Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Brief Report
Hilar cholangiocarcinoma associated with immunoglobulin G4-positive plasma cells and elevated serum immunoglobulin G4 levels
- Pages: 349-353
- First Published: 28 February 2018
Unusual presentation of a patient with a hepatic mass meeting multiple criteria for IgG4-sclerosing cholangitis but was ultimately found to be cholangiocarcinoma. Several published case reports describe patients with suspected cholangiocarcinoma who are later found to have IgG4-sclerosing cholangitis, but few reports have demonstrated the reverse.
Original Articles
Daclatasvir and sofosbuvir treatment of decompensated liver disease or post-liver transplant hepatitis C virus recurrence in patients with advanced liver disease/cirrhosis in a real-world cohort
- Pages: 354-363
- First Published: 27 February 2018
Seventy-seven patients with a life expectancy <1 year due to hepatitis C-related decompensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh C) or recurrent hepatitis C with advanced fibrosis following a liver transplant were treated with daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir, with or without ribavirin, for 24 weeks in a US expanded access program. Twelve weeks after treatment, a sustained HCV virologic response was observed in 84% overall (90% transplant group; 62% decompensated group) by modified intention-to-treat analysis, and 96% (97% transplant; 89% decompensated) as-observed, with 6 deaths and 30 serious adverse events primarily related to advanced liver disease. The combination of daclatasvir and sofosbuvir (with or without ribavirin) was efficacious and generally well tolerated in this group of real-world patients with advanced and life-threatening hepatitis C disease.
Early and late changes in natural killer cells in response to ledipasvir/sofosbuvir treatment
- Pages: 364-375
- First Published: 01 March 2018
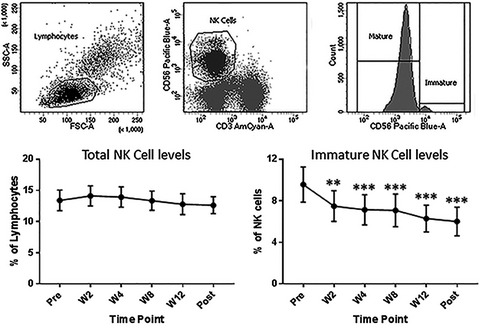
With current direct acting antivirals suppression of HCV viral load is almost universal, however, restoration of innate immune function may not always be the case. Failure to recover NK cell function after successful DAA therapy could have several relevant clinical implications such as, protection from re-infection and requires further study.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease contributes to subclinical atherosclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 376-392
- First Published: 26 February 2018
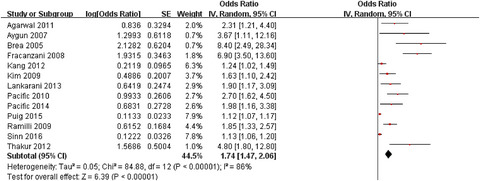
1. NAFLD patient exhibited a significant higher risk of subclinical atherosclerosis. 2. The presence of NAFLD yielded a remarkable higher risk of increased carotid artery intima-media thickness/plaques, arterial stiffness, coronary artery calcification and endothelial dysfunction. 3. NAFLD patient will benefit from screening and surveillance of early atherosclerosis.
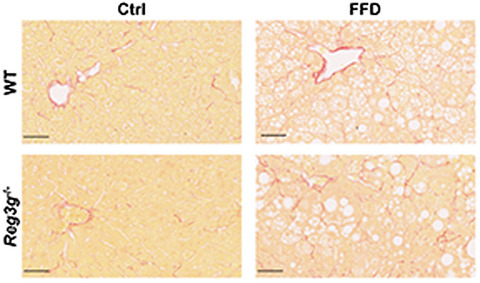
The Role of Intestinal C-type Regenerating Islet Derived-3 Lectins for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Pages: 393-406
- First Published: 28 February 2018
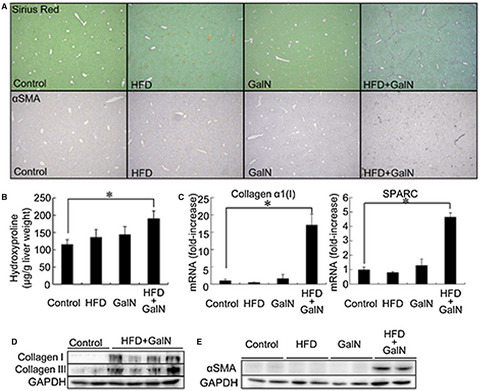
Tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis stimulates fibrosis in the steatotic liver in mice
- Pages: 407-420
- First Published: 13 February 2018
Changes in natural killer cells and exhausted memory regulatory T Cells with corticosteroid therapy in acute autoimmune hepatitis
- Pages: 421-436
- First Published: 26 February 2018
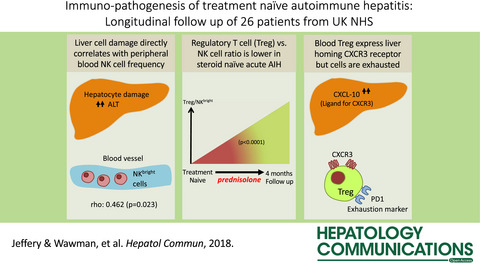
In this UK-AIH consortium longitudinal immune profiling study the frequencies and phenotypes of leukocyte subsets in the peripheral blood of treatment naïve Autoimmune hepatitis patients before and after four months on corticosteroid therapy were examined. The study identifies that activated effector NK cell frequencies correlate with biochemical measurements of hepatitis and in the treatment naïve state compared to remission are elevated over Treg, which possess an exhausted, memory phenotype; thus inadequate regulation of NK cells by Treg may play a role in AIH pathogenesis and contribute to liver injury.
Influence of spontaneous splenorenal shunts on clinical outcomes in decompensated cirrhosis and after liver transplantation
- Pages: 437-444
- First Published: 09 February 2018
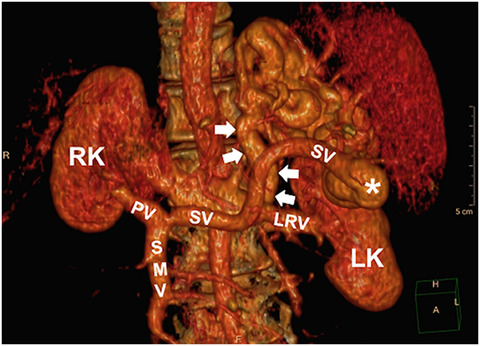
Cirrhosis and portal hypertension can lead to the formation of spontaneous splenorenal shunts (SSRS) that may divert portal blood flow to the systemic circulation and reduce hepatic perfusion. We evaluated clinical outcomes after liver transplant evaluation according to the presence or absence of SSRS at a large U.S. center. SSRS was present in 23% of 741 liver transplant candidates and did not independently predict mortality or receipt of liver transplantation, and among liver transplant recipients, SSRS did not predict post-transplant mortality or graft failure.
The molecular adsorbent recirculating system in posthepatectomy liver failure: Results from a prospective phase I study
- Pages: 445-454
- First Published: 08 March 2018
A single blood test adjusted for different liver fibrosis targets improves fibrosis staging and especially cirrhosis diagnosis
- Pages: 455-466
- First Published: 05 March 2018
Special Article
Liver stiffness measurement predicted liver-related events and all-cause mortality: A systematic review and nonlinear dose–response meta-analysis
- Pages: 467-476
- First Published: 13 February 2018
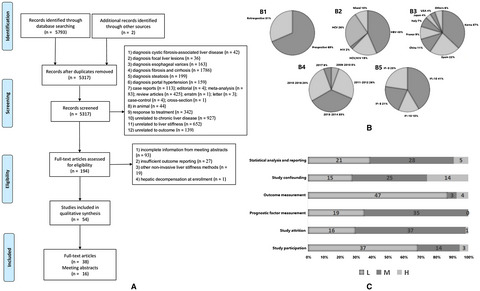
This review aims to consider the dose-response association of liver stiffness measurement with liver-related events and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic liver disease, which might contribute to the routine clinical application of LSM in predicting LREs in the management of patients with CLD.