Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
The effects of extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes polymorphisms on intervertebral disc degeneration
- First Published: 20 November 2024
Understanding the genetic variations of genes can predict which individuals have a higher probability of developing IDD, enabling earlier prevention. Currently, there is a lack of systematic integration regarding the acellular matrix degradation enzyme polymorphism in IDD. A notable correlation between the MMP-9 rs17576 mutation and an elevated susceptibility to disc degeneration.
Targeting nucleus pulposus cell death in the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration
- First Published: 18 December 2024
pH: A major player in degenerative intervertebral disks
- First Published: 18 December 2024
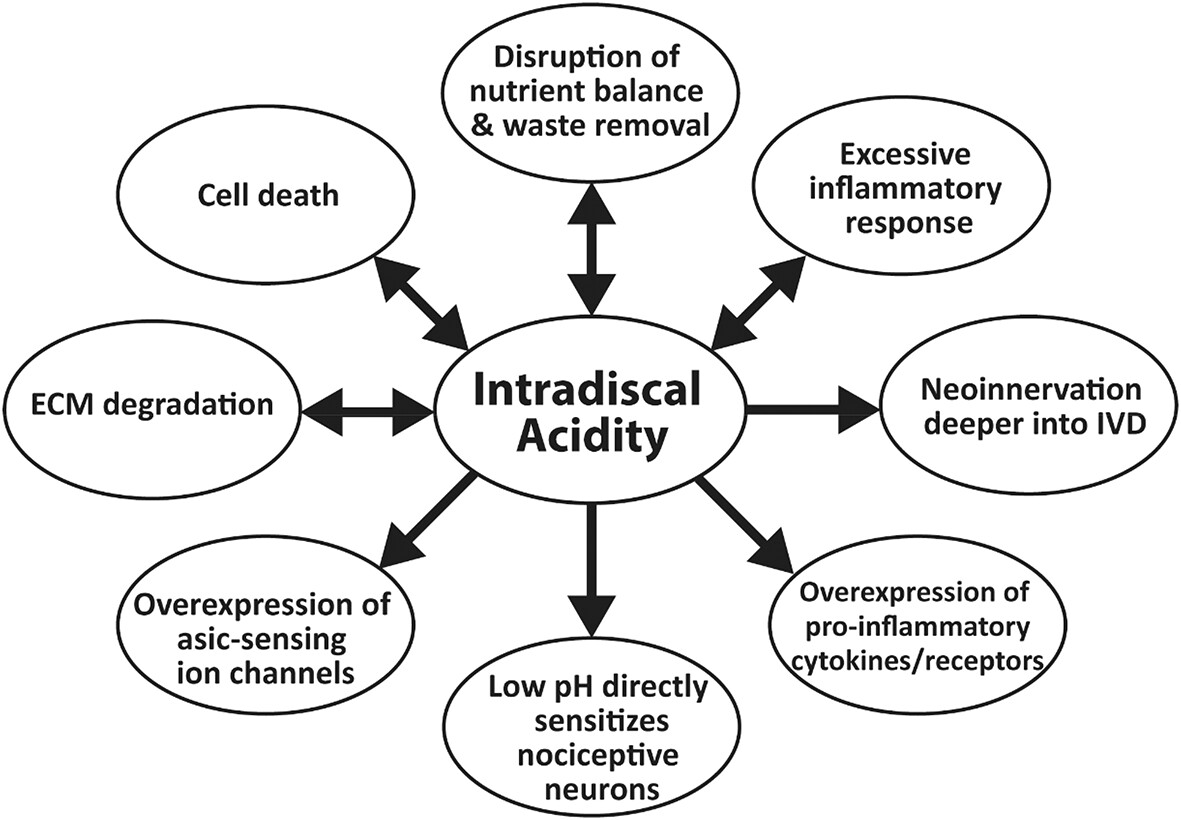
Chronic lower back pain, often caused by degenerative disk disease (DDD), is a major global health issue with significant socioeconomic impact. Although the relationship between disk degeneration and pain is well-established, the role of low pH in contributing to pain has been underexplored. This review examines how hyperacidity in DDD affects the intervertebral disk, potentially contributing to pain through mechanisms like cell catabolism, neoinnervation, and inflammation, and emphasizes the need for further research to better understand these processes and improve treatment options.
How to improve the mechanical safety of a novel spinal implant while saving costs and time
- First Published: 25 December 2024
This manuscript shows how the scientific literature can be used to proof that a novel spinal implant meets all necessary safety and performance standards for clinical application. The scientific literature has gained more and more importance for this purpose over the last few years, but still a structured approach from literature to implant approval has not yet been described anywhere so far. This work aims to close the gap between science and practical application in this field.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Inactivation of Tnf-α/Tnfr signaling attenuates progression of intervertebral disc degeneration in mice
- First Published: 08 October 2024
Gut microbiome dysbiosis is associated with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis in symptomatic patients
- First Published: 10 October 2024
This study is the “first” to report a significant association of gut microbiome dysbiosis and the association with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis in symptomatic patients, noting pro-inflammatory bacterial taxa. This work provides a foundation for future work addressing the role of the gut microbiome in association with spine health and disease.
Identifying critical modules and biomarkers of intervertebral disc degeneration by using weighted gene co-expression network
- First Published: 18 October 2024
A novel spine tester TO GO
- First Published: 27 October 2024
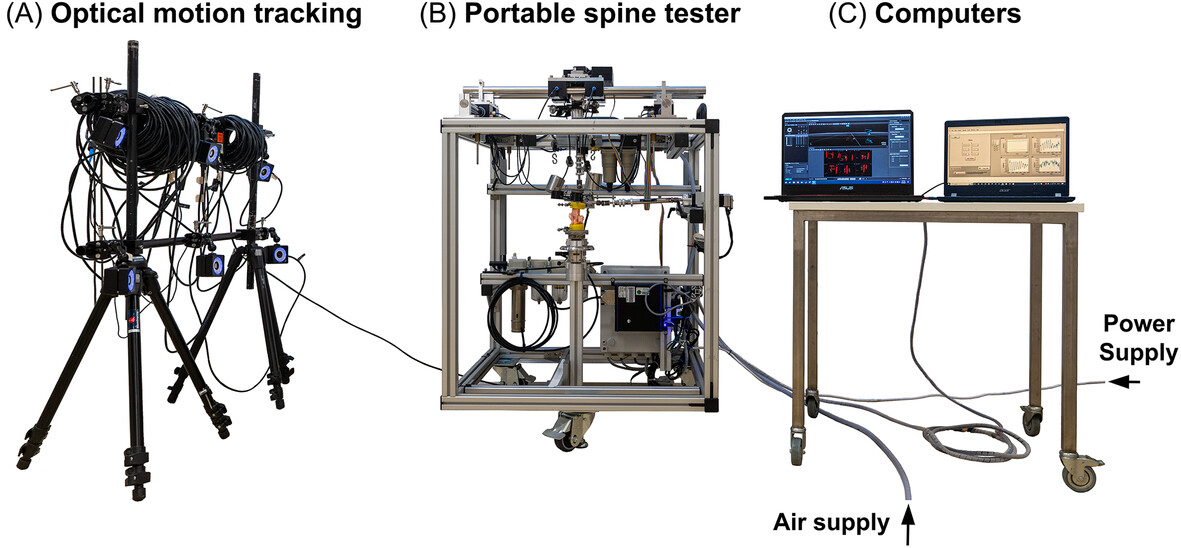
Biomechanical testing after spinal animal experiments is often neglected because testing machines for flexibility measurement are large and difficult to transport, and the same specimen can only be used ex vivo for either biomechanics or biology. With the help of a new portable spine tester, the same specimen can be used for both biological and biomechanical testing, avoiding additional animals and improving the 3R principle. The machine has been validated for future use in any lab all over the world.
Finite element analysis of two-level discontinuous cervical hybrid revision surgery strategy to reduce biomechanical responses of adjacent segments
- First Published: 31 October 2024
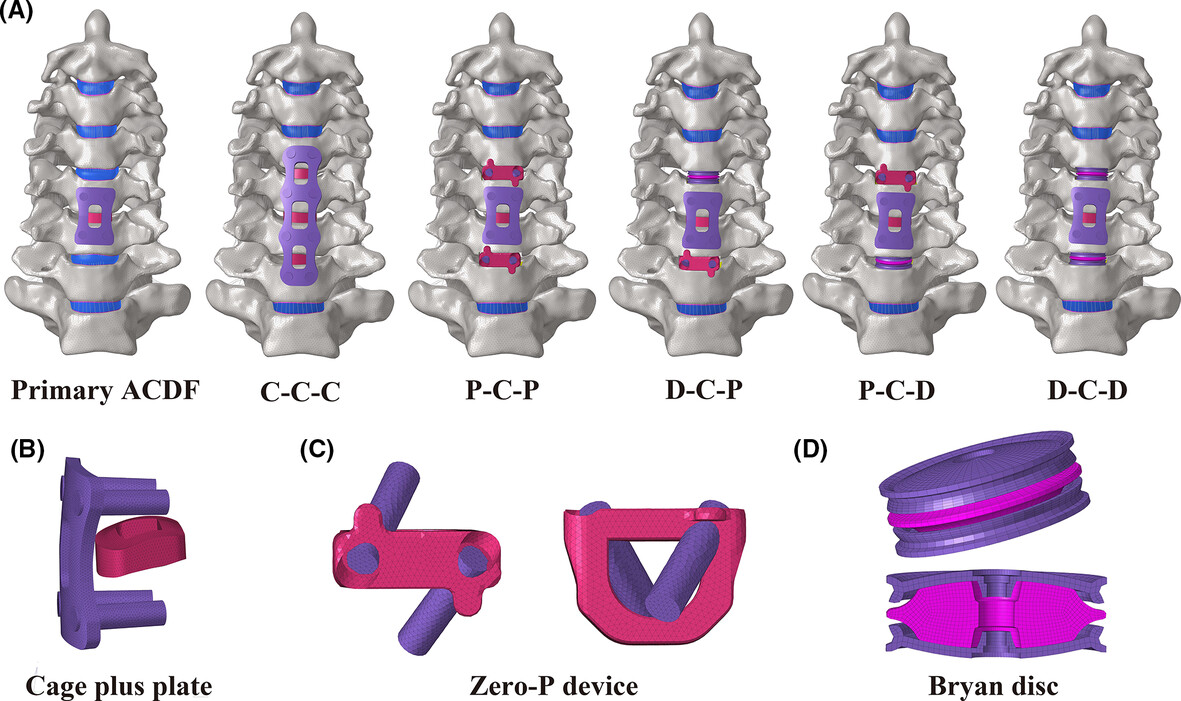
This finite element study Innovatively investigated the biomechanical characteristics of hybrid surgery to treat two-level discontinuous ASD in ACDF revision surgery. The results indicated that D-C-D, P-C-D, and D-C-P are good revision surgery choices on reducing the biomechanical responses, and D-C-D was the best choice. P-C-P can be the best recommendation when it does not meet the CDA indications.
The proteomic landscape of extracellular vesicles derived from human intervertebral disc cells
- First Published: 05 November 2024
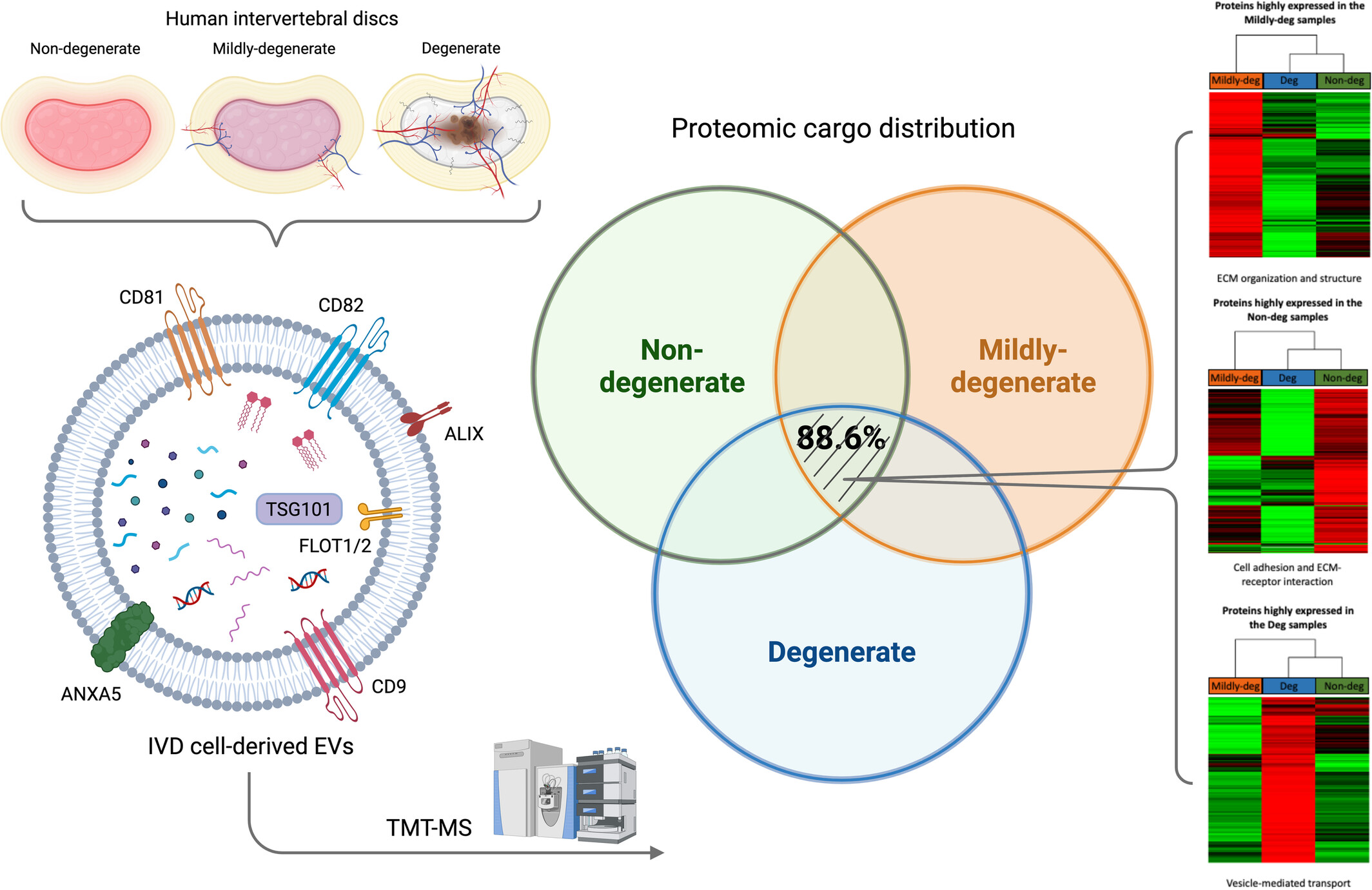
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from human intervertebral disc cells present markers CD9, CD81, CD82, ALIX, FLOT1/2, TSG101, and ANXA5 with differential expression levels linked to the degenerative grade of the tissue. The proteomic cargo is majorly shared but the expression levels vary with degeneration grade. The differentially expressed proteins are associated with (1) cell adhesion and ECM–receptor interaction, (2) ECM organization and structure, and (3) vesicle-mediated transport in the non-, mildly-, and degenerate samples, respectively.
Melatonin attenuates degenerative disc degression by downregulating DLX5 via the TGF/Smad2/3 pathway in nucleus pulposus cells
- First Published: 13 November 2024
Preclinical development and characterisation of PP353, a formulation of linezolid for intradiscal administration
- First Published: 14 November 2024
Preclinical development and characterization of a linezolid formulation for percutaneous intradiscal administration to treat chronic low back pain associated with Modic changes type 1. In vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo studies demonstrate that a suspension of micronized linezolid is suitable for intradiscal administration, is efficacious in a sheep model of intradiscal bacterial infection, and is well tolerated.
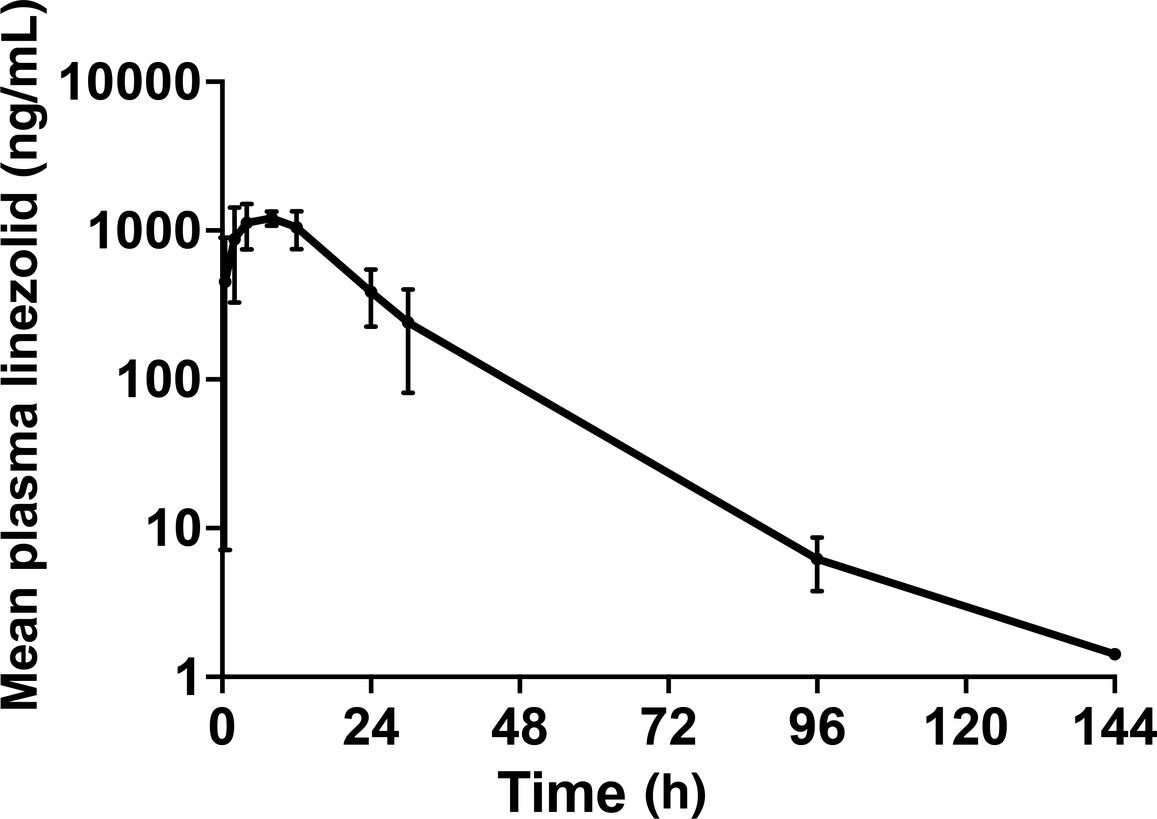
Pharmacokinetics of PP353, a formulation of linezolid for intervertebral disc administration, in patients with chronic low back pain and Modic change Type 1: A first-in-human, Phase 1b, open-label, single-dose study
- First Published: 14 November 2024
Effect of cigarette smoke exposure and cessation on regional diffusion properties in rat intervertebral discs
- First Published: 14 November 2024
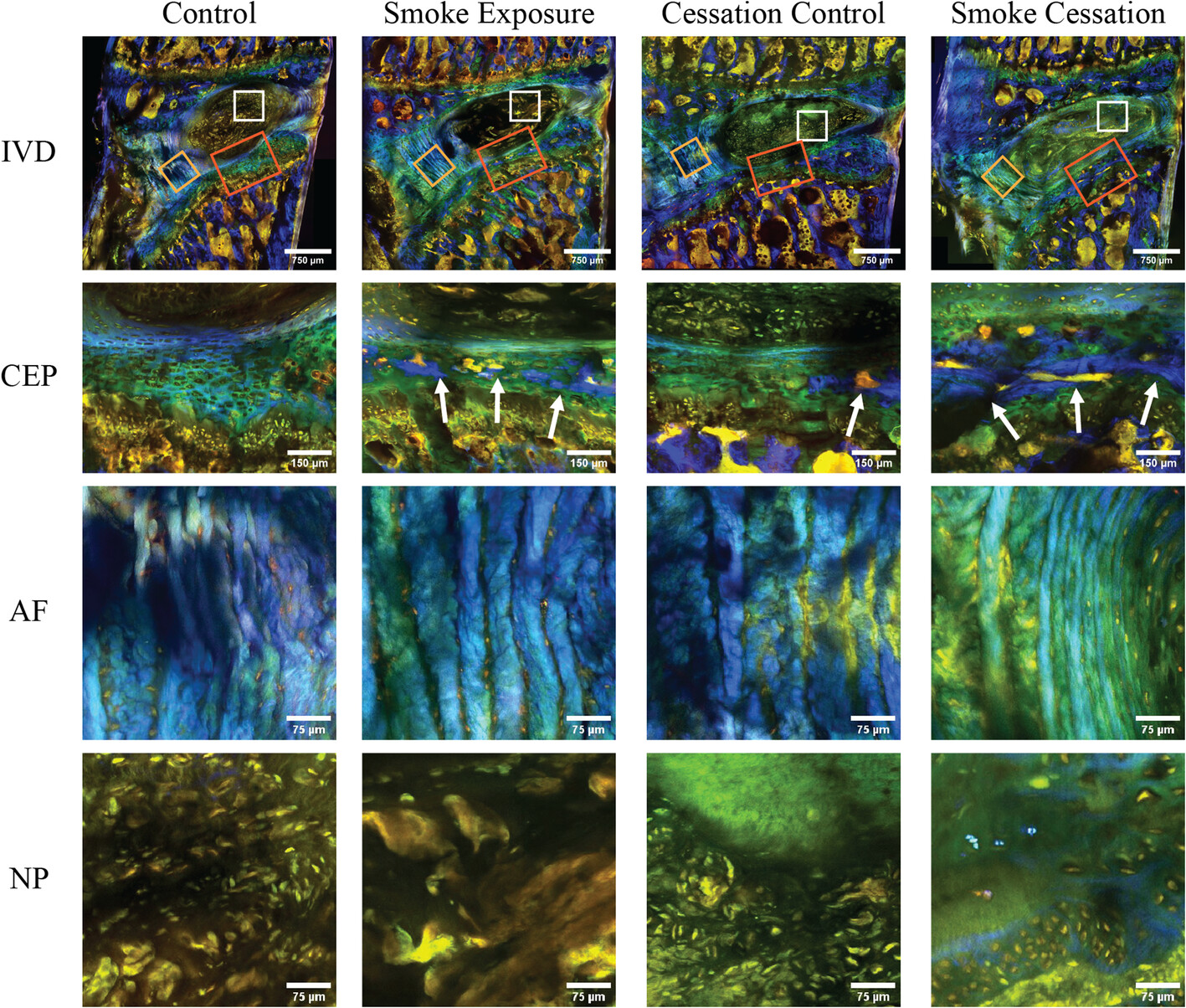
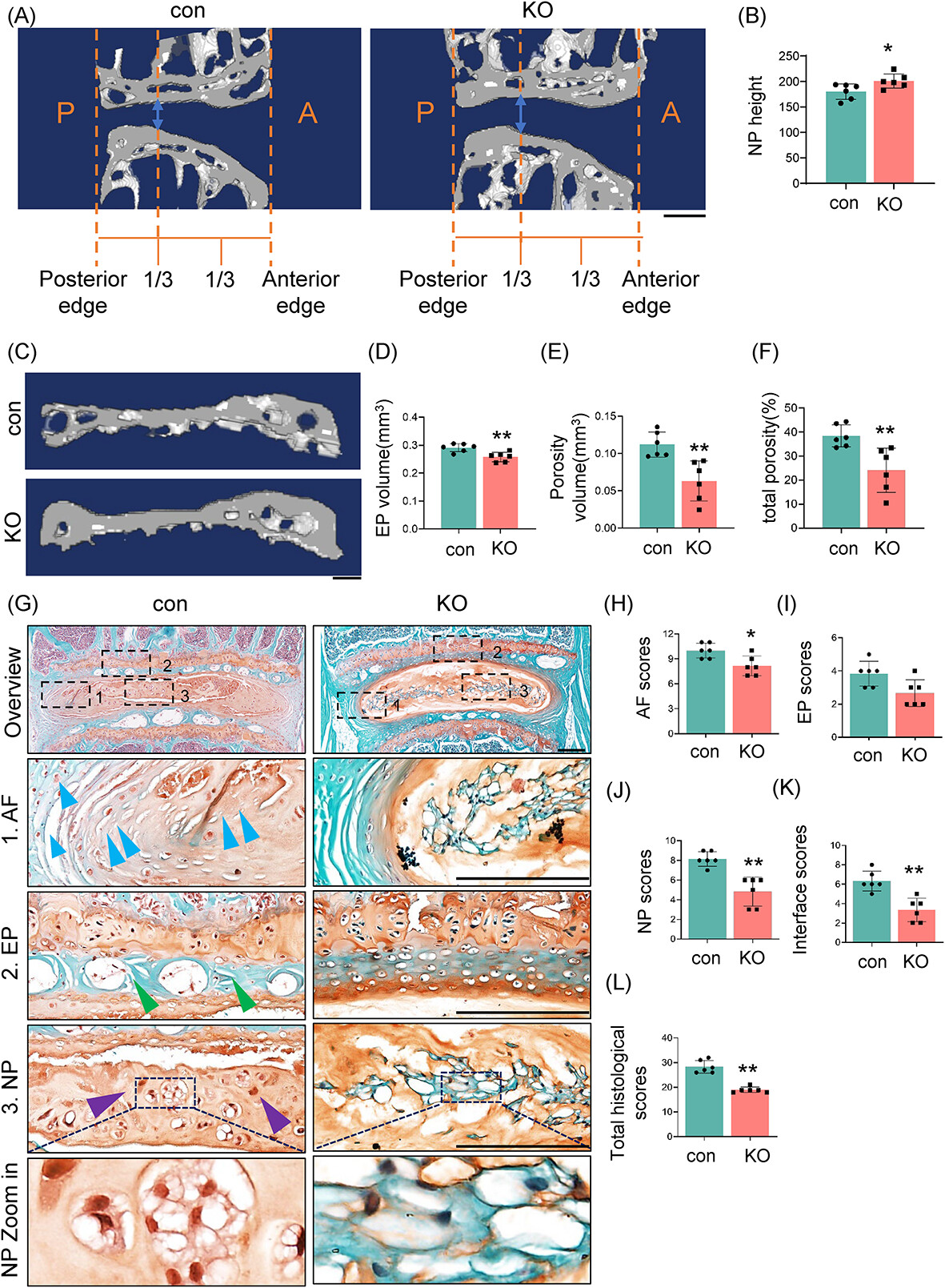
The spatial–temporal remodeling progression of the intervertebral disc in the context of cigarette smoke exposure and smoking cessation remains unclear. This study established a smoke exposure Sprague–Dawley rat model to quantify solute diffusivity and tissue porosity regionally, and to characterize disc morphologic structure. It demonstrated that 2 months of smoke exposure led to regional intervertebral disc remodeling, as evidenced by altered structural composition and solute diffusion properties, particularly in the cartilage endplate region, and that smoke cessation failed to reverse the detrimental impact of smoke exposure.
Distinct clinical characteristics of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with asymmetrical ESR1 expression in paraspinal muscle progenitor cells
- First Published: 26 November 2024
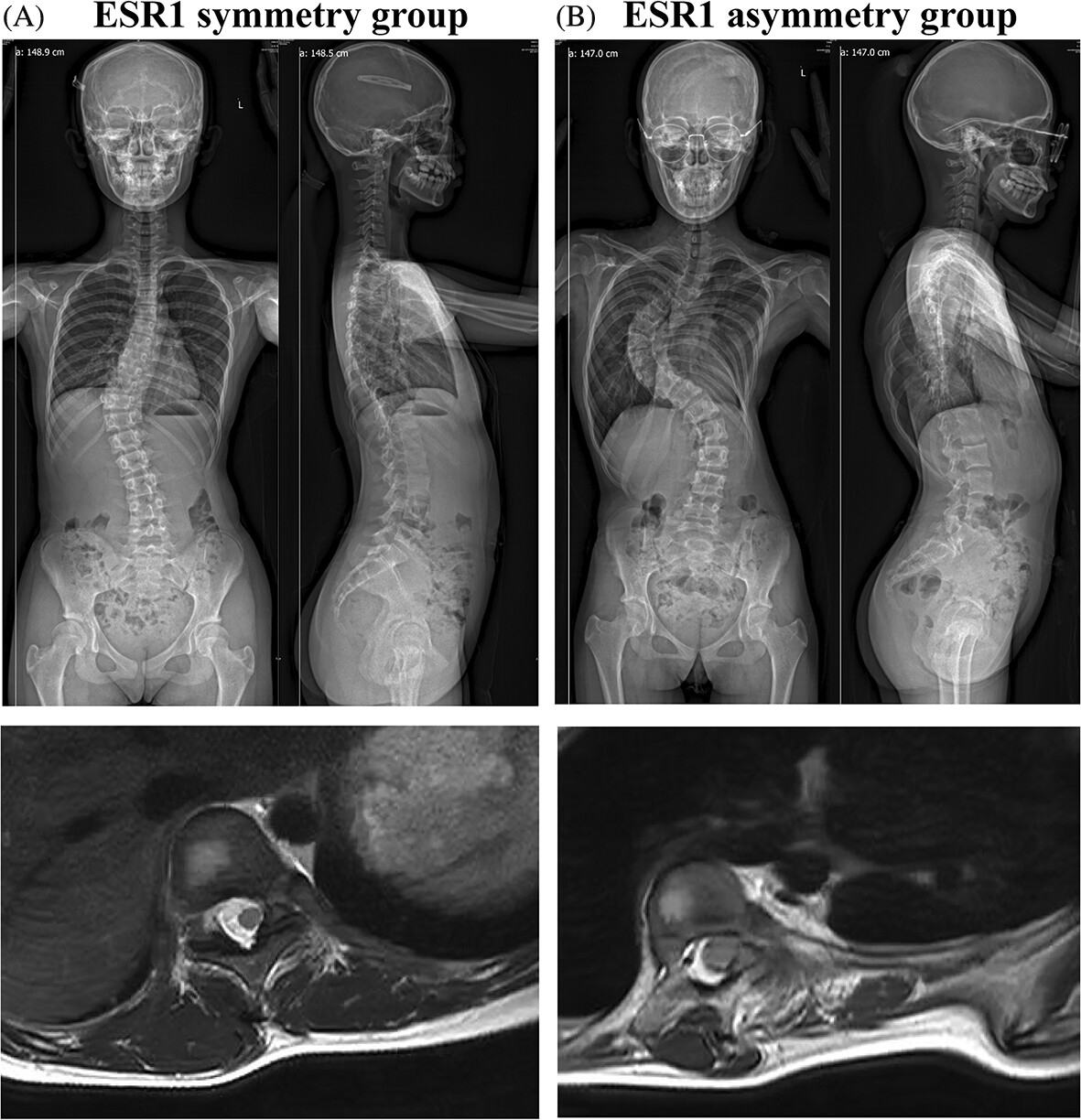
Clinical characteristics of AIS with asymmetrical ESR1 expression in paraspinal muscle progenitor cells were investigated. There were 48% AIS patients with significantly decreased ESR1 expression in concave paraspinal muscle progenitor cells, while asymmetrical ESR1 expression was correlated with asymmetrical paraspinal muscle CSA, asymmetrical fatty infiltration, and more severe scoliotic deformity.
Clinical efficacy and biomechanical analysis of a novel hollow pedicle screw combined with kyphoplasty for the treatment of Kümmell disease
- First Published: 06 December 2024
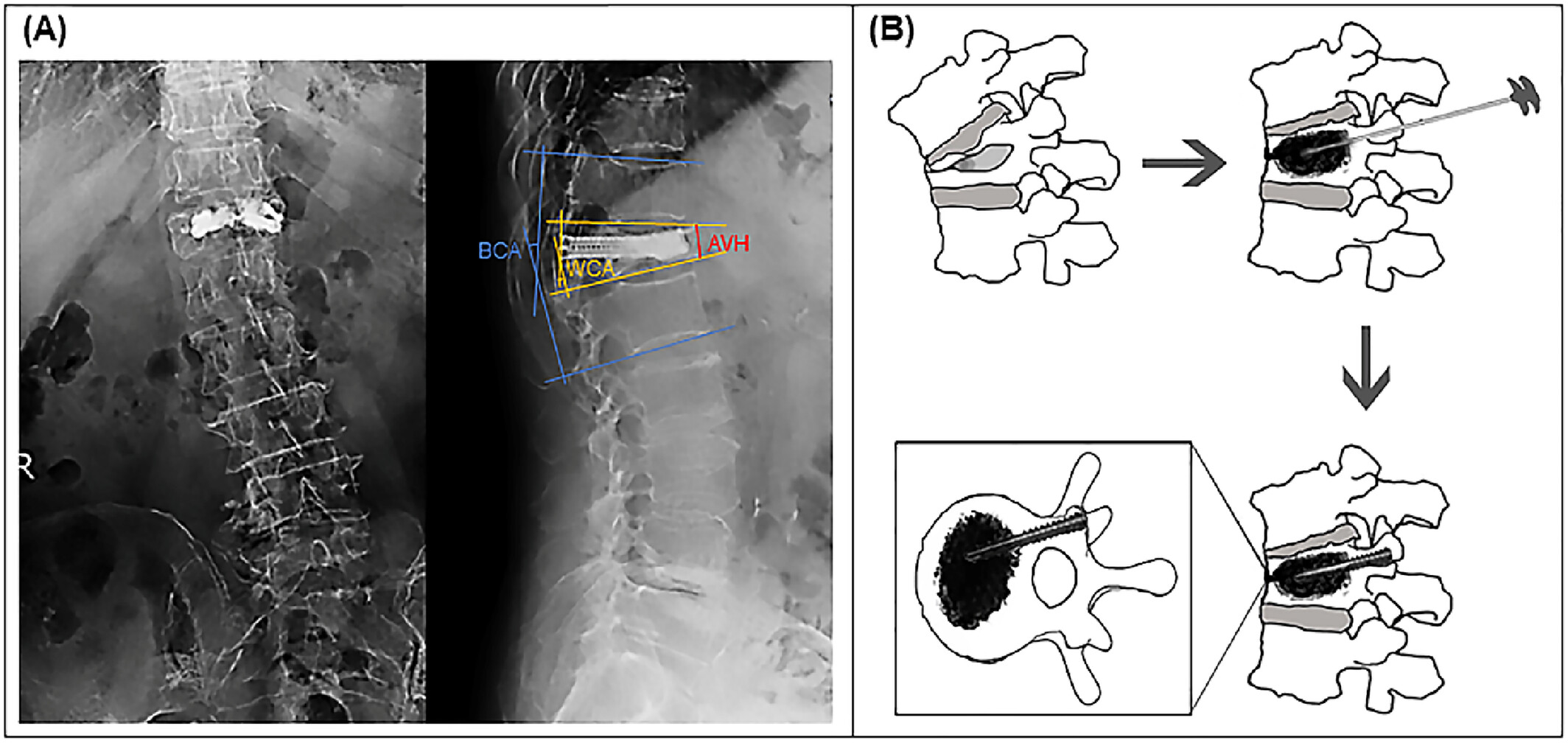
Bone cement displacement, resulting in severe back pain and exacerbation of kyphosis, was a chronic complication after vertebral augmentation in the treatment of Kümmell disease (KD). Data of patients treated with PKP and HPS-KP were collected and evaluated. Through finite element biomechanical analysis of different surgical methods in the treatment of KD, it was found that the operation using a hollow pedicle screw was more effective in preventing the occurrence of bone cement displacement.
Investigating the causal links between inflammatory cytokines and scoliosis through bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis
- First Published: 11 December 2024
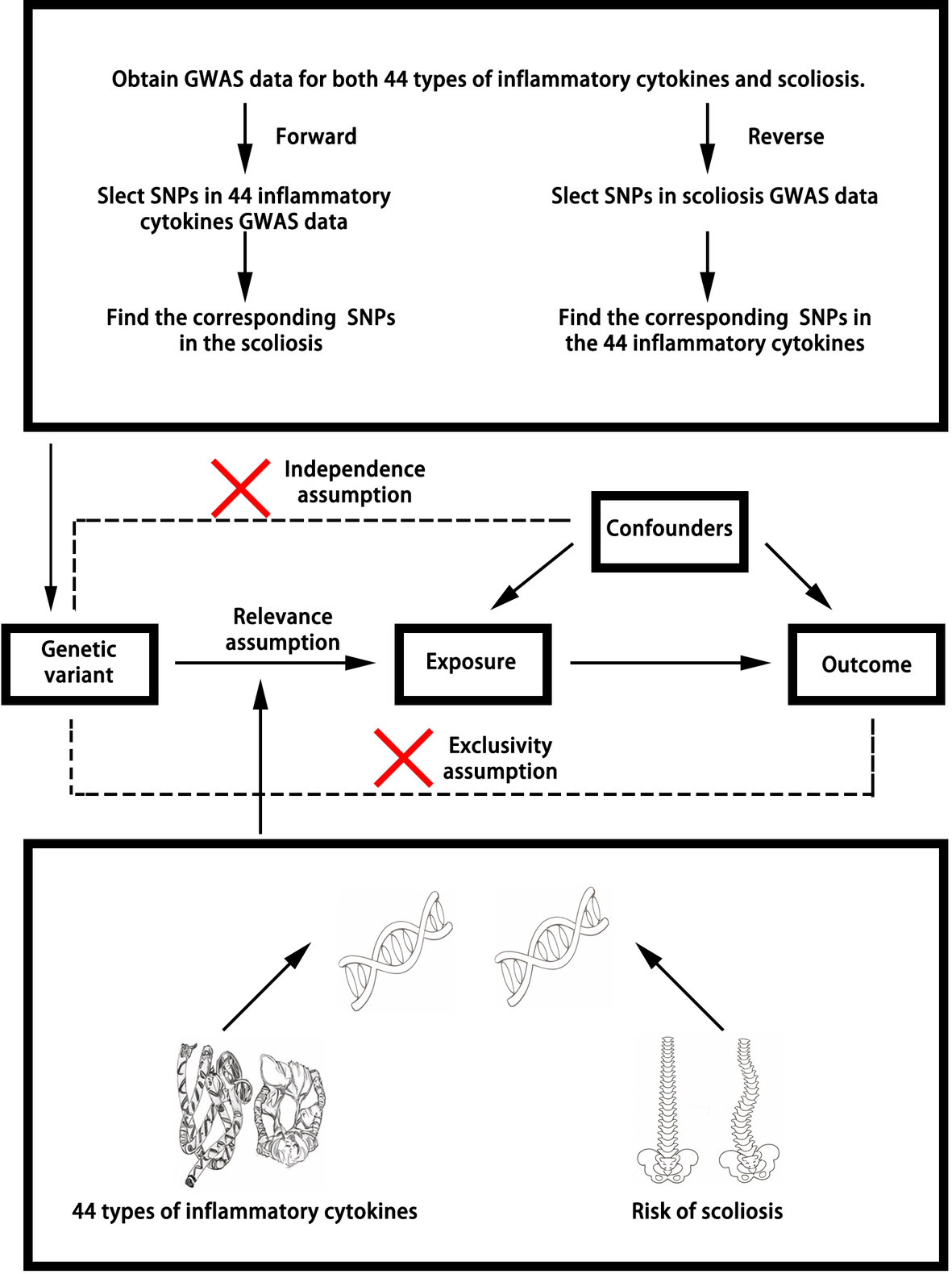
This study explores the genetic-level causal relationships between inflammatory cytokines and scoliosis using bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. The results demonstrate a significant association between the cytokine Resistin (RETN) and scoliosis progression, suggesting RETN as a potential therapeutic target.
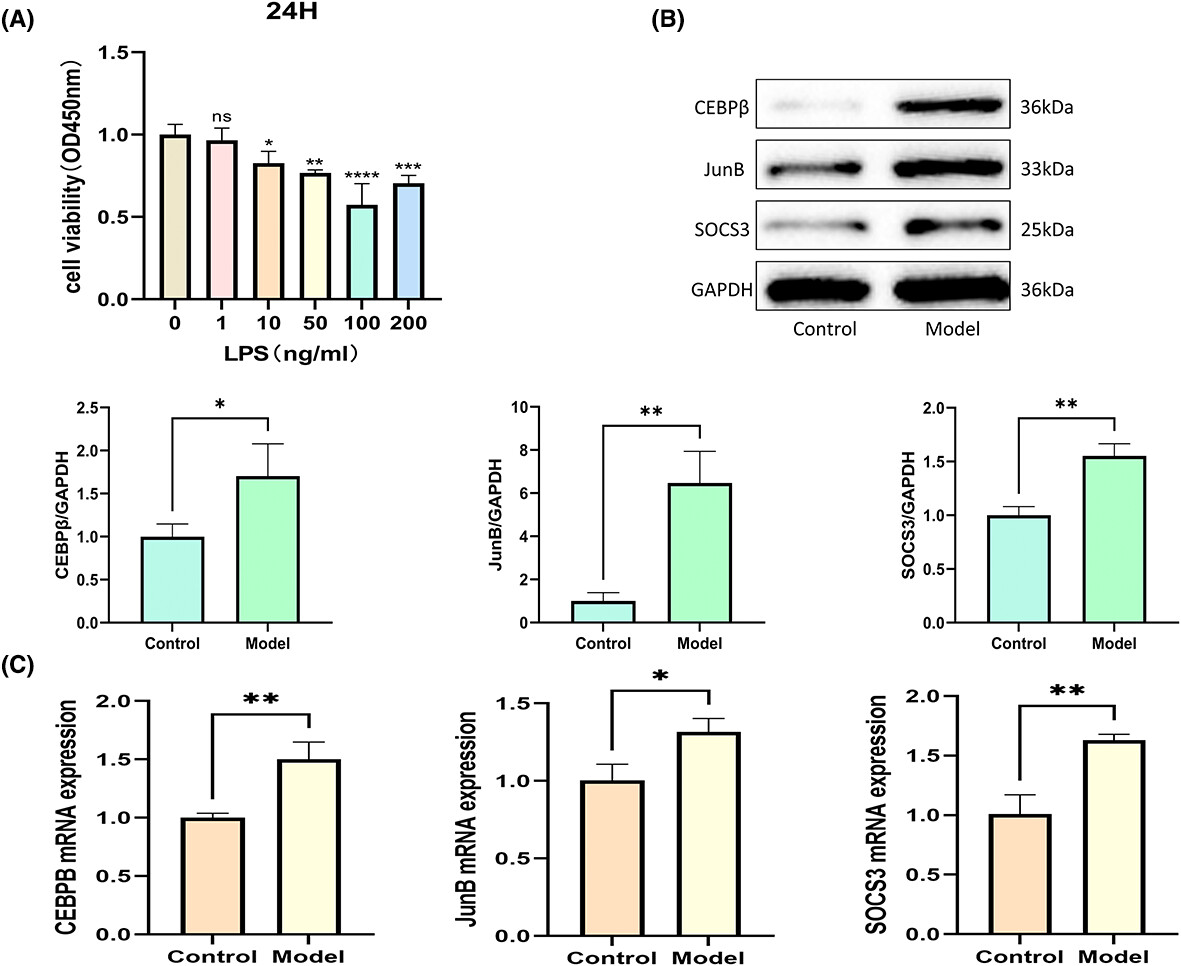
Exploring the therapeutic potential of puerarin on intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- First Published: 11 December 2024
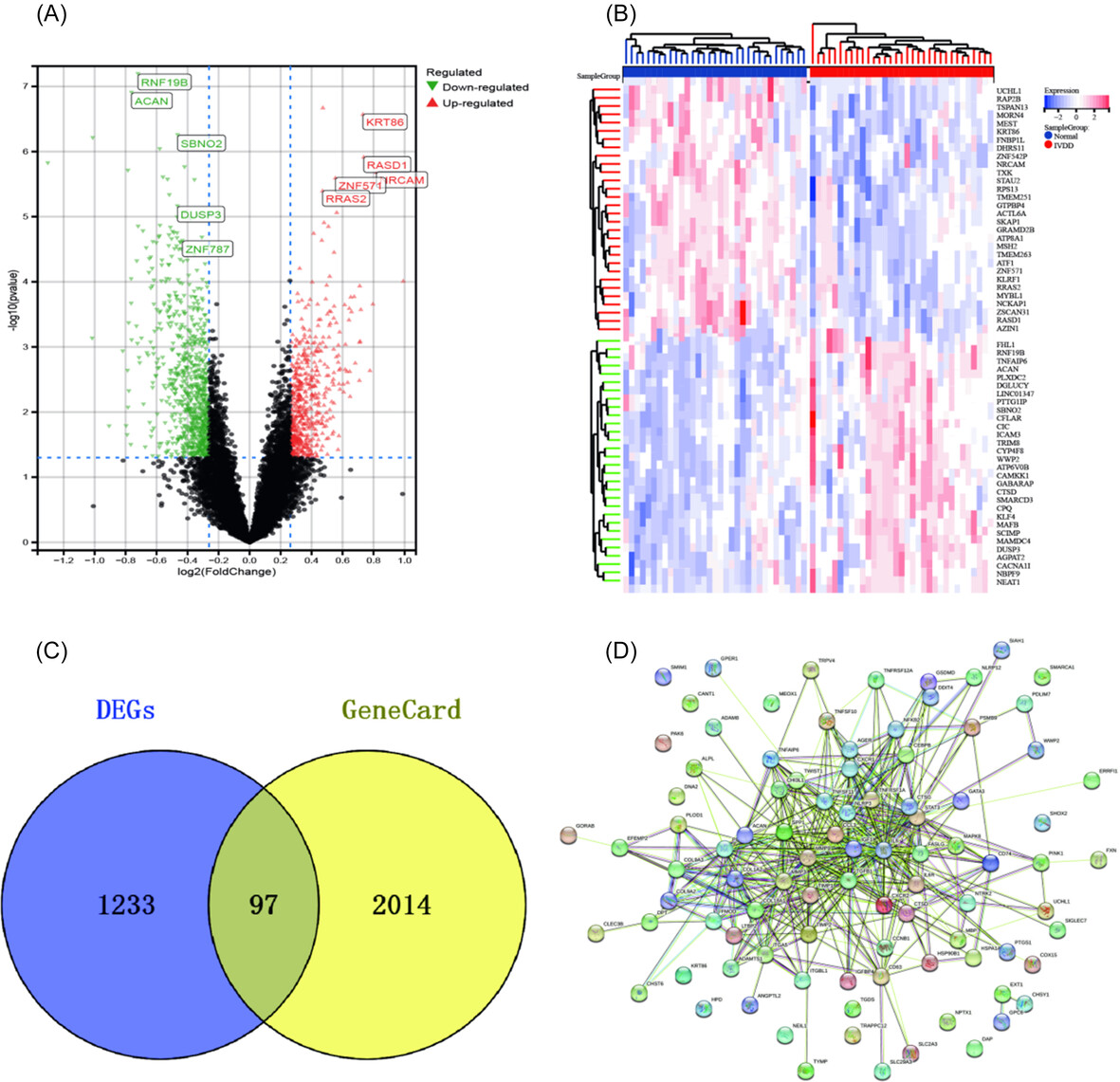
Network pharmacology and bioinformatics analyses suggest that puerarin may mitigate intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) by inhibiting nucleus pulposus (NP) cell apoptosis. This hypothesis was validated through in vitro experiments, which demonstrated that puerarin significantly reduces apoptosis in NPCs.
The genetic causal association between arthritis and low back pain
- First Published: 13 December 2024

Genetically determined rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteoarthritis (OA), knee osteoarthritis (KOA), and hip osteoarthritis (HOA) were found to have causal associations with an increased risk of low back pain. HOA exhibited a particularly strong causal association with an elevated risk of low back pain. Further research is needed to uncover the underlying mechanisms behind the causal relationships between HOA and low back pain.
Scoliosis instrumentation alters primary and coupled motions of the spine: An in vitro study using entire thoracolumbar spine and rib cage specimens
- First Published: 18 December 2024
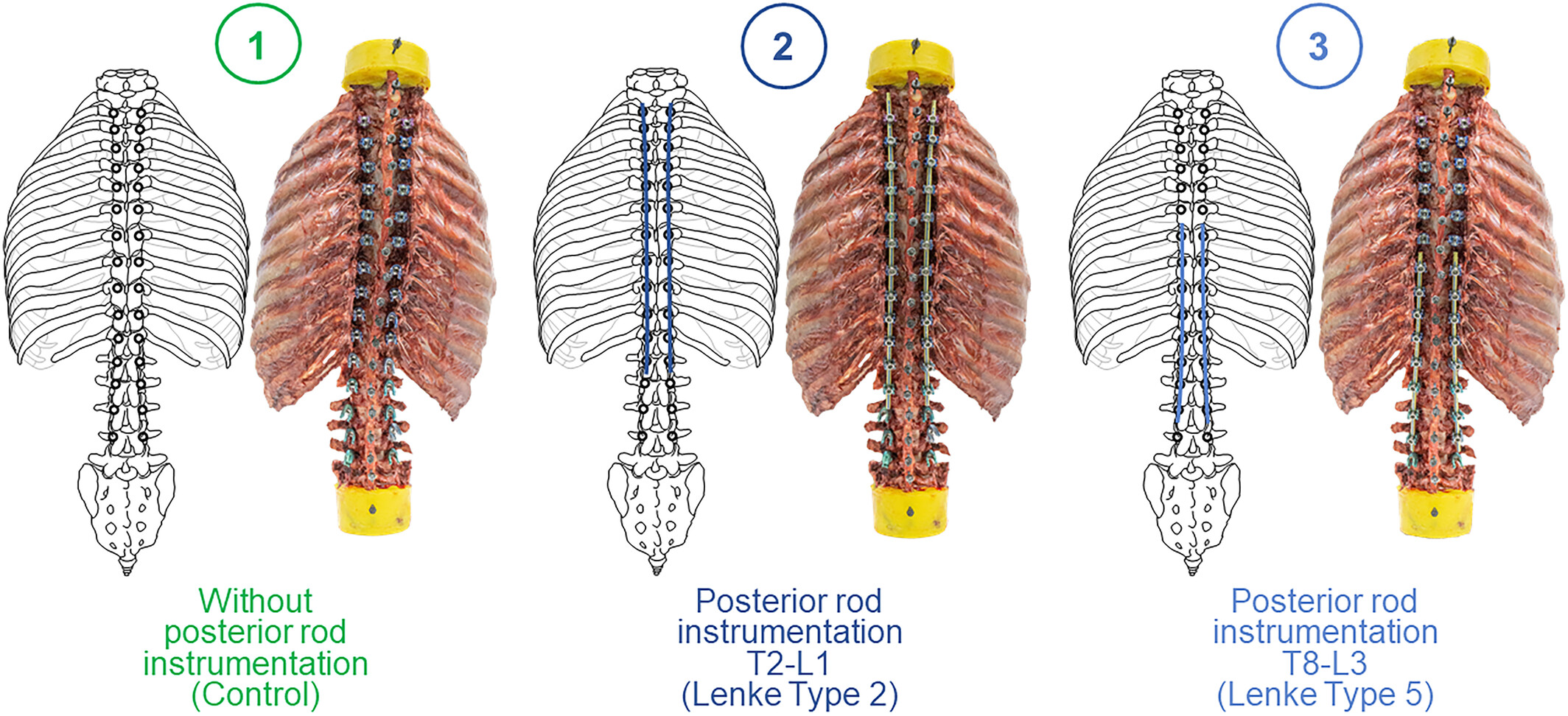
Six human thoracic and lumbar spine specimens (C7-S) with entire rib cage from young adult donors (26–45 years) without clinically relevant deformity were biomechanically tested to investigate primary and coupled motions of all segments without instrumentation and with posterior rod instrumentations ranging from T2 to L1 and from T8 to L3. Instrumentation was found to significantly (p < 0.05) reduce the primary flexibility in all motion directions and to diminish the natural coupling behavior between lateral bending and axial rotation, primarily in the upper thoracic spine, potentially causing correction loss and junctional deformity in the long-term.
Bone morphogenetic proteins, DNA methylation, and gut microbiota interaction in lumbar disc degeneration: A multi-omics Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 20 December 2024
This study, employing multiomics approaches, revealed that the genes associated with lumbar disc degeneration are regulated by DNA methylation and identified genetic variances between gene expression and the gut microbiota. These findings lay the foundation for future targeted functional studies, potentially leading to the development of suitable therapeutic interventions and disease prevention strategies.
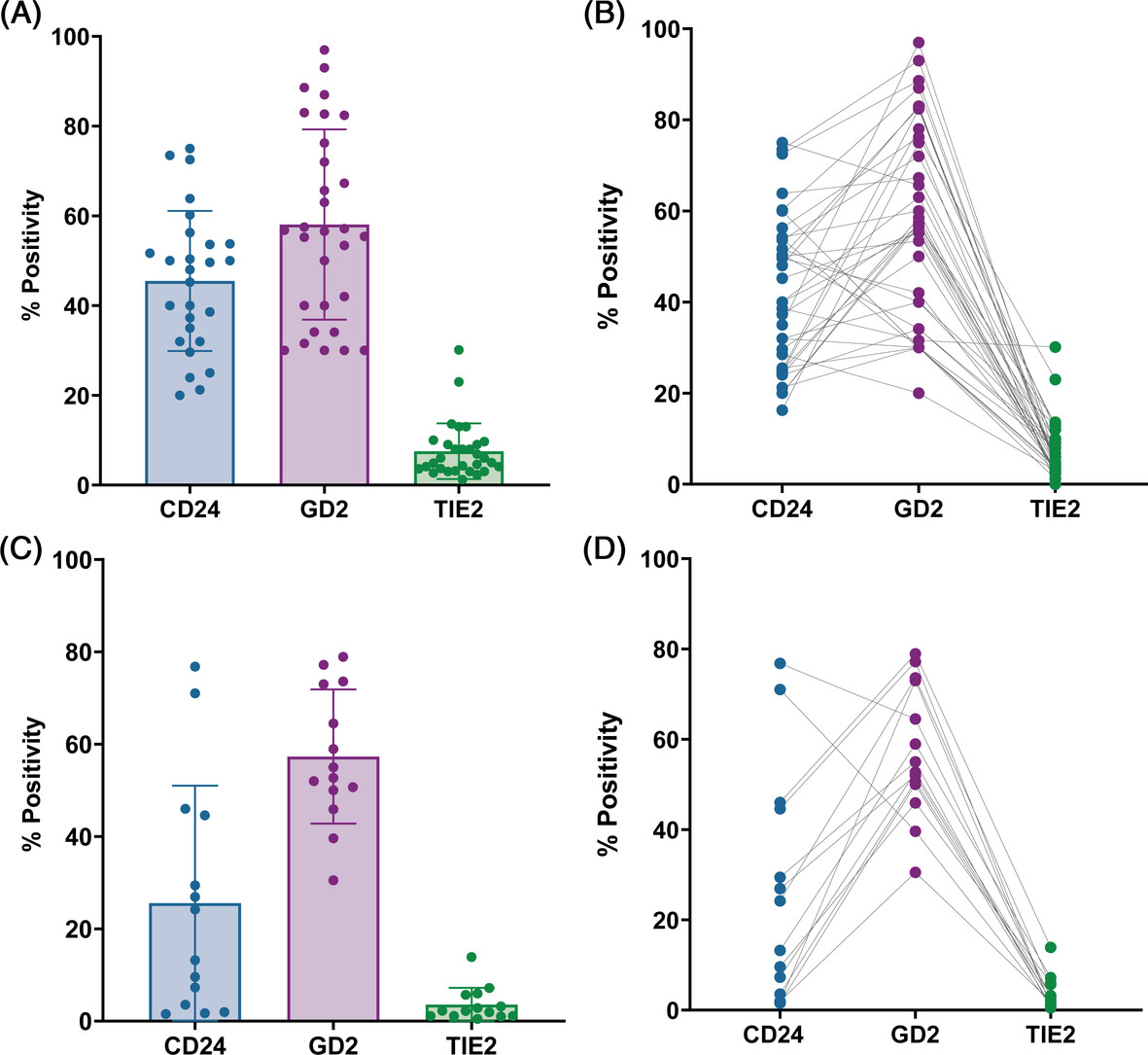
CD24 Positive Nucleus Pulposus Cells in Adult Human Intervertebral Discs Maintain a More Notochordal Phenotype Than GD2 Positive Cells
- First Published: 23 December 2024
In vitro and ex vivo screening of microRNA combinations with enhanced cell penetrating peptides to stimulate intervertebral disc regeneration
- First Published: 25 December 2024
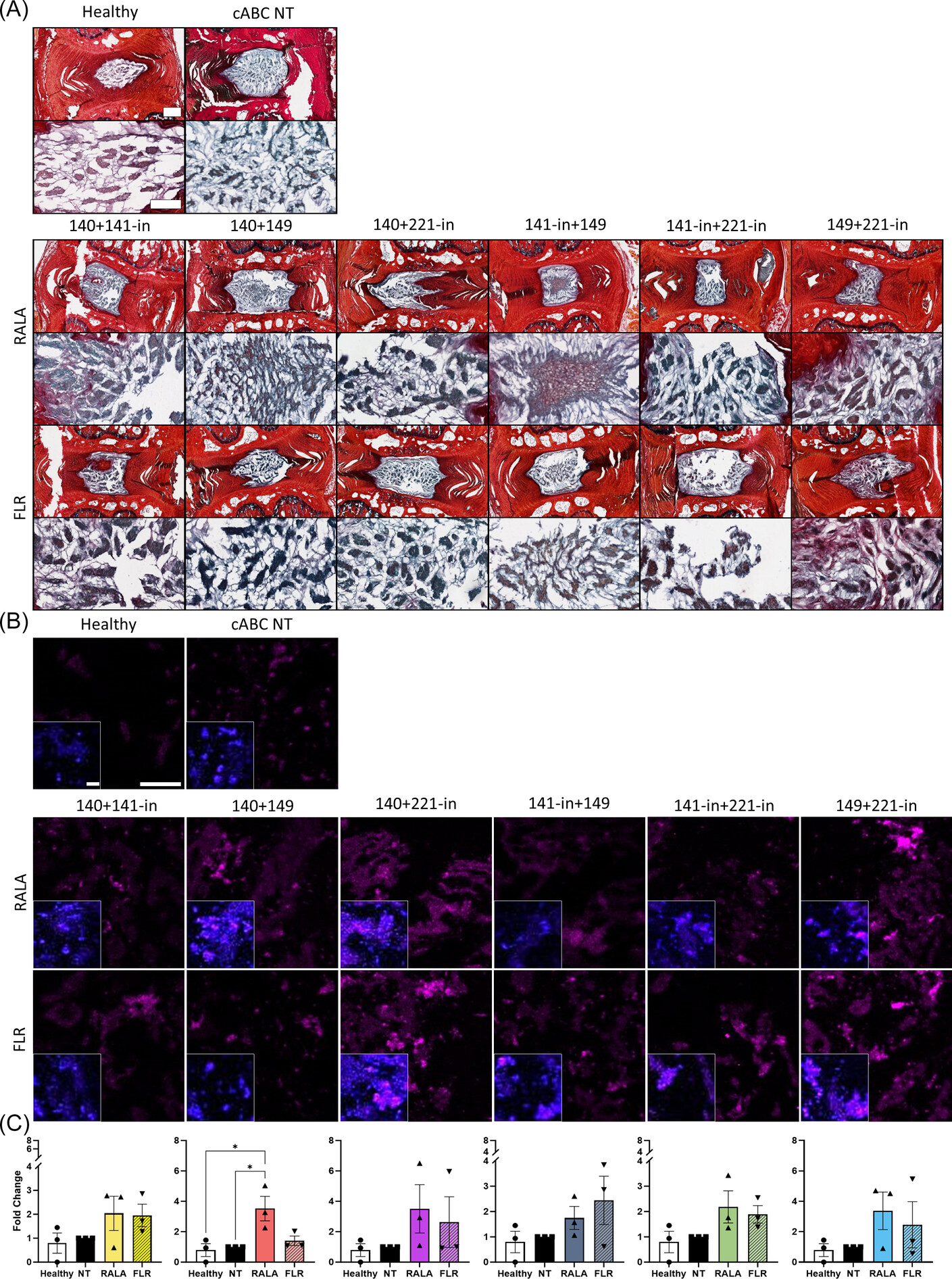
There is a current unmet need in the development of regenerative therapies for degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Here microRNAs were delivered with enhanced cell penetrating peptides, both individually and in pairs, with the aim of correcting the homeostatic anabolic:catabolic imbalance. We find that in an ex vivo organ model of the mildly degenerate disc, an anti-catabolic niche can be generated that can foster discogenic potential.
CORRECTION
Correction to “Development and validation of deep learning models for identifying the brand of pedicle screws on plain spine radiographs”
- First Published: 26 November 2024