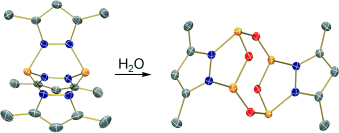
Preparation of Ligand-Stabilized [P4O4]2+ by Controlled Hydrolysis of a Janus Head Type Diphosphorus Trication†
Jan J. Weigand Dr.
Institut für Anorganische und Analytische Chemie and Graduate School of Chemistry, WWU Münster, Corrensstrasse 30, 48149 Münster (Germany), Fax: (+49) 251-83-33108
Search for more papers by this authorKai-Oliver Feldmann
Institut für Anorganische und Analytische Chemie and Graduate School of Chemistry, WWU Münster, Corrensstrasse 30, 48149 Münster (Germany), Fax: (+49) 251-83-33108
Search for more papers by this authorAntje K. C. Echterhoff
Institut für Anorganische und Analytische Chemie and Graduate School of Chemistry, WWU Münster, Corrensstrasse 30, 48149 Münster (Germany), Fax: (+49) 251-83-33108
Search for more papers by this authorAndreas W. Ehlers Dr.
Department of Organic and Inorganic Chemistry, VU University Amsterdam (The Netherlands)
Search for more papers by this authorKoop Lammertsma Prof. Dr.
Department of Organic and Inorganic Chemistry, VU University Amsterdam (The Netherlands)
Search for more papers by this authorJan J. Weigand Dr.
Institut für Anorganische und Analytische Chemie and Graduate School of Chemistry, WWU Münster, Corrensstrasse 30, 48149 Münster (Germany), Fax: (+49) 251-83-33108
Search for more papers by this authorKai-Oliver Feldmann
Institut für Anorganische und Analytische Chemie and Graduate School of Chemistry, WWU Münster, Corrensstrasse 30, 48149 Münster (Germany), Fax: (+49) 251-83-33108
Search for more papers by this authorAntje K. C. Echterhoff
Institut für Anorganische und Analytische Chemie and Graduate School of Chemistry, WWU Münster, Corrensstrasse 30, 48149 Münster (Germany), Fax: (+49) 251-83-33108
Search for more papers by this authorAndreas W. Ehlers Dr.
Department of Organic and Inorganic Chemistry, VU University Amsterdam (The Netherlands)
Search for more papers by this authorKoop Lammertsma Prof. Dr.
Department of Organic and Inorganic Chemistry, VU University Amsterdam (The Netherlands)
Search for more papers by this authorWe gratefully acknowledge the FCI (fellowship for J.J.W. and K.O.F.), the DFG (WE 4621/2-1), the European PhosSciNet (CM0802), and the International Research Training Group (IRTG 1444). J.J.W. thanks Prof. F. E. Hahn (WWU Münster) for his generous support and Dr. R. Wolf for helpful discussions. The authors thank J. Stierstorfer (LMU Munich, Raman) and Dr. A. Hepp (WWU, NMR) for their help.
Graphical Abstract
Auf zu neuen Ufern: Die stufenweise Hydrolyse eines Diphosphor-Trikations ist eine effiziente Methode, ein ungewöhnliches ligandenstabilisiertes Dikation mit einem neuartigen kationischen [P4O4]2+-Gerüst herzustellen (siehe Schema, grau C, Blau N, rot O, orange P). Diese Reaktion unterstreicht das Potenzial des Diphosphor-Trikations als Quelle für Phosphor-Bausteine, mit denen neuartige kationische Ring- und Clustersysteme aufgebaut werden können.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| ange_201001363_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf12 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1V. G. Nenajdenko, N. E. Shevchenko, E. S. Balenkova, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 229.
- 2
- 2aR. Weiss, F. G. Pühlhofer, N. Jux, K. Merz, Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 3969;
10.1002/1521-3757(20021018)114:20<3969::AID-ANGE3969>3.0.CO;2-H Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3815;10.1002/1521-3773(20021018)41:20<3815::AID-ANIE3815>3.0.CO;2-8 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 2bF. G. Pühlhofer, R. Weiss, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 1002;
- 2cR. Weiss, S. M. Huber, F. Pühlhofer, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 3530;
- 2dR. Weiss, S. M. Huber, F. W. Heinemann, P. Audebert, F. Pühlhofer, Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 8228;
10.1002/ange.200602693 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 8059;
- 2eR. Weiss, F. G. Pühlhofer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 547, and references therein.
- 3
- 3aR. Weiss, S. Engel, Synthesis 1991, 1077;
- 3bR. Weiss, S. Engel, Angew. Chem. 1992, 104, 239; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1992, 31, 216.
- 4
- 4aR. Reed, R. Réau, F. Dahan, G. Bertrand, Angew. Chem. 1993, 105, 464; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1993, 32, 399;
- 4bG. Bouhadir, R. W. Reed, R. Réau, G. Bertrand, Heteroat. Chem. 1995, 6, 371.
- 5
- 5aA. Schmidpeter, S. Lochschmidt, W. S. Sheldrick, Angew. Chem. 1985, 97, 214; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1985, 24, 226;
- 5bA. Schmidpeter, S. Lochschmidt, K. Karaghiosoff, W. S. Sheldrick, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1985, 1447;
- 5cA. Schmidpeter, S. Lochschmidt, Inorg. Synth. 1990, 27, 253;
- 5dB. D. Ellis, C. A. Dyker, A. Decken, C. L. B. Macdonald, Chem. Commun. 2005, 1965;
- 5eP. Kilian, A. M. Z. Slawin, J. D. Woollins, Dalton Trans. 2006, 2175;
- 5fB. D. Ellis, C. L. B. Macdonald, Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 6864.
- 6
- 6aJ. J. Weigand, N. Burford, A. Decken, A. Schulz, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 4868;
- 6bJ. J. Weigand, N. Burford, R. J. Davidson, T. S. Cameron, P. Seelheim, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17943.
- 7
- 7aI. Krummenacher, I. Fernández, H. Rüegger, F. Weigend, F. Breher, Dalton Trans. 2009, 5335;
- 7bA. Steiner, D. Stalke, Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 4846;
- 7cI. Kuzu, I. Krummenacher, J. Meyer, F. Armbruster, F. Breher, Dalton Trans. 2008, 5836, and references therein.
- 8A full description of the technical and experimental details and X-ray diffraction data for 1[OTf]3 and 2[OTf]2 are given in the Supporting Information. CCDC 766183 (1[OTf]3) and 766184 (2[OTf]2) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
- 9Phosphane 6 was prepared according to a modified procedure: S. Fischer, L. K. Peterson, Can. J. Chem. 1974, 52, 3981.
- 10Seven contacts; shortest: dPO=2.665(2) Å.
- 11A. Bondi, J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 441.
- 12A. F. Holleman, E. Wiberg, N. Wiberg, Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie, 102nd ed., de Gruyter, Berlin, 2007, Anhang V.
10.1515/9783110177701 Google Scholar
- 13
- 13aE. D. Glendening, A. E. Reed, J. E. Carpenter, F. Weinhold, NBO Version 3.;
- 13bE. D. Glendening, A. E. Reed, J. E. Carpenter, F. Weinhold, Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 899.
- 14The Supporting Information provides a full description of the computational details, a comparison of the theoretical and experimentally obtained 31P chemical shifts, and a summary of the NBO analysis.
- 15N. Burford, P. J. Ragogna, Dalton Trans. 2002, 4307.
- 16S. Fischer, J. Hoyano, L. K. Peterson, Can. J. Chem. 1976, 54, 2710.
- 17The 31P NMR spectrum of dissolved 2[OTf]2 shows very small amounts of a second product (<2 %; δ=86.8 ppm), which we tentatively assign to the cis isomer.[14]
- 18
- 18aS. Berger, S. Braun, H.-O. Kalinowski, 31 P NMR-Spektroskopie, Georg Thieme, Stuttgart, 1993, Vol. 3;
- 18bA. C. Chapman, J. Homer, D. J. Mowthorpe, R. T. Jones, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1965, 121.
- 19T. O. Denisova, E. V. Amel’chenkova, I. S. Kislina, N. B. Librovich, S. E. Nefedov, Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 51, 1755.
- 20
- 20aM. Mühlhäuser, B. Engels, C. M. Marian, S. D. Peyerimhoff, P. J. Bruna, M. Jansen, Angew. Chem. 1994, 106, 578;
10.1002/ange.19941060509 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1994, 33, 563;
- 20bA. Tellenbach, M. Jansen, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 3759.
- 21J. C. Tebby, Handbook of Phosphorus-31 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Data, CRC, Boca Raton, 1990.
Citing Literature
This is the
German version
of Angewandte Chemie.
Note for articles published since 1962:
Do not cite this version alone.
Take me to the International Edition version with citable page numbers, DOI, and citation export.
We apologize for the inconvenience.