. Li, X.-Y. Lu, S. Lin, Z.-J. Shi, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 3875; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3817;
- 9dX. Guo, R. Yu, H. Li, Z. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17387;
- 9eM. Itazaki, K. Ueda, H. Nakazawa, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 3363;
10.1002/ange.200805112 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3313;
- 9fC. Gunanathan, L. J. W. Shimon, D. Milstein, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3146;
- 9gL. Zhao, C.-J. Li, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 7183; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7075;
- 9hL.-B. Han, Y. Ono, S. Shimada, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2752;
- 9iZ. Li, L. Cao, C.-J. Li, Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 6625; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6505;
- 9jT. Kawashima, T. Takao, H. Suzuki, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11006;
- 9kD. R. Stuart, K. Fagnou, Science 2007, 316, 1172.
- 10For recent reviews, see:
- 10aM. Kienle, S. R. Dubbaka, K. Brade, P. Knochel, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 4166;
- 10bS. V. Ley, A. W. Thomas, Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 5558;
10.1002/ange.200300594 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5400.
- 11
- 11aW. B. Tolman, Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 227;
- 11bC. X. Zhang, H.-C. Liang, E. Kim, J. Shearer, M. E. Helton, E. Kim, S. Kaderli, C. D. Incarvito, A. D. Zuberbühler, A. L. Rheingold, K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 634;
- 11cH. V. Obias, Y. Lin, N. N. Murthy, E. Pidcock, E. I. Solomon, M. Ralle, N. J. Blackburn, Y.-M. Neuhold, A. D. Zuberbühler, K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 12960;
- 11dS. Itoh, M. Taki, H. Nakao, P. L. Holland, W. B. Tolman, L. Que, Jr., S. Fukuzumi, Angew. Chem. 2000, 112, 409;
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 398;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(20000117)39:2<398::AID-ANIE398>3.0.CO;2-2 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 11eV. Mahadevan, M. J. Henson, E. I. Solomon, T. D. P. Stack, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10249;
- 11fA. Kunishita, H. Ishimaru, S. Nakashima, T. Ogura, S. Itoh, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4244;
- 11gM. Taki, S. Teramae, S. Nagatomo, Y. Tachi, T. Kitagawa, S. Itoh, S. Fukuzumi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6367.
- 12
- 12aW. Hub, S. Schneider, F. Doerr, J. D. Oxman, F. D. Lewis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 701;
- 12bJ. C. Scaiano, S. García, H. García, Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 5929;
- 12cO. Brede, A. Maroz, R. Hermann, S. Naumov, J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 8081.
- 13I. Cepanec, M. Litvić, J. Udiković, I. Pogorelić, M. Lovrić, Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 5614.
Citing Literature
This is the
German version
of Angewandte Chemie.
Note for articles published since 1962:
Do not cite this version alone.
Take me to the International Edition version with citable page numbers, DOI, and citation export.
We apologize for the inconvenience.