Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
research papers
SAXS study of the formation and structure of polynuclear thorium(IV) colloids and thorium dioxide nanoparticles
- Pages: 281-287
- First Published: 18 January 2022
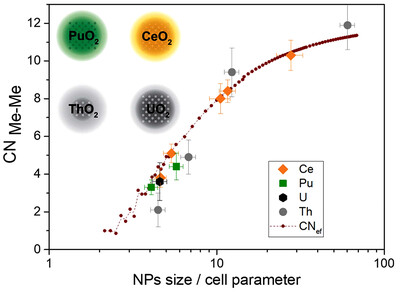
Effective coordination numbers from EXAFS: general approaches for lanthanide and actinide dioxides
- Pages: 288-294
- First Published: 27 January 2022
X-ray spectroscopic study of chemical state in uranium carbides
- Pages: 295-302
- First Published: 27 January 2022
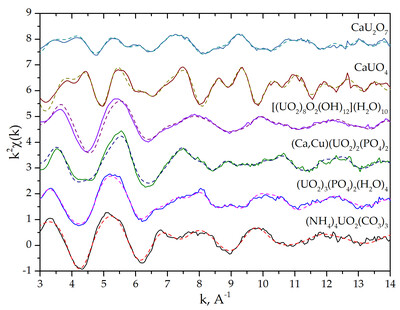
From EXAFS of reference compounds to U(VI) speciation in contaminated environments
- Pages: 303-314
- First Published: 08 February 2022
In situ beam reduction of Pu(IV) and Bk(IV) as a route to trivalent transuranic coordination complexes with hydroxypyridinone chelators
- Pages: 315-322
- First Published: 25 February 2022
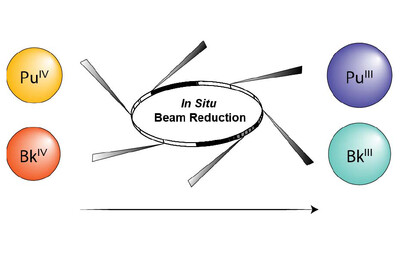
X-ray absorption spectroscopy was used to probe the interactions between an octadentate hydroxypyridinone chelator and two transuranic elements in microgram quantities – plutonium and berkelium – within buffered solutions. Despite the precedence for chelation-driven stabilization of the tetravalent oxidation state of actinides with this ligand, in situ reductive decomposition yielded plutonium(III) and berkelium(III) coordination complexes.
Quantifying electron cascade size in various irradiated materials for free-electron laser applications
- Pages: 323-330
- First Published: 15 February 2022
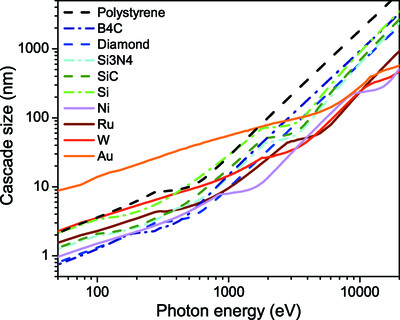
Studying electron- and X-ray-induced electron cascades in solids is essential for various research areas at free-electron laser facilities, such as X-ray imaging, crystallography, pulse diagnostics or X-ray-induced damage. To better understand the fundamental factors that define the duration and spatial size of such cascades, this work investigates the electron propagation in ten solids relevant for the applications of X-ray lasers. Using classical Monte Carlo simulation in the atomic approximation, the dependence of the cascade size on the incident electron or photon energy and on the target parameters is studied.
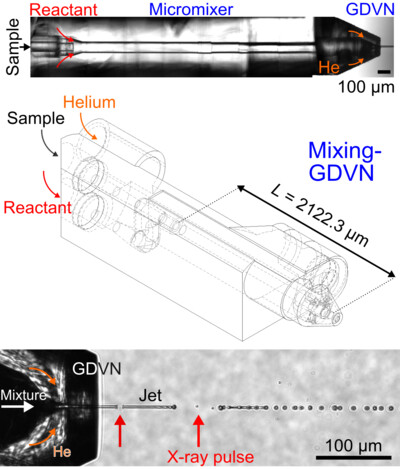
3D printed devices and infrastructure for liquid sample delivery at the European XFEL
- Pages: 331-346
- First Published: 15 February 2022
Generating coherent and ultrashort X-ray pulses via HHG-seeding in storage rings
- Pages: 347-354
- First Published: 19 January 2022
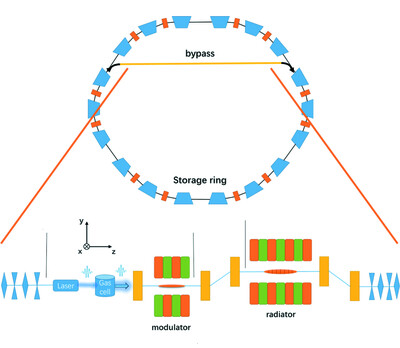
A method that utilizes the recent external light from high-harmonic generation (HHG) to coherent light at shorter wavelength is proposed. Numerical simulations with parameters of a diffraction-limited storage ring demonstrate the generation of coherent pulse trains with photon energy as high as 2 keV, pulse duration as short as ∼10 fs and high peak brightness directly from an HHG source at 13 nm.
Synchrotron radiation transmission by two coupled flat microchannel plates: new opportunities to control the focal spot characteristics
- Pages: 355-362
- First Published: 19 January 2022
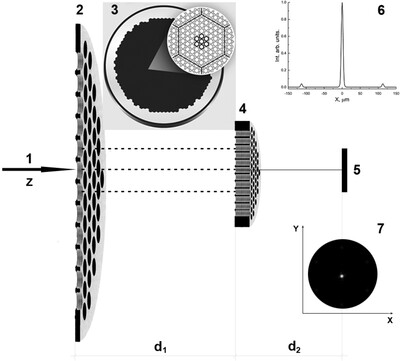
Transmission properties and diffraction patterns generated by synchrotron radiation at the exit of an assembled couple of microchannel plates (MCPs) are inivestigated. A theoretical model to simulate the patterns and properties of the soft X-ray beam emerging from this couple of MCPs is presented and discussed.
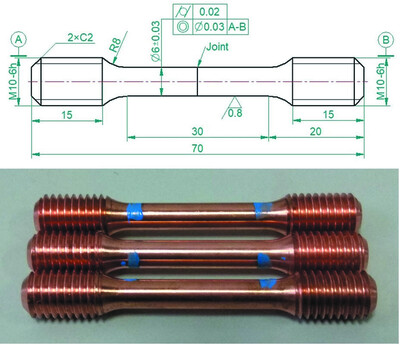
Vacuum joints of CuCrZr alloy for high-heat-load photon absorber
- Pages: 363-368
- First Published: 08 February 2022
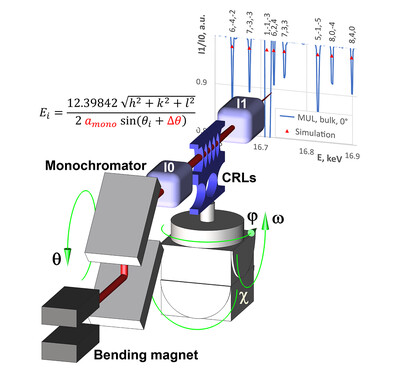
Using diffraction losses of X-rays in a single crystal for determination of its lattice parameters as well as for monochromator calibration
- Pages: 369-376
- First Published: 08 February 2022
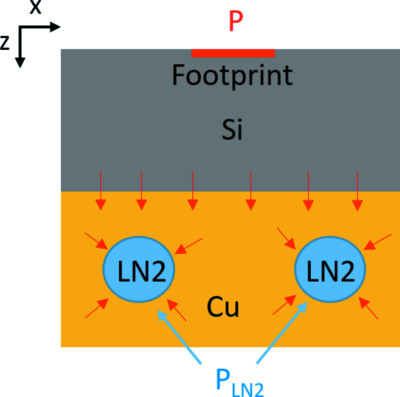
Cryo-cooled silicon crystal monochromators: a study of power load, temperature and deformation
- Pages: 377-385
- First Published: 08 February 2022
Trapezoid-kinoform zone plate lens – a solution for efficient focusing in hard X-ray optics
- Pages: 386-392
- First Published: 15 February 2022
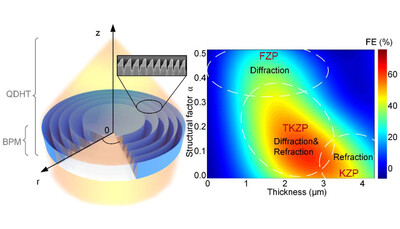
A new theoretical approach for computing the focusing performance of X-ray optics with circularly symmetry shape was developed. Greyscale electron beam lithography was applied to generate 3D kinoform zones in Au for hard X-rays for the first time. The novel trapezoid kinoform zone plate lens demonstrates significantly high diffraction efficiency well beyond that of conventional X-ray optics.
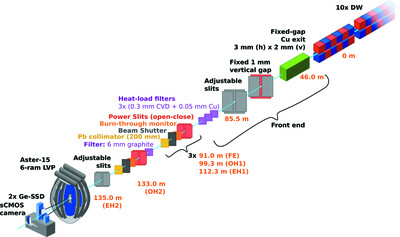
Fast automated energy changes at synchrotron radiation beamlines equipped with transfocator or focusing mirrors
- Pages: 393-399
- First Published: 15 February 2022
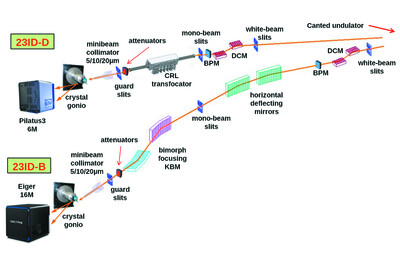
Procedures for fully automated X-ray energy changes at undulator-based synchrotron radiation beamlines with Kirkpatrick–Baez focusing mirrors or a long transfocator consisting of compound refractive lenses are presented. The procedures maintain beam intensity after the monochromator, beam position at the sample, beam attenuation, and the beam focusing distance.
Beamline commissioning for microscopic measurements with ultraviolet and soft X-ray beam at the upgraded beamline BL-13B of the Photon Factory
- Pages: 400-408
- First Published: 16 February 2022
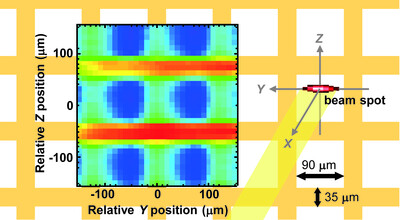
Beamline BL-13B of the Photon Factory and the end-station have been upgraded, enabling microscopic XPS, XAS, and ARPES measurements with a spatial resolution that is comparable with the size of the focused beam. Beam profile evaluation and experimental demonstration of microscopic measurements are presented.
Extreme conditions research using the large-volume press at the P61B endstation, PETRA III
- Pages: 409-423
- First Published: 22 February 2022
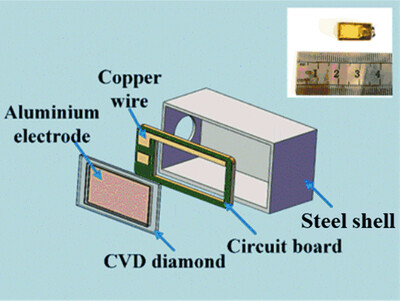
A polycrystalline diamond micro-detector for X-ray absorption fine-structure measurements
- Pages: 424-430
- First Published: 16 February 2022
A cell design for correlative hard X-ray nanoprobe and electron microscopy studies of catalysts under in situ conditions
- Pages: 431-438
- First Published: 15 February 2022
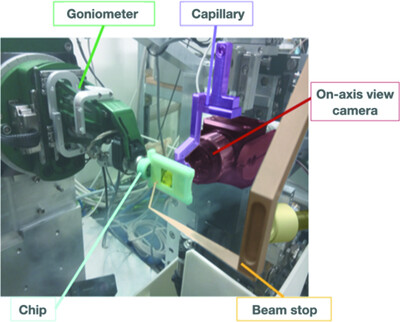
Implementation of wedged-serial protein crystallography at PROXIMA-1
- Pages: 439-446
- First Published: 17 January 2022
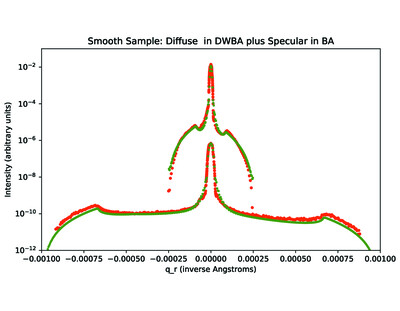
Diffuse X-ray scattering from polished silicon: application of the distorted wave Born approximation
- Pages: 447-455
- First Published: 08 February 2022
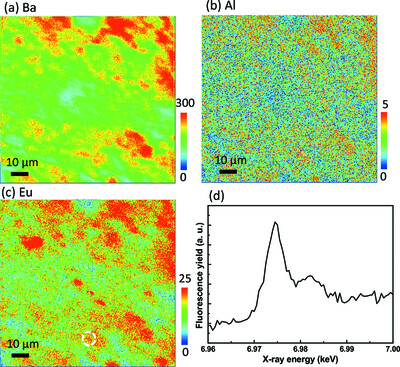
Visualizing the valence states of europium ions in Eu-doped BaAl2O4 using X-ray nanoprobe mapping
- Pages: 456-461
- First Published: 18 January 2022
Wiggler radiation at a low-emittance storage ring and its usage for X-ray absorption spectroscopy
- Pages: 462-469
- First Published: 18 January 2022
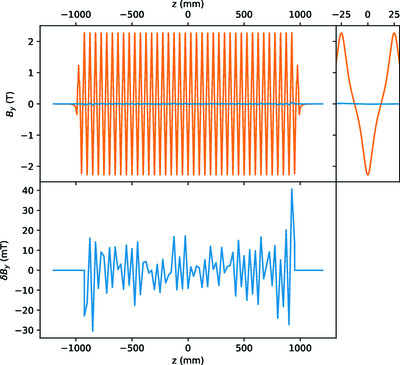
Experimental and computational studies of wigglers on low-emittance storage rings are reported. EXAFS spectra for possible distortions originating from the source imperfection are also examined. It is concluded that wigglers are still an appropriate class of insertion devices, also on low-emittance synchrotrons.
A new route to obtain fluorescence X-ray absorption spectra of compounds and to remove the self-absorption induced nonlinearity in the spectra
- Pages: 470-479
- First Published: 08 February 2022
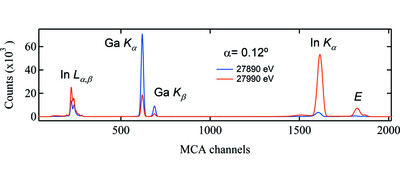
High-speed free-run ptychography at the Australian Synchrotron
- Pages: 480-487
- First Published: 17 January 2022
The implementation of high-speed ptychography on the Australian Synchrotron XFM beamline in presented. It includes a free-run data collection mode where dead time is eliminated and scan time is optimized. This data collection mode is compatible with fast-scanning X-ray fluorescence mapping with extremely high data acquisition rates over large areas, demonstrated at up to 140 µm2 s−1 with 13× spatial resolution enhancement compared with the beam size.
Fast and noise-tolerant determination of the center of rotation in tomography
- Pages: 488-495
- First Published: 19 January 2022
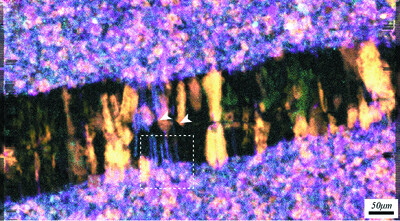
Synchrotron radiation analysis of root dentin: the roles of fluoride and calcium ions in hydroxyapatite remineralization
- Pages: 496-504
- First Published: 19 January 2022
Early root carious lesions require an optimal amount of both free fluoride and calcium ions in the oral environment to initiate a hydroxyapatite remineralization on root dentin. This study elucidates the role of fluoride and calcium to maintain the abundance of hydroxyapatite on acid-challenged root dentin with a novel approach – using synchrotron radiation.
A wide-field micro-computed tomography detector: micron resolution at half-centimetre scale
- Pages: 505-514
- First Published: 19 January 2022
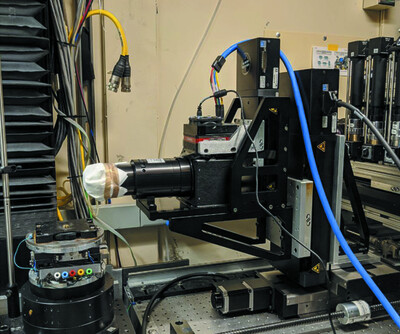
A custom wide-field lens and a new-generation megapixel camera enabled micro-CT scanning over a 3.5 mm × 5 mm field of view at 1 µm resolution/0.5 µm pixel size at Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory's Advanced Light Source and Argonne National Laboratory's Advanced Photon Source using a phantom with micron-scale features. This novel combination of resolution and field of view was designed for broad applicability to any setting in which micron-scale structures need to be characterized comprehensively in three dimensions over mm to cm.
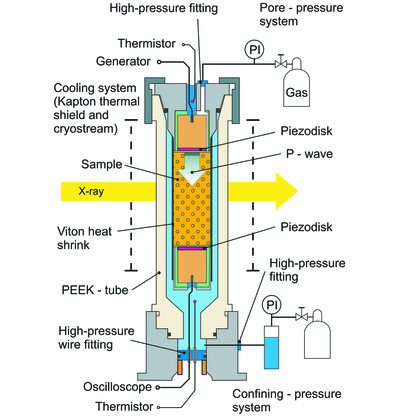
Environmental cell for in situ X-ray synchrotron micro-CT imaging with simultaneous acoustic measurements
- Pages: 515-521
- First Published: 27 January 2022
In situ tomographic study of a 3D-woven SiC/SiC composite part subjected to severe thermo-mechanical loads
- Pages: 522-531
- First Published: 27 January 2022
beamlines
Operational status of the X-ray powder diffraction beamline at the SESAME synchrotron
- Pages: 532-539
- First Published: 17 January 2022
Scanning structural mapping at the Life Science X-ray Scattering Beamline
- Pages: 540-548
- First Published: 17 January 2022
Fully automated measurement system for temperature-dependent X-ray total scattering at beamline BL04B2 at SPring-8
- Pages: 549-554
- First Published: 18 January 2022
A setup for millisecond time-resolved X-ray solution scattering experiments at the CoSAXS beamline at the MAX IV Laboratory
- Pages: 555-562
- First Published: 16 February 2022
I21: an advanced high-resolution resonant inelastic X-ray scattering beamline at Diamond Light Source
- Pages: 563-580
- First Published: 22 February 2022
ID23-2: an automated and high-performance microfocus beamline for macromolecular crystallography at the ESRF
- Pages: 581-590
- First Published: 22 February 2022
obituaries
addenda and errata
Guidelines for de novo phasing using multiple small-wedge data collection. Corrigendum
- Page: 593
- First Published: 15 February 2022
A figure in the article by Baba et al.[(2021), J. Synchrotron Rad.28, 1284–1295] is corrected.
Single-shot experiments at the soft X-FEL FERMI using a back-side-illuminated scientific CMOS detector. Corrigendum
- Page: 594
- First Published: 15 February 2022
The article by Léveillé et al.[(2022), J. Synchrotron Rad.29, 103–110] is corrected.