Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
FRONT COVER
Front Cover
- First Published: 31 March 2025

The cover image illustrates the molecular structure of GA+PhOH deep eutectic solvents (DESs) with multiple active sites, and highlights their exceptional selectivity in recognizing and capturing NH3 from the outlet gas mixture (NH3/N2/H2) in the ammonia synthesis industry. It demonstrates their potential for efficient gas separation and industrial applications in synthetic ammonia processes.
BACK COVER
Back Cover
- First Published: 31 March 2025

Fluorescent probes have become essential tools for real-time, non-destructive imaging of cell membrane microdomains, deformation, and fusion. The inherent fluidity of the cell membrane, composed of self-assembled phospholipids, underlies key processes such as adhesion, migration, phagocytosis, and signal transduction. This review summarizes recent advancements in probe design and provides insights into future research directions for understanding membrane dynamics and related therapeutic developments.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Fluorescent probes for the visualization of membrane microdomain, deformation, and fusion
- First Published: 30 December 2024
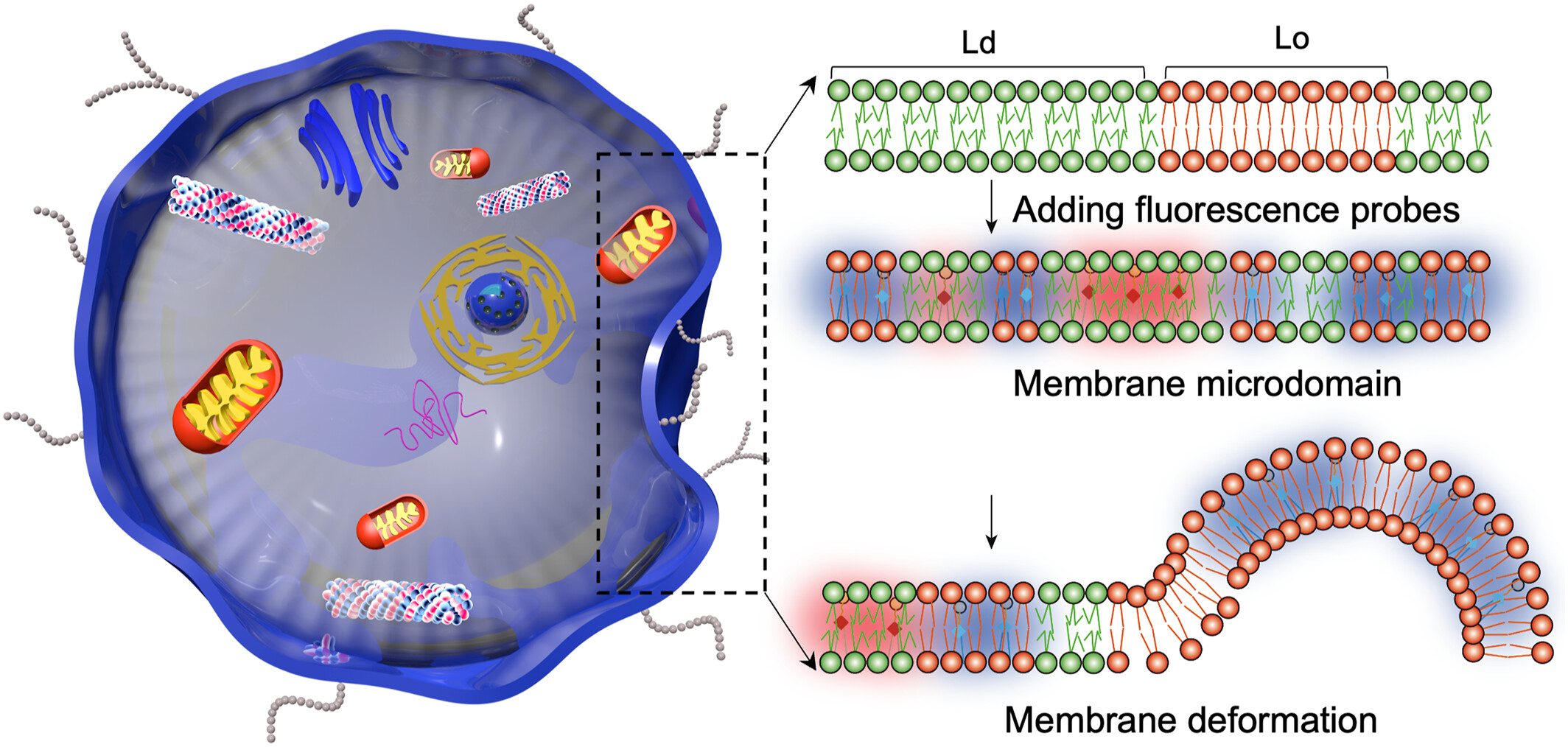
Fluorescent probes have emerged as vital tools to image the microdomains of cell membranes and explore more complex processes such as membrane fusion and fission. This review systematically summarizes the latest advancements in the application of fluorescent probes for cell membrane imaging, aiming to our understanding of the mechanisms underlying membrane dissociation, reorganization, fusion, and separation, and fostering research and therapeutic development for membrane-associated diseases.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The controllable of BODIPY dimers without installing blocking groups as both fluorescence and singlet oxygen generators
- First Published: 21 July 2024
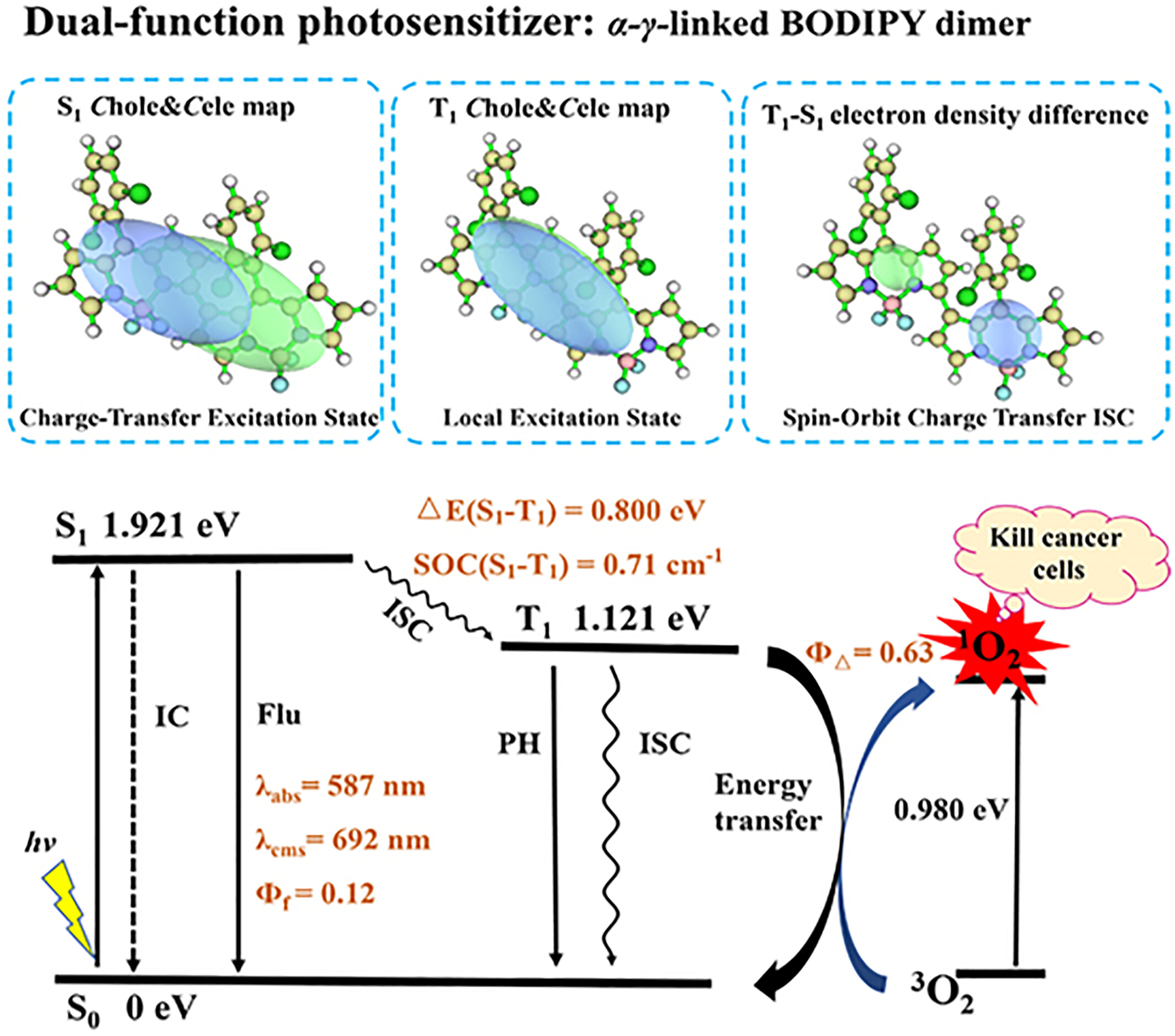
The dihedral angle between the two BODIPY units in the T1 state significantly influences intersystem crossing process in BODIPY dimers. The α-γ-linked BODIPY dimer exhibits notable charge transfer during the S1→T1 transition, corresponding to a transition from the 1CT to 3LE state, driven by the SOCT-ISC mechanism. With large SOC, low energy gap Es1t1, and strong conjugation, the α-γ-linked BODIPY dimer can significantly promote the generation of singlet oxygen and long-wavelength fluorescence.
Facile preparation of alkali metal-modified hollow nanotubular manganese-based oxide catalysts and their excellent catalytic soot combustion performance
- First Published: 15 July 2024
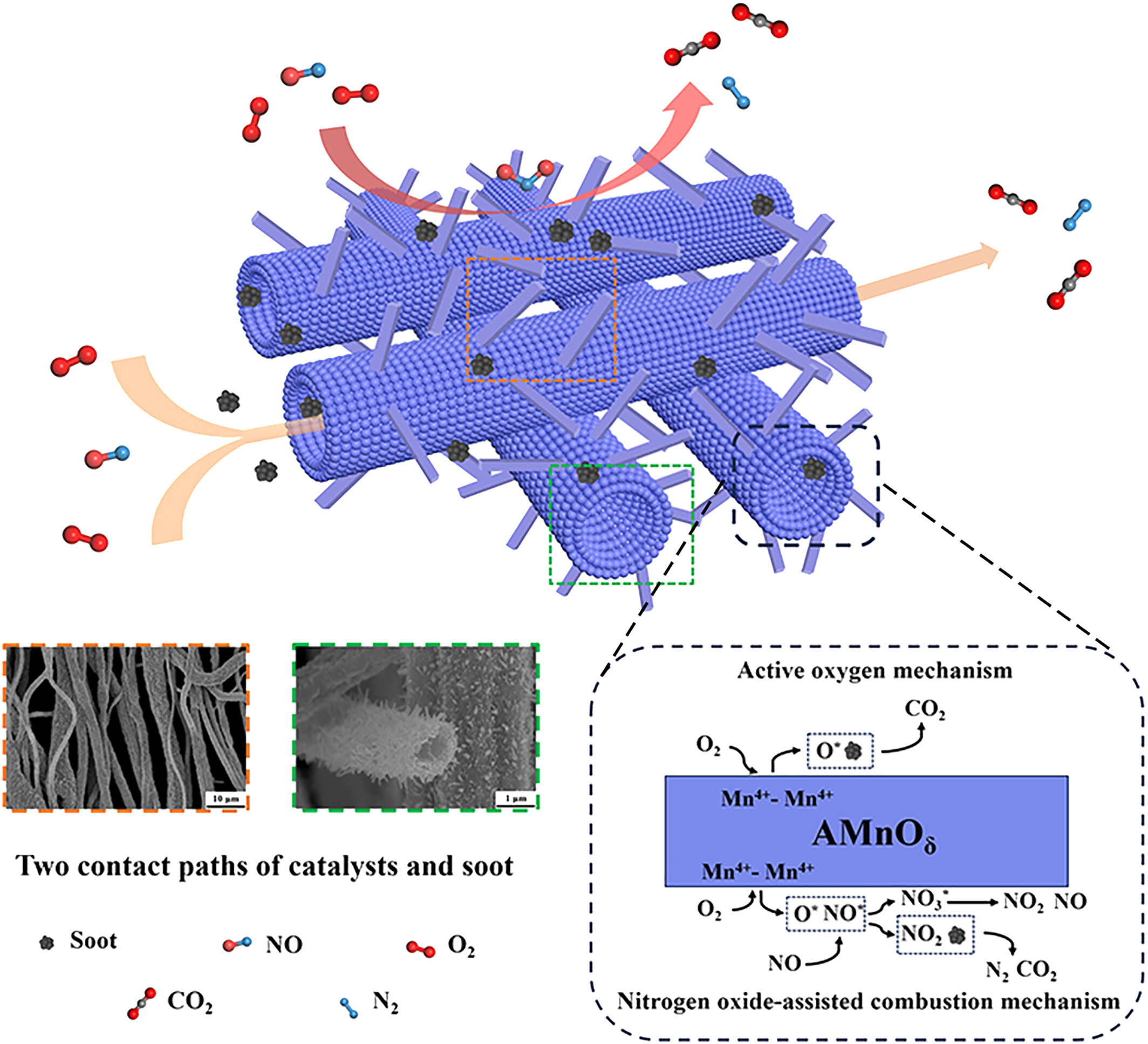
A series of alkali metal-modified hollow nanotubular Mn-based oxide catalysts with a special structure were prepared using centrifugal spinning. The prepared catalysts show excellent catalytic performance in catalytic soot combustion through active oxygen mechanism and nitrogen oxide-assisted combustion mechanism, and have the potential for industrial practical application.
Unveiling the unexpected sinking and embedding dynamics of surface supported Mo/S clusters on 2D MoS2 with active machine learning
- First Published: 08 August 2024
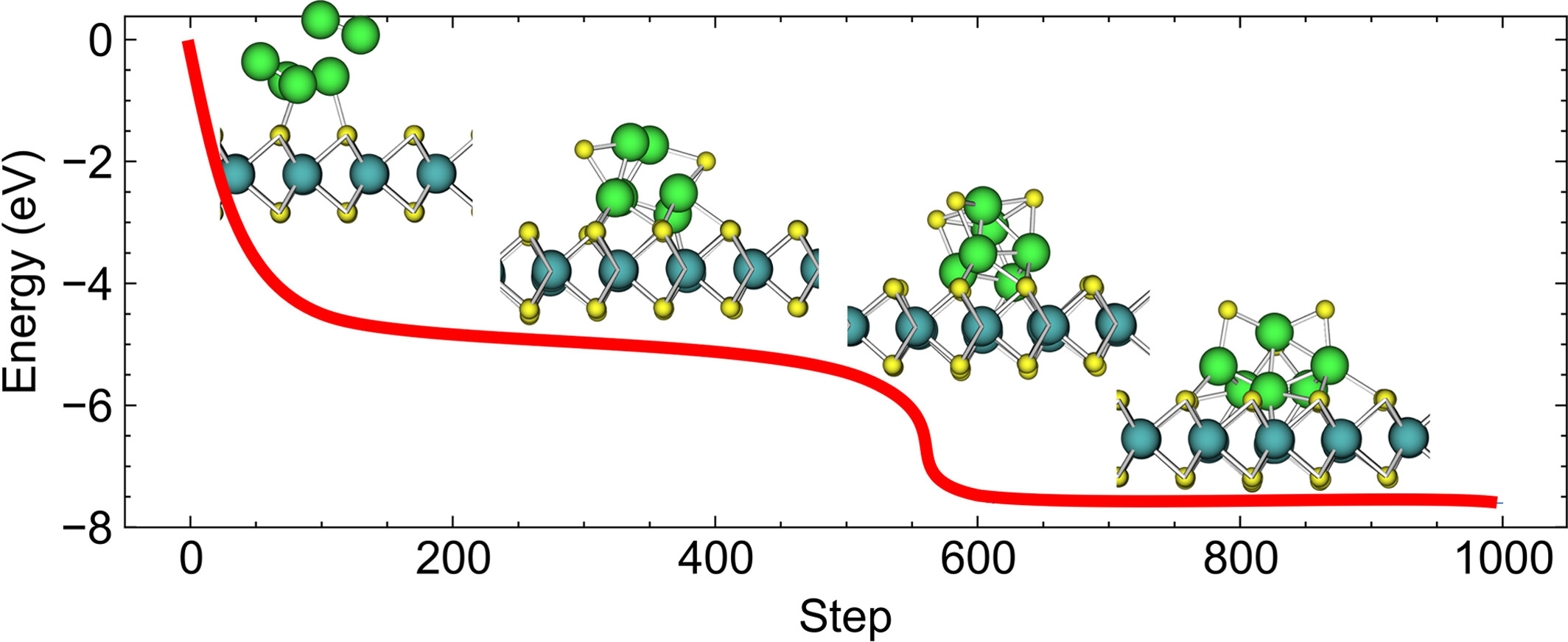
By employing active machine learning potential into Monte Carlo simulations, we interestingly disclosed that Mo clusters always sink and embed themselves in MoS2 layers. In contrast, S clusters float on perfect surfaces. On the defective surface, a few S atoms fill the vacancy and rest S clusters float on the top. Such significant structural reconstructions should be carefully taken into account.
Visual detection of anti-icing fluids freezing by a low-temperature viscosity-sensitive aggregation-induced emission probe
- First Published: 27 August 2024
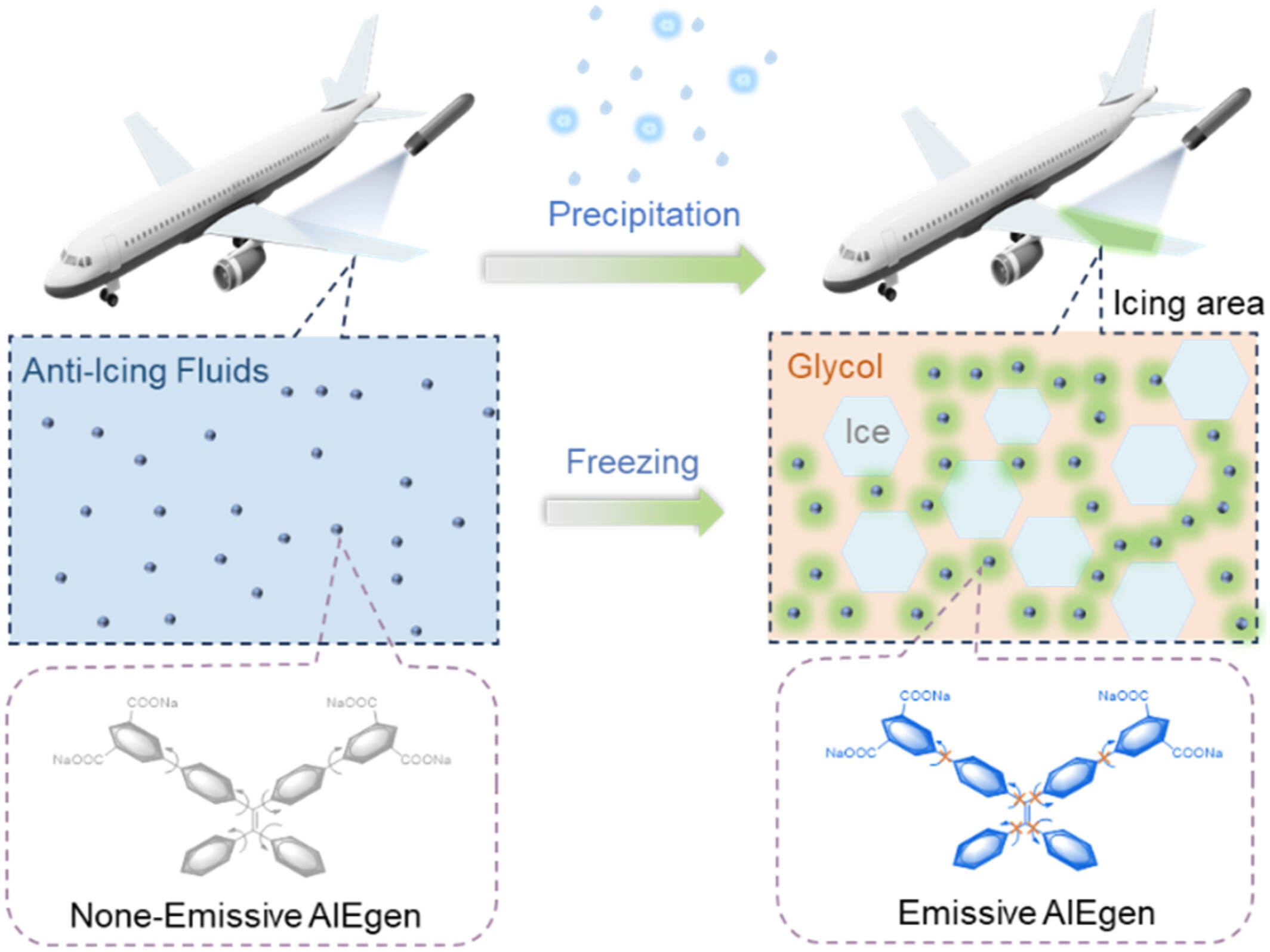
In this study, we designed a low-temperature viscosity-sensitive AIE probe called TPE-2B4C for visual monitoring ice formation in anti-icing liquids. This probe can dissolve in anti-icing fluids and exhibit no fluorescent background signal even at low temperatures. After freezing, TPE-2B4C molecules move from the water phase to higher viscosity ethylene glycol, leading to an obvious increase in green fluorescence signal.
Ru@NiMoS aggregate with boosted electrochemical catalysis for enhanced electrochemiluminescence and lidocaine detection
- First Published: 11 September 2024
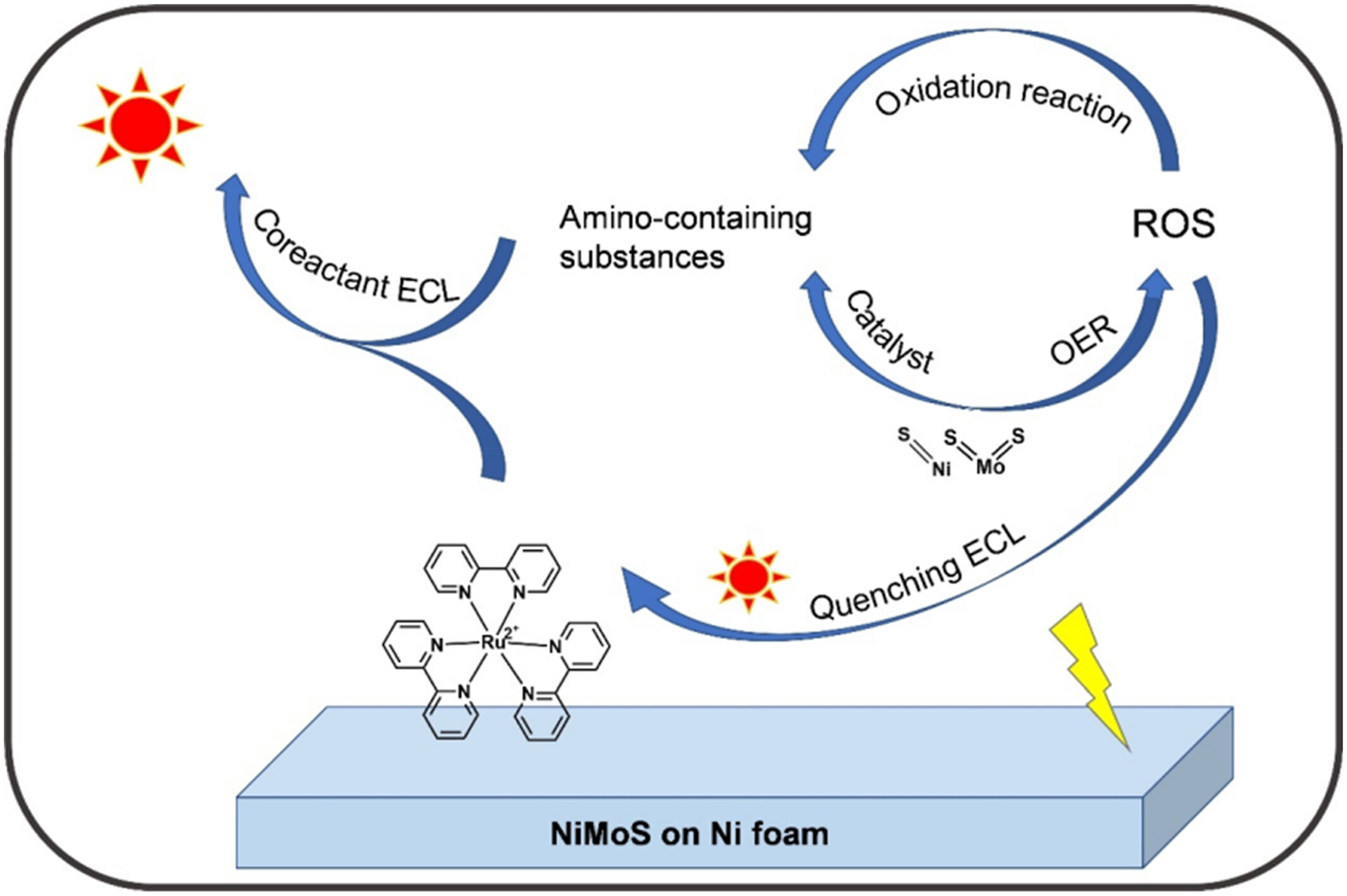
A binder-free Ru@NiMoS electrode was engineered by in situ growth of two-dimensional NiMoS nanosheets on nickel foam. This process effectively promoted the electrostatic-driven aggregation of Ru(bpy)32+, harnessing the synergistic effect to enhance electrochemiluminescence (ECL) performance. The integration (Ru@NiMoS) achieved an impressive ECL efficiency of 70.1%, marking an impressive 36.9-fold enhancement over conventional Ru. Additionally, its ECL intensity was found to be remarkably 172.2 times greater than that of Ru. Within the Ru(bpy)32+/TPA system, NiMoS emerged as a pivotal electrochemical catalyst, markedly boosting both the oxygen evolution reaction and the generation of reactive intermediates. Leveraging these distinctive properties, a highly efficient ECL sensor for lidocaine detection was developed. This sensor exhibited a linear response within the concentration range of 1 nM to 1 μM and achieved a remarkably low detection limit of 0.22 nM, underlining its substantial potential for practical application.
Nile red-based AIEgen for highly fluorescent polymer particles and its application in light-scattering fluorescent films
- First Published: 28 September 2024
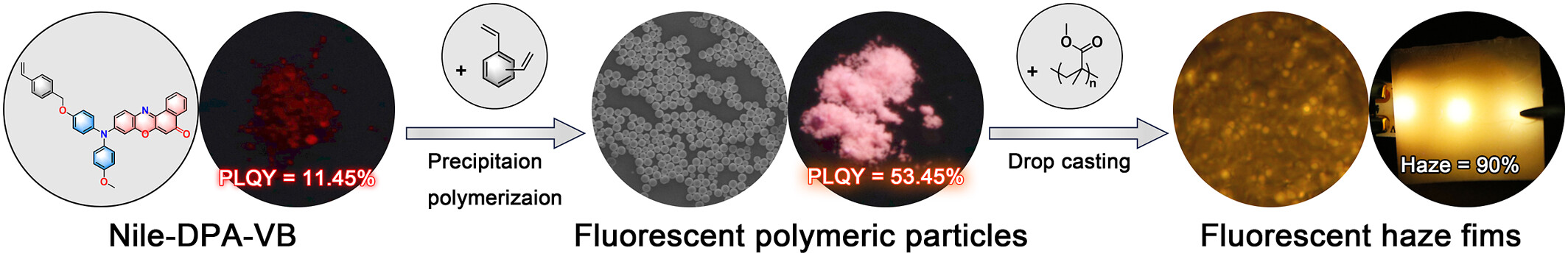
Based on Nile red, an AIEgen of Nile-DPA-VB was synthesized, exhibiting the high-efficiency solid-state luminescence. The luminescence was further promoted by aggregation microenvironment manipulation through taking Nile-DPA-VB as the monomer for precipitation polymerization. Thus, highly fluorescent polymer particles based on the AIE-active Nile red derivative were harvested, demonstrating their promising application in functional film.
Rational design of deep eutectic solvents with low viscosities and multiple active sites for efficient recognition and selective capture of NH3
- First Published: 05 January 2025
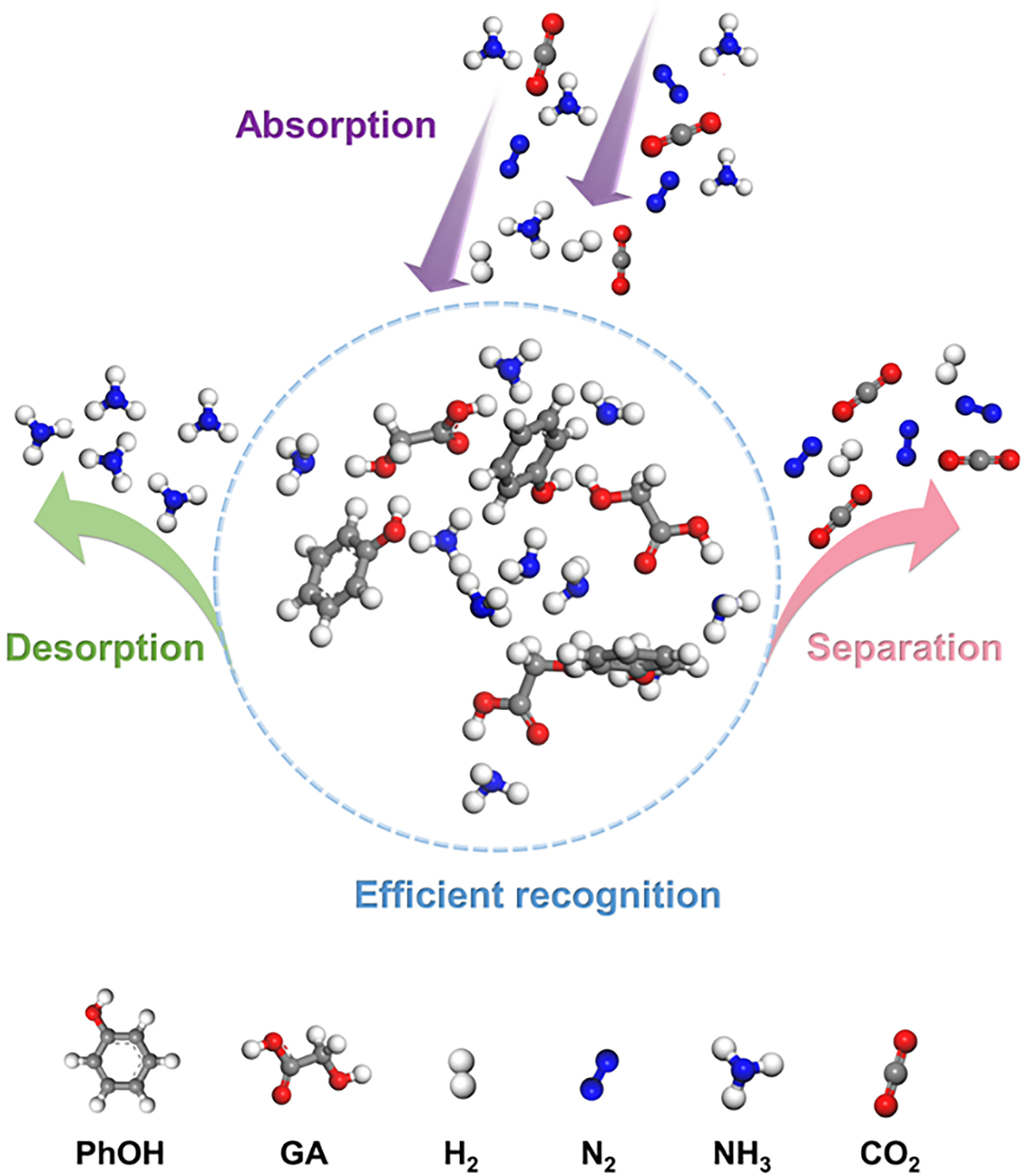
A class of GA + PhOH DESs with multiple active sites and low viscosities were prepared. GA + PhOH DESs exhibited extremely fast NH3 absorption rates, high NH3 solubilities, good regeneration performance and efficient recognition of NH3 from CO2, N2 and H2 in mixed gases. The selectivity of NH3/CO2 is higher than that of the majority of ILs and DESs.
A COVID-19 rapid antigen test employing upconversion nanoparticles
- First Published: 05 January 2025
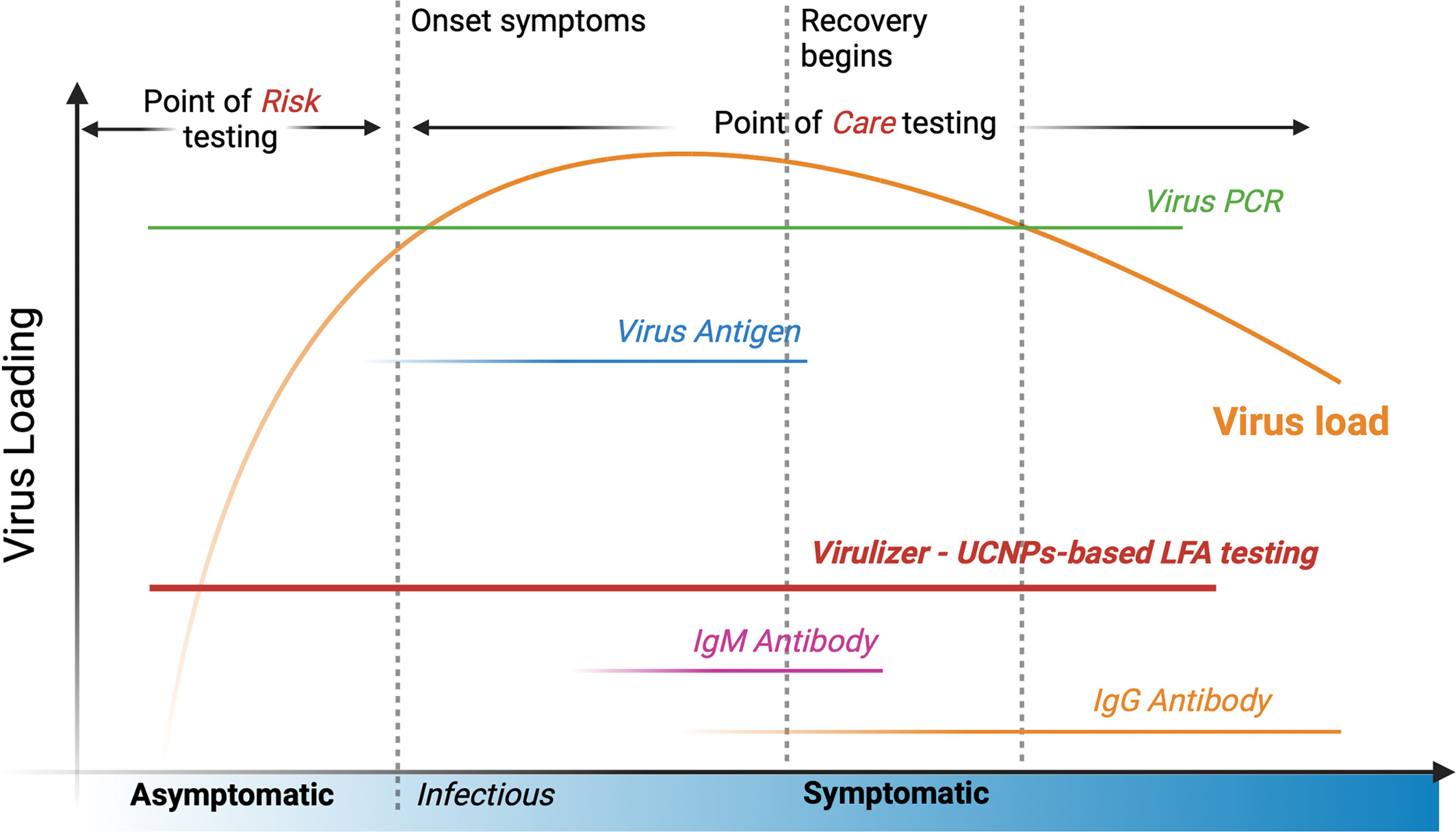
Current RAT strips suffer from low sensitivity and are ineffective at detecting infections when viral loads are low, which limits early detection capabilities. The development of highly doped UCNPs-based LFA testing (Virulizer) significantly improves detection sensitivity to identify infections at the onset of infectiousness rather than the onset of symptoms. Its ability to screen early-stage infections far surpasses that of traditional viral antigen and antibody tests, with sensitivity and accuracy comparable to PCR testing.
Development of a novel Cu (I) π-complexation adsorbent for ultra-deep desulfurization from a carbon dioxide stream
- First Published: 04 January 2025
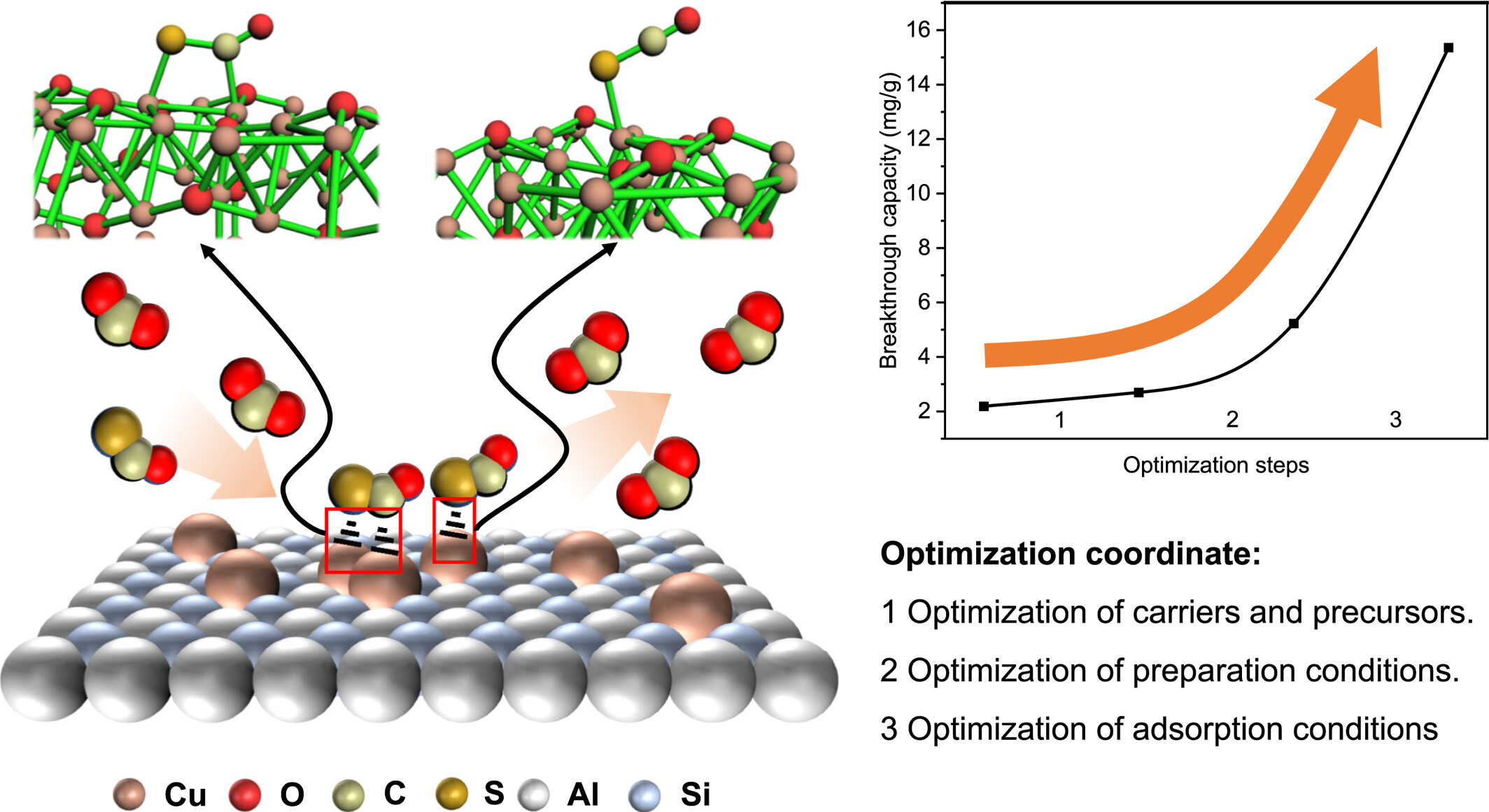
The left side of this graphic illustrates the mechanism by which the newly synthesized Cu(I)-based adsorbent absorbs carbonyl sulfide (COS). Cu atoms supported on ZSM-5 can selectively absorb COS from a mixture gas stream flowing without adsorbing carbon dioxide. The S atom in COS can form a chemical bond, or alternatively, both the S and C atoms can simultaneously form chemical bonds with two adjacent Cu atoms. While the right side illustrates the increase in breakthrough capacity corresponding to each optimization step.
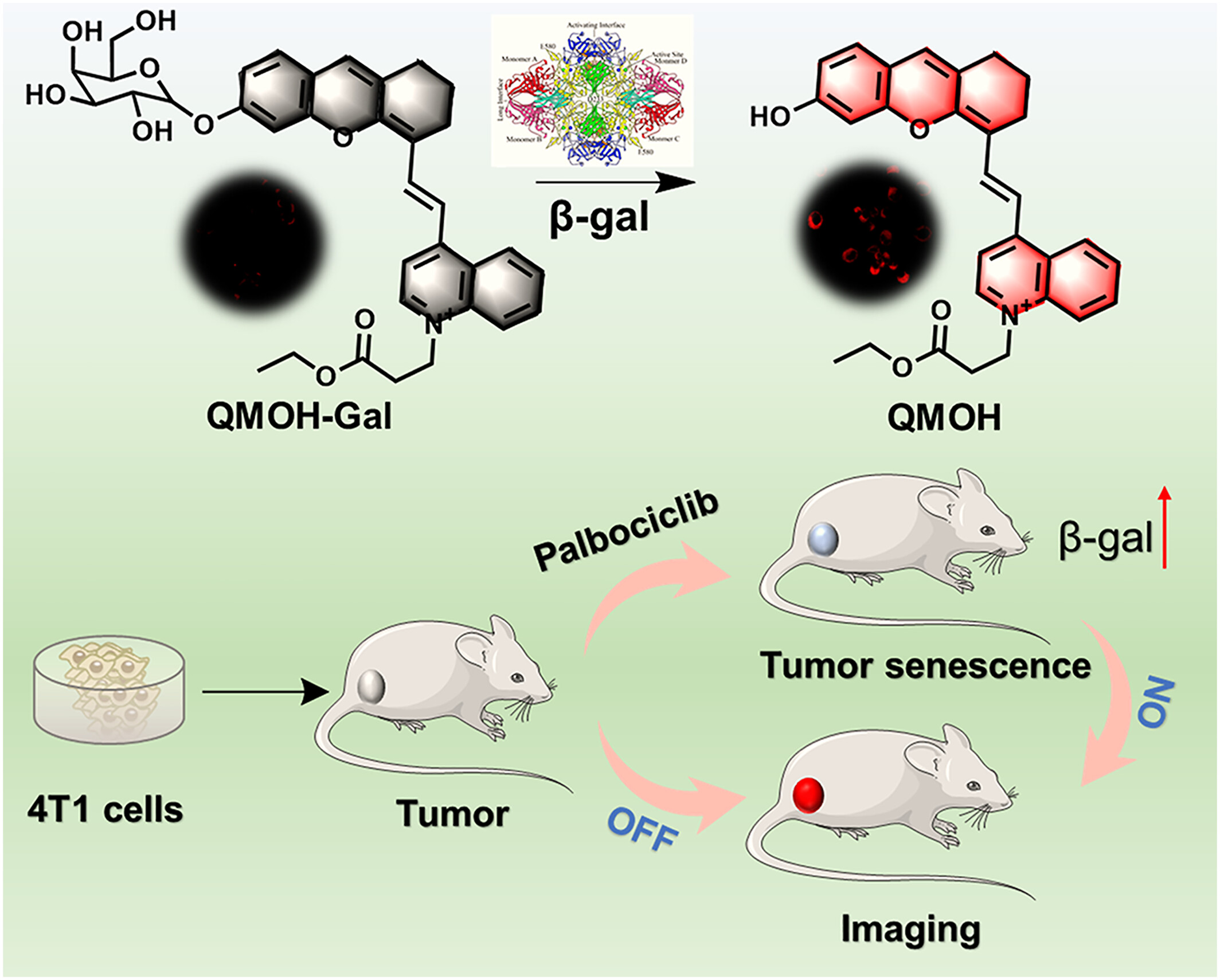
A β-galactosidase activated near-infrared fluorescent probe for tracking cellular senescence in vitro and in vivo
- First Published: 05 January 2025