Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine
Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover
- Page: i
- First Published: 15 March 2019

The cover image based on Original Article Identification of a pathogenic mutation in ATP2A1 via in silico analysis of exome data for cryptic aberrant splice sites by Christine C. Bruels, DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.552.
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Could a chimeric condition be responsible for unexpected genetic syndromes? The role of the single nucleotide polymorphism-array analysis
- First Published: 09 January 2019
In this paper, is reported the identification of two chimeric patients, a rare finding if sexual abnormalities are absent. However, their chimeric condition is responsible at least for the Silver–Russell phenotype observed in one of the two patients. By single nucleotide polymorphism-array analyses, it was possible to clearly define the mechanism responsible for this unusual finding, underlining the importance of this technique in bringing out the perhaps submerged world of chimeras.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations in Japanese women with ductal carcinoma in situ
- First Published: 16 January 2019
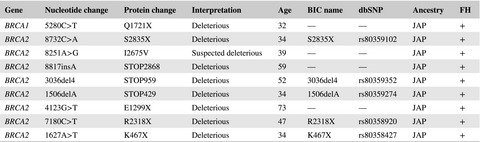
DCIS is equally as prevalent in patients who were BRCA mutation carriers as in high familial-risk women who were noncarriers, but occurs at earlier age. BRCA2 carriers have higher incidence in DCIS than that of BRCA1 carriers, and tend to be higher grade and more frequently ER positive and lower proliferation. Total relatives with BC DX ≥2, age at diagnosis ≤35y and ER+/HER2+ might be independent predictors for BRCA mutation in Japanese women with DCIS and patients of these risk factors should be recommended to receive genetic counseling and BRCA testing. DCIS is equally as prevalent in patients who were BRCA mutation carriers as in high familial-risk women who were noncarriers, but occurs at earlier age. We found only one case of DCIS raised in BRCA1 carrier which had same pathological feature with independently and simultaneously occurred invasive cancer of triple negative. BRCA2 carriers have higher incidence in DCIS than that of BRCA1 carriers, and tend to be higher grade and more frequently ER-positive, PR-positive, and lower proliferation.
A comprehensive study of immunology repertoires in both preoperative stage and postoperative stage in patients with colorectal cancer
- First Published: 09 January 2019
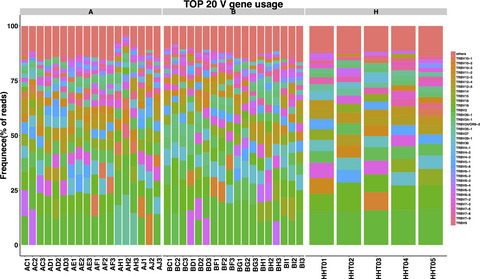
In conclusion, colorectal cancer (CRC) patients were presented with different immune repertoire in comparison with healthy controls. In this study, significant difference in TRBV and TRBJ gene usage in between case and control group could provide some potential bio-marker for the diagnosis and the treatment of the patients with CRC.
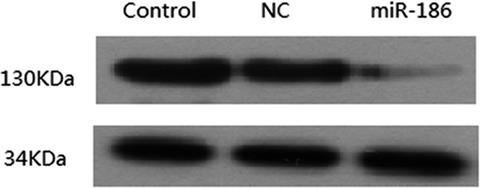
MicroRNA-186 is associated with hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- First Published: 21 December 2018
Molecular diagnosis of somatic overgrowth conditions: A single-center experience
- First Published: 13 February 2019
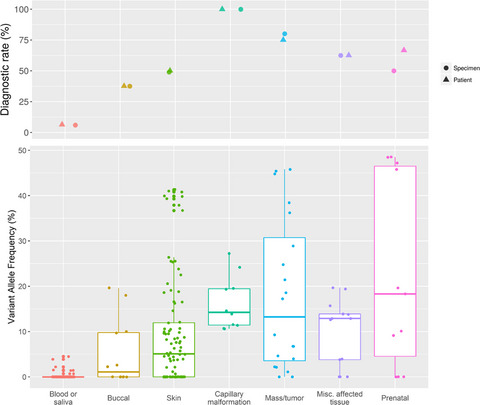
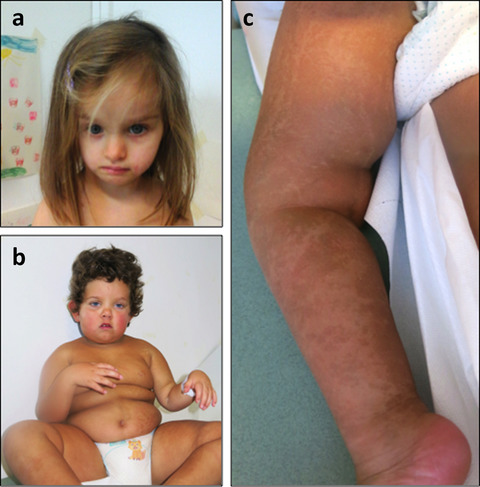
Clinical genetic testing with deep next-generation sequencing of 166 specimens from 80 patients with suspected mosaic overgrowth conditions resulting a 45%–61% diagnostic yield and was highly influenced by the tissue submitted and phenotype. Three prenatal cases illustrate remaining challenges in prenatal diagnosis of mosaic overgrowth syndromes.
Mutation analysis of common deafness genes among 1,201 patients with non-syndromic hearing loss in Shanxi Province
- First Published: 28 January 2019
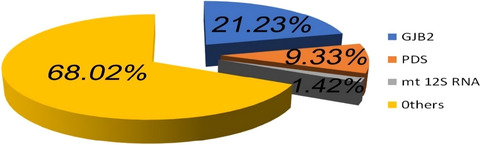
Hearing impairment is one of most frequent birth defects. Here, we have investigated the molecular etiology of non-syndromic deafness patients in Shanxi Province, which has the highest frequency of birth defects in China. In our research, it was found that c.235delC in GJB2 and c.919-2A>G (IVS7-2A>G) in SLC26A4 were the highest frequency pathogenic variants in Shanxi Province. Taken together, our data will enrich the database of deafness mutations and will help clinical diagnosis, treatment, and genetic counseling of hearing impairment.
Unknown mutations and genotype/phenotype correlations of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis in patients from Saudi Arabia and Pakistan
- First Published: 01 January 2019
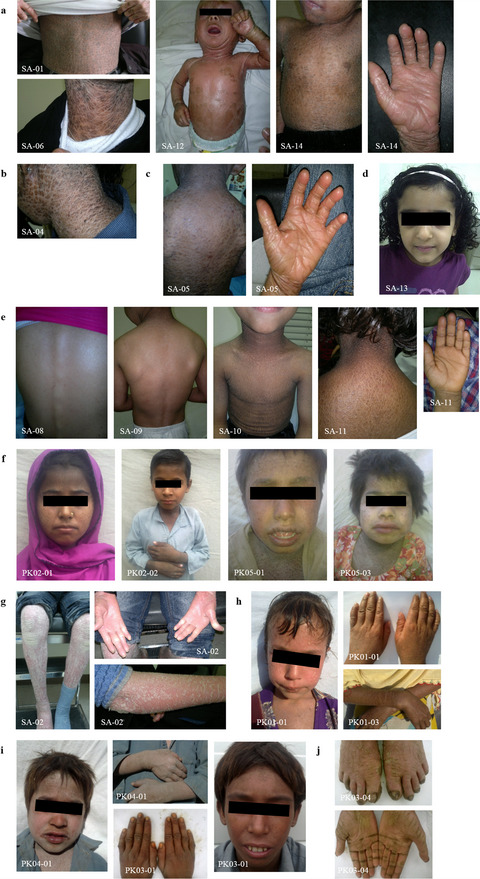
Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI) is a phenotypically and genetically heterogeneous skin disease, associated with defects in the skin permeability barrier. Here, we have detected mutations in the genes TGM1, ABCA12, CYP4F22, NIPAL4, and ALOXE3 in 19 consanguineous families from Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Pakistan. Our results revealed new insights into genotype/phenotype correlations and contribute to expanding the mutational spectrum of ARCI.
The protective role of rs56103835 against breast cancer onset in the Iranian population
- First Published: 31 January 2019
Bilateral striatal necrosis due to homoplasmic mitochondrial 3697G>A mutation presents with incomplete penetrance and sex bias
- First Published: 08 January 2019
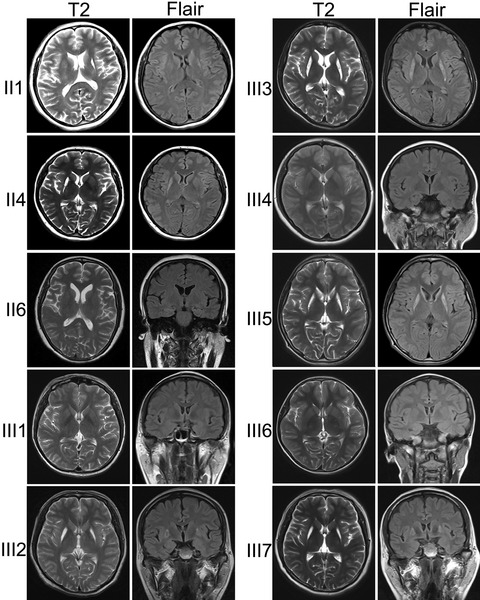
In a maternal inherited family, bilateral striatal necrosis was associated with homoplasmic mitochondrial 3697G>A mutation that resulted in an isolated defect of complex I. Although no possible modifier genes on the X chromosome were found, male offspring presented with severe spastic dystonia and complete penetrance, but the female offspring showed mild symptom and low penetrance.
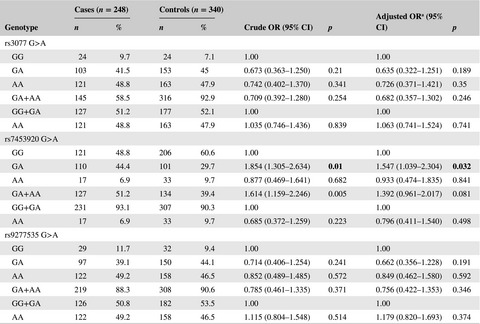
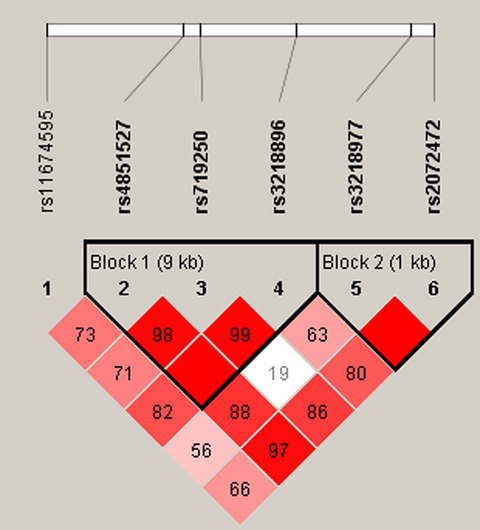
Association between the IL1R2 rs2072472 polymorphism and high-altitude pulmonary edema risk
- First Published: 22 January 2019
High expression of FAM13A was associated with increasing the liver cirrhosis risk
- First Published: 02 January 2019
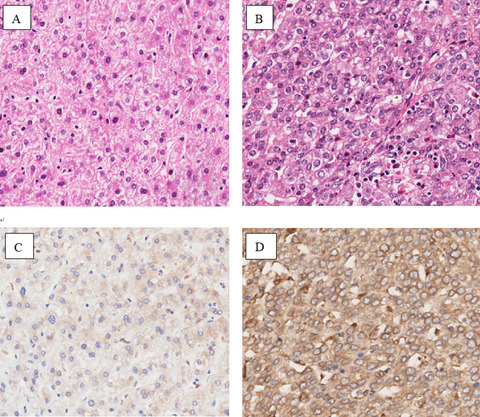
This study aimed to explore whether FAM13A polymorphisms influenced the liver cirrhosis risk. We analyzed the expression of the FAM13A gene in liver cirrhosis tissues by immunohistochemistry. The relationship between FAM13A gene polymorphism and liver cirrhosis was studied by association analysis. Our findings demonstrated that the high expression of FAM13A was associated with an increased risk of liver cirrhosis.
Association of human leukocyte antigens-DQB2/DPA1/DPB1 polymorphism and pulmonary tuberculosis in the Chinese Uygur population
- First Published: 01 January 2019
Prenatal cell-free DNA screening for fetal aneuploidy in pregnant women at average or high risk: Results from a large US clinical laboratory
- First Published: 31 January 2019
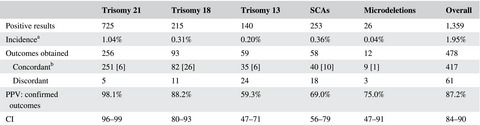
This study demonstrates that this cfDNA prenatal screening assay, QNatal® Advanced™, provides highly accurate discrimination between affected and unaffected pregnancies among a population of pregnant women at average or high risk for fetal genetic abnormalities. This has significant implications for patient care in the general obstetrical population. Increased understanding of assay performance facilitates improved clinical care and appropriate medical management for all patients.
Association of the TBK1 mutation p.Ile334Thr with frontotemporal dementia and literature review
- First Published: 22 January 2019
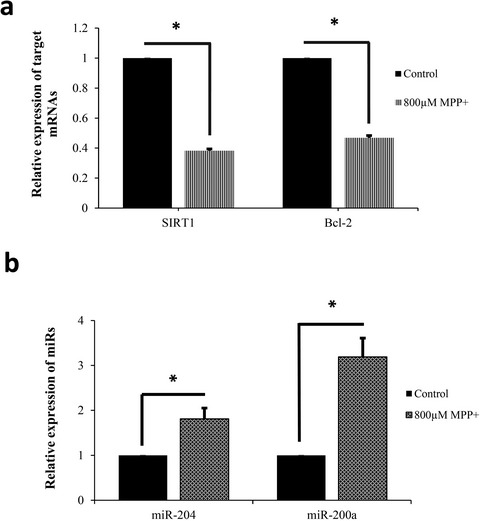
Upregulation of miR-200a and miR-204 in MPP+-treated differentiated PC12 cells as a model of Parkinson’s disease
- First Published: 03 February 2019
Rare copy number variants contribute pathogenic alleles in patients with intestinal malrotation
- First Published: 10 January 2019
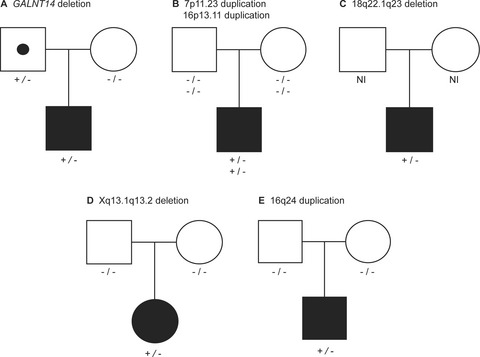
We analyzed array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) data from 47 individuals with intestinal malrotation and identified six rare copy number variants (CNVs), of which five involved known syndrome loci. Two of the known syndromes (Cornelia de Lange type 5 and 18q terminal deletion syndrome) have not previously been associated with intestinal malrotation.
Genetic analysis of the relation of telomere length-related gene (RTEL1) and coronary heart disease risk
- First Published: 08 January 2019
Identification of a pathogenic mutation in ATP2A1 via in silico analysis of exome data for cryptic aberrant splice sites
- First Published: 28 January 2019
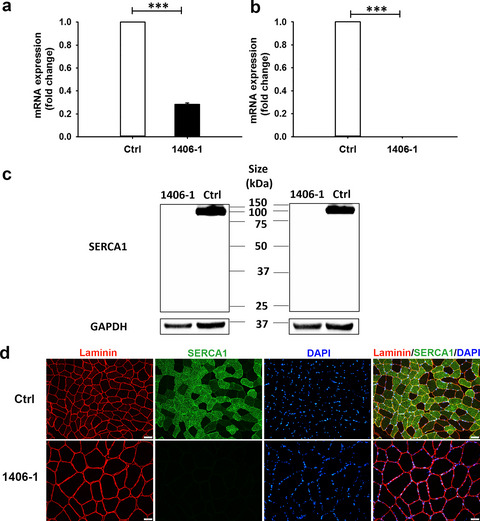
We developed a novel bioinformatics pipeline to identify potentially aberrant novel essential splice site (PANESS) mutations in next-generation sequencing data, and used it successfully to identify a pathogenic splice site mutation in ATP2A1 for a family with a myotonic phenotype. The pathogenic nature of the mutation was confirmed via RT-PCR, western blot, and immunohistochemistry, along with functional studies in Drosophila.
The 6q25.1 rs2046210 polymorphism is associated with an elevated susceptibility to breast cancer: A meta-analysis of 261,703 subjects
- First Published: 28 January 2019
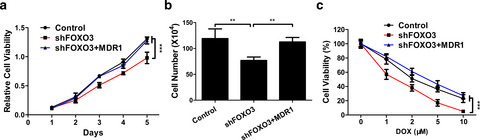
Forkhead box O3 promotes colon cancer proliferation and drug resistance by activating MDR1 expression
- First Published: 08 January 2019
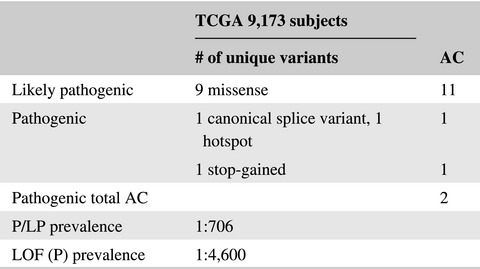
The prevalence of germline DICER1 pathogenic variation in cancer populations
- First Published: 22 January 2019
Interaction of germline variants in a family with a history of early-onset clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- First Published: 24 January 2019
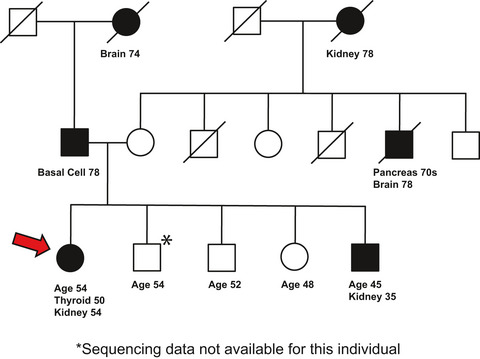
This manuscript addresses the growing need to assign cancer risk to rare variants of uncertain significance. In this manuscript, we have described a proband with a personal history of early-onset renal and thyroid cancers, and a family history of renal and other cancers. Our data suggest the possibility of risk associated with interaction of two or more reported variants and provides the basis for analysis in other families.
Impact of IL1R1 and IL1R2 gene polymorphisms on risk of osteonecrosis of the femoral head from a case–control study
- First Published: 08 January 2019
Is interstitial 8p23 microdeletion responsible of 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis? One case report from birth to puberty
- First Published: 28 January 2019
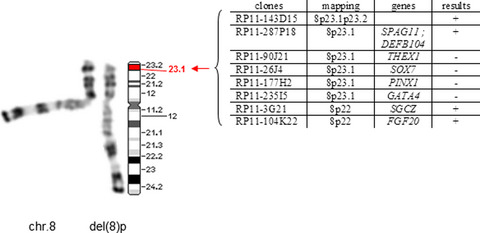
A boy was born with perineal hypospadias, a micropenis and cryptorchidism. An interstitial deletion on chromosome 8's short arm (46, XY, del (8)(p23.1p23.1)) is likely to explain the genital abnormalities since GATA4 and SOX7 genes were deleted. After reviewing the literature, we conclude that a 8p deletion should be searched for also in isolated 46XY DSD cases.
De novo and inherited pathogenic variants in collagen-related osteogenesis imperfecta
- First Published: 24 January 2019
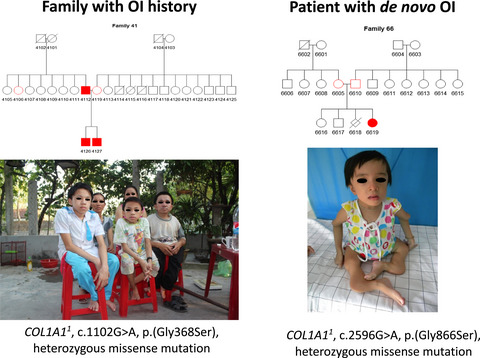
Majority of osteogenesis imperfecta cases have de novo nature. Out of studied 146 collagen-related osteogenesis imperfecta patients from Estonia, Ukraine and Vietnam, 56% harbored de novo mutations. de novo and inherited osteogenesis imperfecta patients differed in phenotype severity and mutational spectrum.
RNA-Seq detects a SAMD12-EXT1 fusion transcript and leads to the discovery of an EXT1 deletion in a child with multiple osteochondromas
- First Published: 10 January 2019
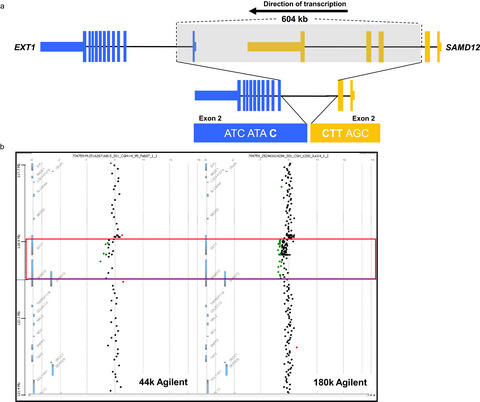
We describe the identification of a diagnostic EXT1 gene fusion in a patient with multiple osteochondromas following extensive negative clinical testing. Follow up reanalysis of clinical results revealed an underlying mosaic chromosomal deletion. The article reveals shortcomings in clinical testing and is the first report of a gene fusion diagnostic of multiple osteochondromas.
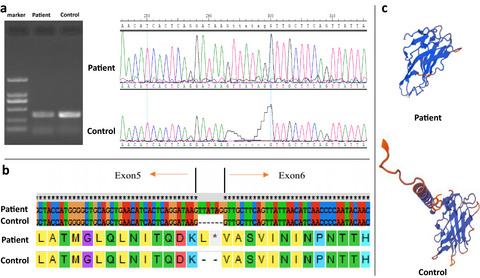
A family with Danon disease caused by a splice site mutation in LAMP2 that generates a truncated protein
- First Published: 03 February 2019
Association between single nucleotide polymorphism (rs4252424) in TRPV5 calcium channel gene and lead poisoning in Chinese workers
- First Published: 21 January 2019
This is the first study to systematically evaluate the contribution of TRPV5 (a calcium channel-related gene) tag-SNPs to Blood lead levels in lead-related occupational workers. In this study, we treated the BLL as a continuous variable and performed a multiple linear regression instead of the logistic regression in traditional case-control study. We successfully indentified that a noble TRPV5 polymorphism rs4252424 is significantly associated with the individuals’ BLL. The following expression quantitative trait loci analysis (eQTL) also highlighted the remarkable protective effect of rs4252424 CT genotype in persons underwent the same external exposure of plumbum.
IL-4 gene polymorphisms and their relation to steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Chinese population
- First Published: 29 January 2019
Clinical application of single-molecule optical mapping to a multigeneration FSHD1 pedigree
- First Published: 21 January 2019
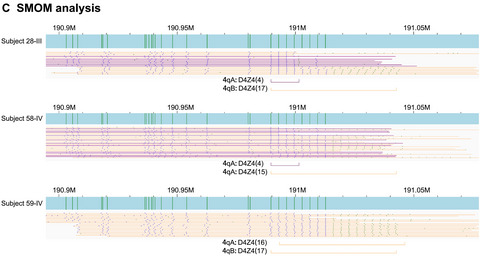
Single-optical molecule mapping (SMOM) was investigated as a new tool for the molecular diagnosis of FSHD1. Benchmarking against gold standard Sothern blot hybridization and FISH combing, SMOM analysis of a five-generation FSHD1 pedigree, correctly identified the founding 4qA disease-causing allele with a shortened D4Z4 array of 4 repeat units and the corresponding nondisease 4qB allele.
Protein informatics combined with multiple data sources enriches the clinical characterization of novel TRPV4 variant causing an intermediate skeletal dysplasia
- First Published: 28 January 2019

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 (TRPV4) is an ion channel permeable to Ca2+ that is sensitive to physical, hormonal, and chemical stimuli. This protein is expressed in many cell types, including osteoclasts, chondrocytes, and sensory neurons. As such, pathogenic variants of this gene are associated with skeletal dysplasias and neuromuscular disorders. The novel c.2401A>G (p.K801E) variant of TRPV4 is described using protein informatics, molecular modeling, genomic exome analysis, and clinical study to confirm the pathogenicity for the variant.
REVIEW ARTICLES
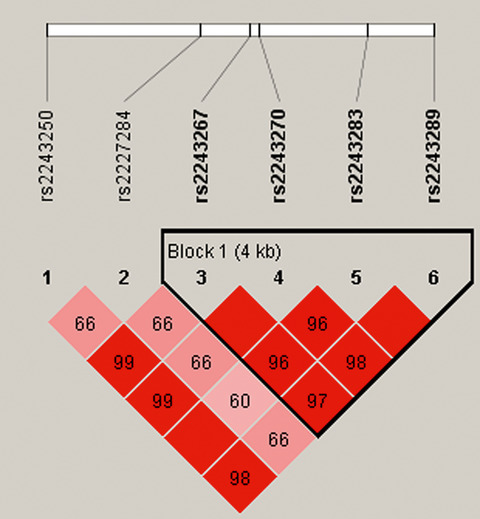
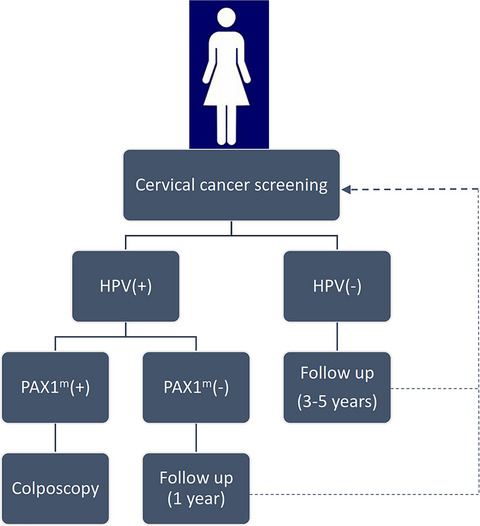
The promising role of PAX1 (aliases: HUP48, OFC2) gene methylation in cancer screening
- First Published: 12 January 2019
A multidisciplinary approach to the clinical management of Prader–Willi syndrome
- First Published: 29 January 2019
Unmet medical needs of individuals with Prader–Willi syndrome make it a rare disease that models the importance of multidisciplinary approaches to care with collaboration between academic centers, medical homes, industry, and parent organizations. Establishment of centers motivates collaboration of experts to provide evidence-based new standards of care, increases the knowledge base regarding success of treatments through randomized controlled trials, and offers an additional resource for patient and family concerns.
CLINICAL REPORT
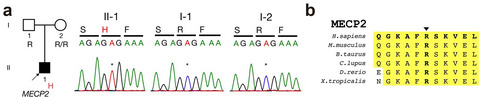
An early seizure variant type of a male Rett syndrome patient with a MECP2 p.Arg133His missense mutation
- First Published: 19 December 2018
METHOD
Evaluation of the detection of GBA missense mutations and other variants using the Oxford Nanopore MinION
- First Published: 13 January 2019
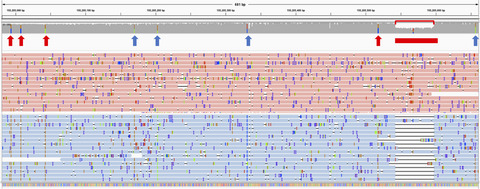
The GBA gene is important in Parkinson's and Gaucher disease, but difficult to sequence due to a highly homologous adjacent pseudogene. Here we present a novel method using long reads on the Oxford Nanopore MinION, which can detect missense mutations and an exonic deletion, with the added advantage of phasing and intronic analysis.