Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Analysis and Identification of Therapeutic Targets for Neuronal Regeneration After Ischemic Stroke
- First Published: 05 May 2025
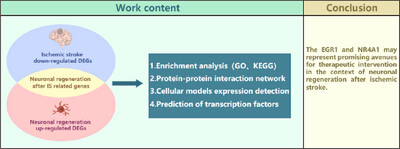
In this study, we screened and analyzed targets associated with neuronal regeneration after ischemic stroke (IS), and detected the expression of corresponding genes in cellular models. Our findings suggest that EGR1 and NR4A1 may represent promising therapeutic targets of neuronal regeneration after IS.
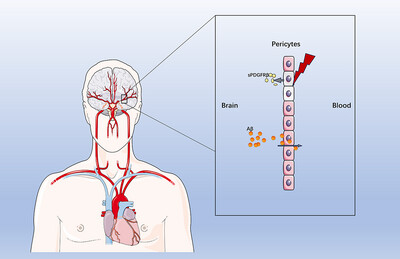
The Soluble Platelet-Derived Growth Factor β Receptor Induces Postoperative Delirium by Downregulating the Clearance of β-Amyloid in the Brain
- First Published: 05 May 2025
Effects of Physical Health, Mental Health, Social Environmental Factors, and Quality of Life on Social Participation of People With Physical Disabilities
- First Published: 05 May 2025
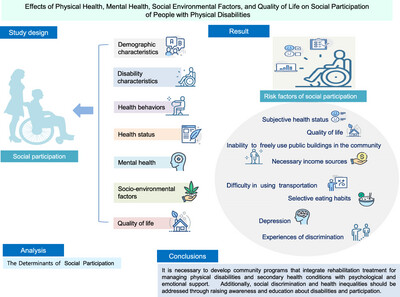
Crude analysis revealed 29 variables in demographic characteristics, disability characteristics, health behaviors, health status, mental health, socio-environmental factors, and QoL that correlated significantly with social participation. The adjusted analysis revealed that difficulties in social participation were influenced in the following order: poor subjective health, lower QoL, inability to freely use public buildings in the community, lack of necessary income sources, difficulty in using transportation, selective eating habits, increased depression, and experiences of discrimination. The explanatory power of the regression model is 46.4%.
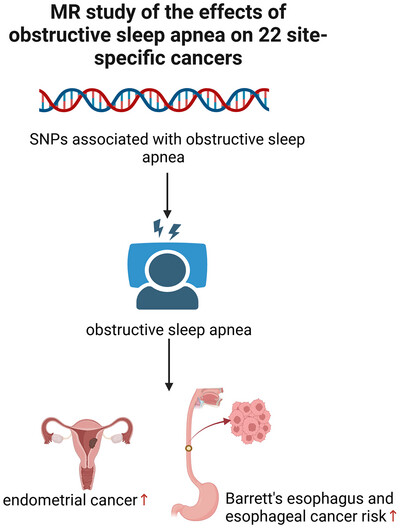
Causal Associations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea With Cancer Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 05 May 2025
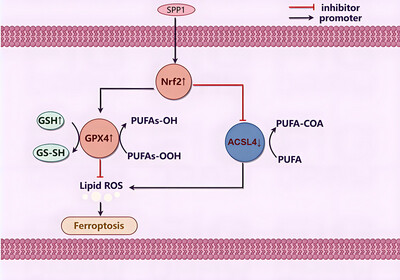
Ability of SPP1 to Alleviate Post-Intracerebral Hemorrhage Ferroptosis via Nrf2/HO1 Pathway
- First Published: 05 May 2025
The Causal Relationship Between Neurotrophic Factors and Delirium: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 05 May 2025
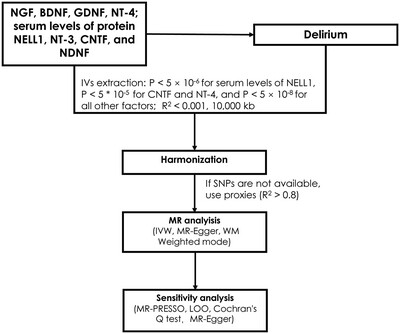
Overview of MR analysis. SNPs: single nucleotide polymorphisms; inverse-variance weighted (IVW); weighted median (WM); leave-one-out (LOO); glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF); ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF); brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); nerve growth factor (NGF); neurotrophin-3 (NT-3); neurotrophin-4 (NT-4); brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); nerve growth factor (NGF); neural epidermal growth factor-like 1 protein NELL1.
BRIEF REPORT
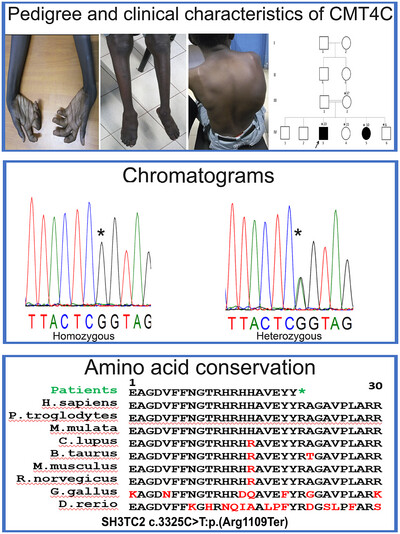
Rare Variants Cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease in Malian Families
- First Published: 05 May 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
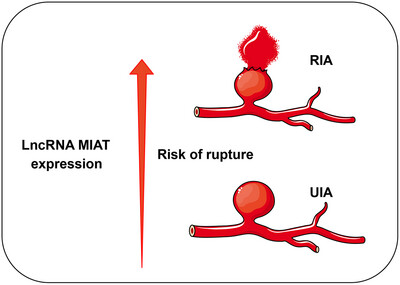
Differential Expression of LncRNA MIAT and Its Clinical Significance in Intracranial Aneurysms
- First Published: 05 May 2025
REVIEW
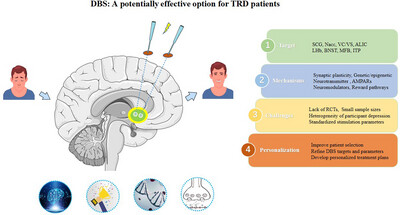
The Targets of Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Review
- First Published: 05 May 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The Moderating Role of Willpower as a Personality Trait in the Relationship Between Social Influence and Moral Disengagement Contradiction
- First Published: 05 May 2025
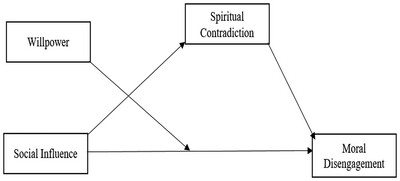
The graphical abstract provides a visual representation of the intricate interplay among willpower, social influence, spiritual contradiction, and moral disengagement. The model posits that social influence has the potential to enhance moral disengagement; however, this effect is tempered by willpower and mediated by spiritual contradiction. Individuals who possess higher levels of willpower demonstrate augmented cognitive control, thereby diminishing the influence of social influence on moral disengagement. Conversely, individuals with lower willpower exhibit a heightened vulnerability to social pressure, which, through spiritual contradiction, amplifies their susceptibility to moral disengagement. This theoretical framework contributes to our understanding of the role of executive function and self-regulation in ethical decision-making, emphasizing the neurocognitive mechanisms underlying moral disengagement in social contexts.
BRIEF REPORT
Cognition-Associated Changes in Retinal Thickness Relate to Limbic and Temporal Cortical Atrophy in Parkinson's Disease
- First Published: 05 May 2025
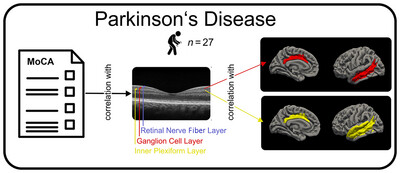
Twenty-seven Parkinson's disease patients underwent cognitive assessment (MoCA), retinal OCT imaging and brain MRI. Thinning in specific retinal layers (IPL, GCL) correlated both with cognitive decline and thinning of temporal and limbic cortices. This supports retinal imaging as a potential biomarker for detecting neurodegeneration-related cognitive decline in the disease.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Risk Factors and Prognostic Implications of Tumor-Related Epilepsy in Diffuse Glioma Patients: A Real-World Multicenter Study
- First Published: 05 May 2025
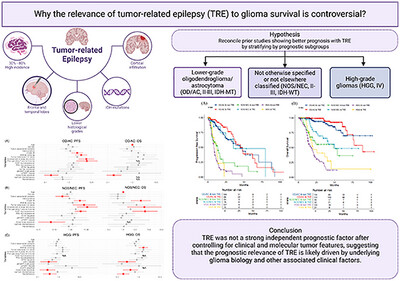
This multi-center retrospective study evaluated the risk factors and prognostic impact of tumor-related epilepsy (TRE) in 1,036 adult patients with diffuse gliomas. Patients were classified into three prognostic groups: OD/AC (IDH-MT, lower-grade gliomas), NOS/NEC (IDH-WT, unclassified grade II-III), and HGG (high-grade gliomas). TRE incidence was highest in OD/AC (44.4%) and lowest in HGG (16.5%). Age was an independent predictor of TRE in OD/AC, while the absence of deep structure involvement was linked to TRE in NOS/NEC and HGG. Univariate analysis showed TRE was associated with longer progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), particularly in NOS/NEC patients (median PFS: 35.2 vs. 13.6 months, P = 0.02). However, TRE was not a significant prognostic factor in multivariate models. These findings suggest TRE's prognostic role is likely influenced by glioma biology and clinical factors rather than being an independent predictor of survival outcomes.
Insomnia Associated With Increased Risk of Atopic Dermatitis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 05 May 2025
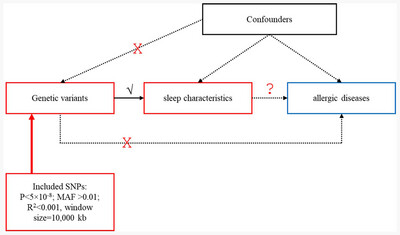
This study used Mendelian randomization to explore the causal relationships between sleep traits and allergic diseases. Results showed that genetically predicted insomnia increased the risk of atopic dermatitis, while an evening chronotype reduced the risk of allergic rhinitis. The analysis confirmed these associations' robustness, highlighting the potential of sleep-based interventions in managing allergic diseases.
Causality Between Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Suicide Attempt: A Mendelian Randomization Study
- First Published: 05 May 2025
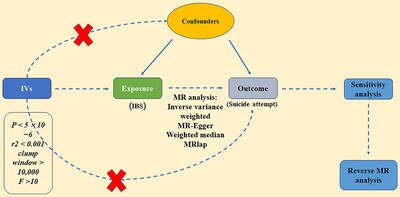
Using univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization (IVW, MR-Egger, weighted median) on large European cohorts, we demonstrate a robust causal relationship between IBS and increased suicide attempt risk. These findings underscore the importance of early detection and targeted intervention in IBS patients to mitigate suicide risk.
Validation of the Spanish Version of the Headache Impact Test (HIT-6) in Patients With Episodic Migraine
- First Published: 05 May 2025
Tangeretin Improves the Memory of Swiss Mice, Suggesting Potential Molecular Interventions Through Animal Behavior Assessments and In Silico Studies
- First Published: 05 May 2025
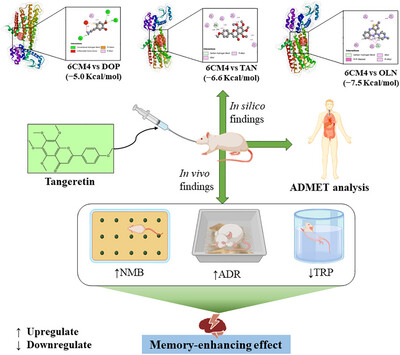
Swiss mice treated with tangeretin showed better performance in marble burying, dust removal, and trained swimming tests, resulting elevation of memory performance, problem-solving, and motor coordination. The compound also demonstrated a remarkable binding affinity toward the D2 receptor with favorable pharmacokinetic properties in in silico analysis indicating as protential therapeutic agent.
Assessment of Sedative Activity of Lonicerin: In Vivo Approach With Pharmacokinetics and Molecular Docking
- First Published: 05 May 2025
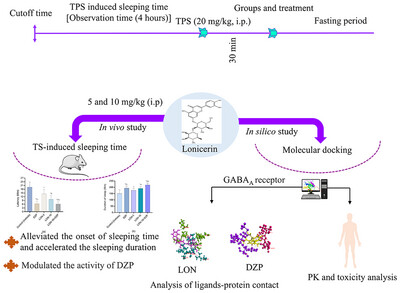
Lonicerin (LON) at doses of 5 and 10 mg/kg reduced sleep latency and increased sleep duration in mice, with combined LON and diazepam showing maximal effects. Computational docking showed LON binds to GABAA receptor sites with a strong affinity (−8.1 kcal/mol), suggesting potential as an insomnia treatment.
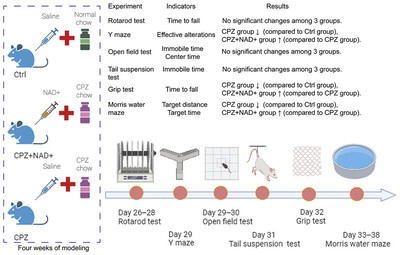
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Supplementation Improves Cuprizone-Induced Multiple Sclerosis-Related Behavioral Changes in C57BL/6J Mice
- First Published: 05 May 2025
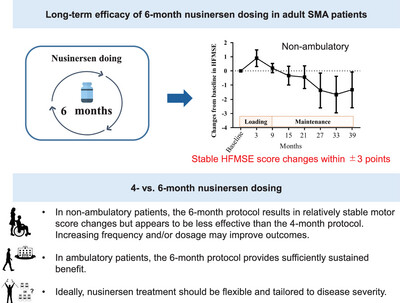
Long-Term Effects of Nusinersen Dosing Frequency on Adult Patients With Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Efficacy of a 6-Month Dosing Interval
- First Published: 05 May 2025
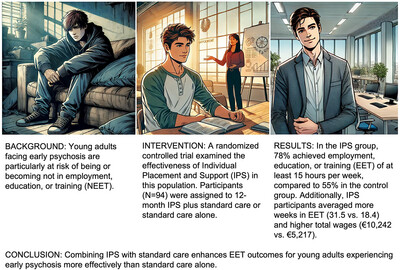
Efficacy of Individual Placement and Support (IPS) on Employment, Education, and Training in Young Adults With Early Psychosis—A Randomized Controlled Trial
- First Published: 05 May 2025
Suppression of Deactivation of Working Memory and Promotion of Activation of Sustained Attention in the Default Mode Network Are Affected by Schizotypy in a Large Sample of Nonclinical Subjects
- First Published: 07 May 2025
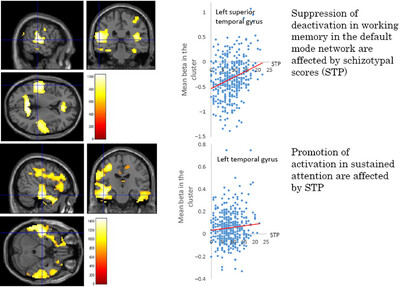
The greater the schizotypy is, the weaker task-induced deactivation of the default mode network is during the task.
The observed cognitive–perceptual deficits were mainly related to disturbances in the default mode network.
Disturbance of the default mode network might be a common feature in both the nonclinical and the clinical schizophrenia spectra.
Pathological Aging of Patients With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Preliminary Longitudinal Study
- First Published: 07 May 2025
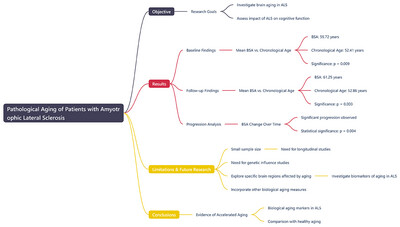
This study utilizes a deep learning approach called Brain Structure Ages (BSA) to demonstrate accelerated and progressive biological brain aging in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), highlighting its potential as a valuable tool for understanding disease progression and informing future therapeutic strategies.
Unraveling the Role of α2δ-1 in Cerebral Hemorrhage: Calcium Overload, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Microglial Apoptosis
- First Published: 07 May 2025
An Examination of the Effect of Parent-Centered Nutrition Education on the Oxidant-Antioxidant Parameters of Children Diagnosed With Autism Spectrum Disorder
- First Published: 13 May 2025
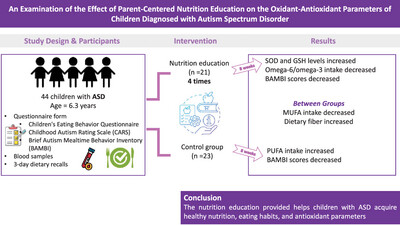
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that produces symptoms from the early years of life. This study was conducted to examine the effect on total antioxidant capacity and antioxidant–oxidant parameters in the diet in children of nutrition education provided by specialist dieticians for the families of children diagnosed with ASD aged 3–18 years. As a result, it shows that the nutrition education provided helps children with ASD acquire healthy nutrition and eating habits, prevents nutritional deficiencies, alleviates nutrition-related symptoms, ensures healthy growth and development, improves the quality of life of families, and reduces stress factors.
Multiple Sclerosis and Seizures: Clinical, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Correlations
- First Published: 07 May 2025

In this study, we used the South Wales MS registry to identify people with multiple sclerosis/clinically isolated syndrome (MS/CIS) and a lifetime history of seizure(s). MR brain images nearest to time of first seizure were reviewed and compared to a contemporary, matched cohort of pwMS without seizures. We identified 49 historical cases co-existent MS/CIS and seizure(s). On January 1st, 2020 we found that 2.4% (23/950, 95% CI 1.4%–3.4%) of the prevalent population of people with MS/CIS had experienced a seizure and 2.1% (20/950, 95% CI 1.2%–3.0%) had a diagnosis of epilepsy, which is higher than the general population (0.76%). Seizure(s) occurred before other symptoms of MS/CIS in 31% and after in 69%. People with MS/CIS and seizure(s) have a higher number of T2 lesions and more marked brain atrophy.
Resting-State Functional Connectivity of Sensorimotor and Default Mode Networks and Lower Limb Performance in Chronic Stroke: A Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 07 May 2025
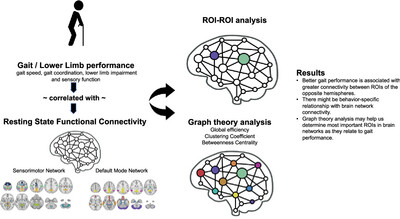
Resting-state connectivity between specific regions of interest (ROI) within SMN and DMN is related to lower limb performance. Interhemispheric connectivity of non-homologous ROIs was associated with better function. Graph theory analysis demonstrated the complex role that an individual ROI has in relation to sensorimotor function of lower extremity.
Assessment of the Psychological Burden Among Family Caregivers of People Living With Dementia, Parkinson's, and Alzheimer's Disease Using the Zarit Burden Interview From Bangladesh
- First Published: 07 May 2025
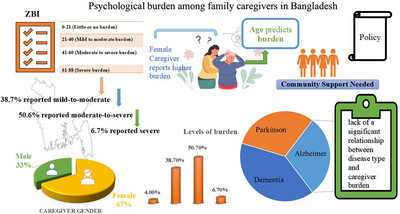
As indicated by Zarit Burden Interview (ZBI) scores, the majority of caregivers experienced moderate to severe burden, according to the study. This study highlights the burden experienced by caregivers of dementia, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease patients in Bangladesh and recommends community interventions to address this issue and inform targeted interventions to reduce caregiver burden.
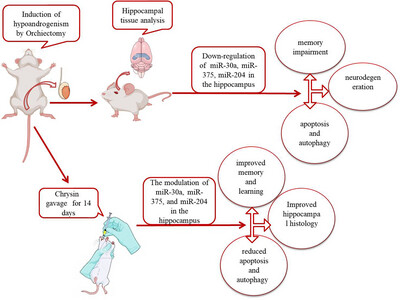
Chrysin Modulates Behavior and Hippocampal Histopathology in Adult Male Hypoandrogenic Rats: The Regulatory Role of miR-30a, miR-375, and miR-204
- First Published: 07 May 2025
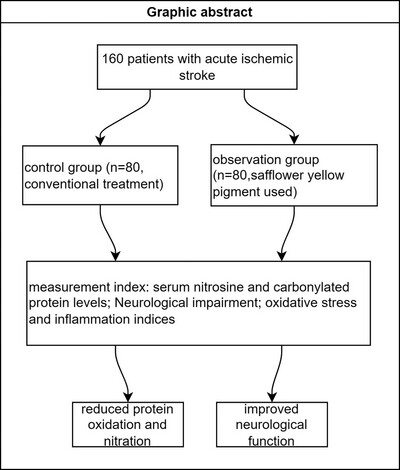
Safflower Yellow Pigment Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Protein Nitration and Oxidative Modulation
- First Published: 08 May 2025
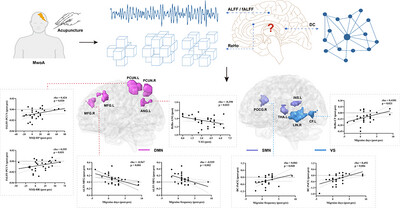
Multi-Spatial Voxel-Scale Modulation of Acupuncture on Abnormal Brain Activity in Migraine Patients Without Aura: A Randomized Study Neuroimaging Trial
- First Published: 08 May 2025
Amelioration of Chronic Ethanol Administration-Induced Learning and Memory Impairments by High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and Ritalin
- First Published: 08 May 2025
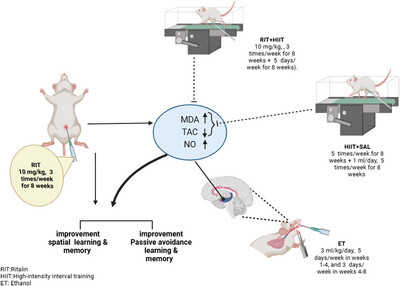
The current study investigated the impacts of 8-week high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and Ritalin, alone and in combination, on cognitive functions and hippocampal oxidative parameters following chronic ethanol consumption in male rats. Adult male rats were divided into eight groups and received one of the following treatments: ethanol 20% (ET) (3 mL/kg/day, orally, 5 consecutive days/week in weeks 1–4, and 3 consecutive days/week in weeks 4–8), Ritalin (RIT) (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneally, three consecutive times/week for 8 weeks), HIIT + SAL (five consecutive times/week for 8 weeks + saline injection), or saline (1 mL/day, intraperitoneally, three consecutive times/week for 8 weeks). Cognitive performance was assessed using the Morris water maze (MWM) and passive avoidance tasks. Oxidative stress markers were measured in the hippocampus. Chronic ethanol consumption caused learning and memory deficits and disrupted oxidant/antioxidant balance in the hippocampus of rats. HIIT potentially improved memory impairments by restoring this balance, whereas Ritalin ameliorated cognitive dysfunction through a mechanism that requires further investigation.
Chronotype Predicts Body Mass Index via Emotion Regulation Strategy Use and Emotional Eating
- First Published: 08 May 2025
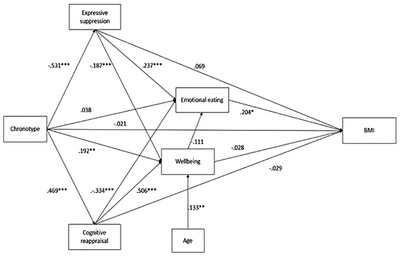
Individuals with an evening chronotype reported greater use of expressive suppression, which was associated with a greater tendency to emotionally eat and a higher body mass index (BMI). In contrast, individuals with a morning chronotype reported more frequent use of cognitive reappraisal, which was associated with reduced emotional eating and a lower BMI. These findings suggest a clear pathway through which chronotype might be associated with BMI, with evening chronotypes at a greater risk of weight gain.
The Effect of Combining Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation and Pain Neuroscience Education in Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain and High Pain Catastrophizing: An Exploratory Clinical, Cognitive, and fMRI Study
- First Published: 08 May 2025
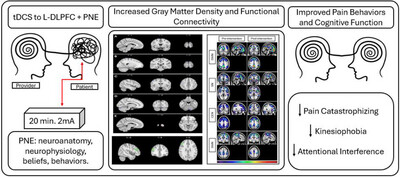
Participants with chronic low back pain and high pain catastrophizing underwent five sessions of tDCS to the left DLPFC and Pain Neuroscience Education (PNE). Participants showed increases in gray matter density and functional connectivity as well as improvements in pain behaviors and cognitive performance. Our clinical and fMRI outcomes shed light on the clinical potential of combining tDCS and PNE, as well as the mechanisms substantiating their effects.
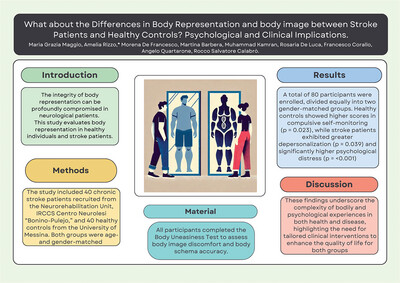
What About the Differences in Body Representation and Body Image Between Stroke Patients and Healthy Controls? Psychological and Clinical Implications
- First Published: 08 May 2025
Combined Effect of HF-rTMS and Whole-Body Vibration Exercise on Cognitive Efficiency in Esports Players With or Without Sedentary Behaviors: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- First Published: 08 May 2025
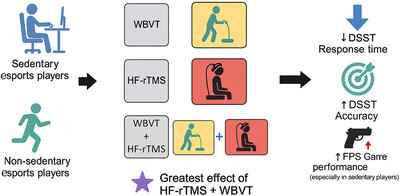
The study demonstrated that sedentary behavior had a detrimental effect on the cognitive function in esports players. Furthermore, HF-rTMS and WBVT, especially in combination, effectively enhanced cognitive performance in esports players, with a more pronounced effect in those with sedentary lifestyles.
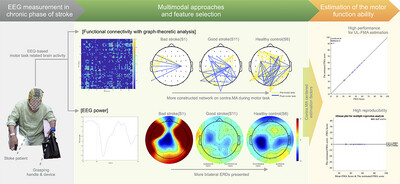
Estimation of Stroke's Motor Function Ability Using Multimodal Biomarkers and the Role of Contralesional Motor Area
- First Published: 08 May 2025
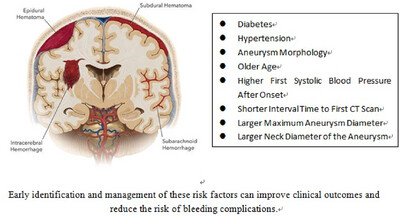
Identification of Risk Factors Influencing Hemorrhage Volume in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- First Published: 08 May 2025
METHOD
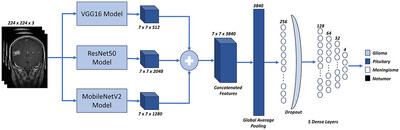
Fusion-Brain-Net: A Novel Deep Fusion Model for Brain Tumor Classification
- First Published: 08 May 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
An Exploratory Analysis of Rhythmic Auditory Stimulation's Impact on Brain Function in Parkinson's Disease Patients With Freezing of Gait
- First Published: 08 May 2025
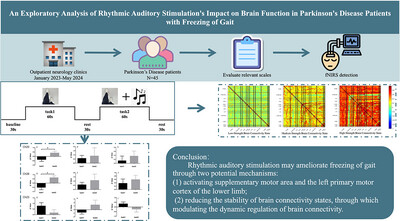
Rhythmic auditory stimulation may ameliorate freezing of gait through two potential mechanisms: (1) activating the supplementary motor area and the left primary motor cortex of the lower limb and (2) reducing the stability of brain connectivity states, through which modulating the dynamic regulation of brain connectivity.
Usefulness of the Support Video “Talking Picture Book” for Overcoming Hesitancy to Start Galcanezumab Therapy
- First Published: 11 May 2025
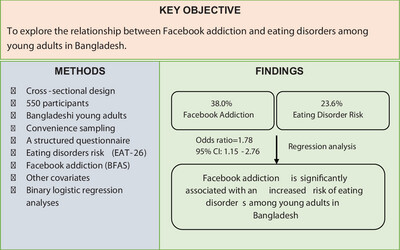
Exploring the Relationship Between Excessive Social Media Use and Eating Disorders Among Young Adults: Evidence From a Bangladesh-Based Cross-Sectional Study
- First Published: 11 May 2025
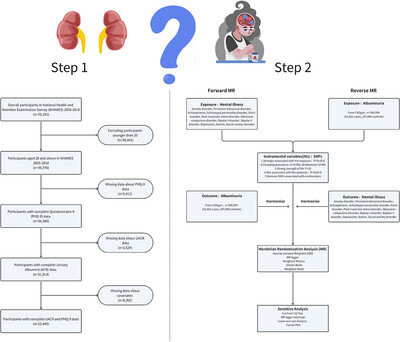
Albuminuria and Mental Illness Risk: Results From National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005–2018 and Mendelian Randomization Analyses
- First Published: 11 May 2025
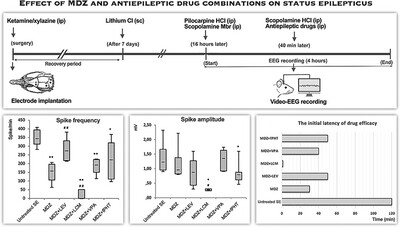
Effective Protection Against Status Epilepticus Caused by Lithium–Pilocarpine: Combination of Midazolam and Lacosamide
- First Published: 11 May 2025
Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Disturbances of Purine Metabolism and Glutamate Metabolism in the Hippocampus of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mouse Model of Depression
- First Published: 11 May 2025
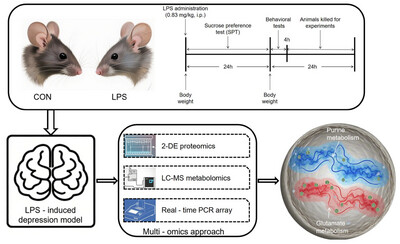
The study focused on a mouse model of depression induced by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and employed innovative multi-omics approaches, including two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) for proteomics, liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) for metabolomics, and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) microarray technology to analyze the hippocampus of mice. Through these techniques, we found that compared to the control group, there were 81 differentially expressed proteins, 44 differential metabolites, and 4 differential mRNAs in the mice treated with LPS. The integrated analysis of this multidimensional data revealed that purine metabolism and glutamate metabolism are the most significantly altered molecular pathways in depression induced by LPS.
Life Beyond Childhood: Insight Into the Lived Experience of 91 Adults With KBG Syndrome Through an Online Patient/Caregiver-Reported Co-Produced Questionnaire
- First Published: 11 May 2025
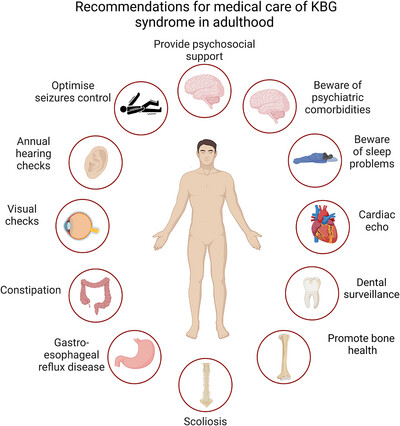
KBG syndrome (KBGS) is one of the most common monogenic causes of ID alongside short stature, macrodontia, and other variable features. Phenotypes in childhood are well documented, but data are lacking about adulthood and how best to support individuals. This study provides essential data on the lived experience of KBGS in adulthood.
REVIEW
Does the Use of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Improve Clinical Outcomes in Adults With Autoimmune Encephalitis? A Systematic Review
- First Published: 12 May 2025
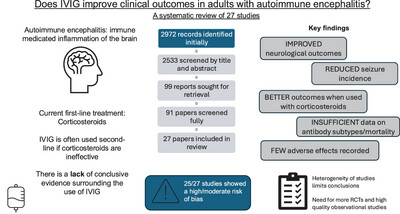
Evidence surrounding the use of IVIG in treating autoimmune encephalitis has yet to be evaluated and yet IVIG is used second line in this condition, after corticosteroids. IVIG is prone to donor shortages and therefore it would prove beneficial to establish whether this is an effective treatment; it can then be prioritised for this condition or others.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Cortical Structure in Nodes of the Default Mode Network Estimates General Intelligence
- First Published: 12 May 2025
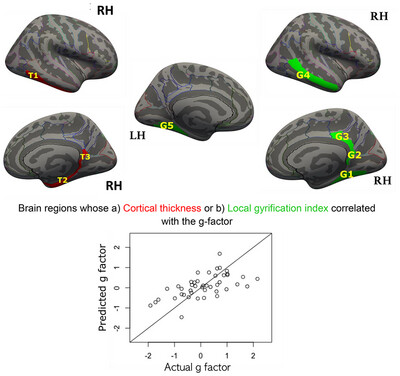
In young, healthy adults, we found that cortical morphology - specifically, the cortical thickness and local gyrification index - in key medial and temporal nodes of the default mode network, correlated reliably with the general intelligence (g) factor. These cortical parameters may be used in a regression model to estimate the g-factor.
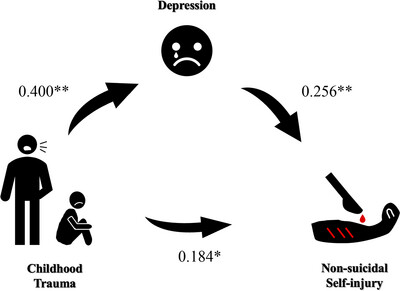
Mediating Role of Depression Severity in the Relationship Between Childhood Trauma and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Among Adolescents With Mood Disorders
- First Published: 13 May 2025
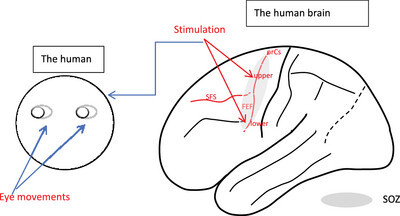
Frontal Eye Field in the Precentral Sulcus: A Direct Electrical Cortical Stimulation Study With Stereo-EEG Electrodes
- First Published: 13 May 2025
Risk Factors and Prognostic Models in Acute Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke: Insights From ASPECTS-Net Water Uptake
- First Published: 13 May 2025
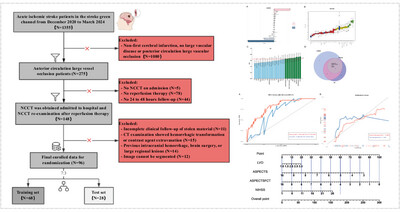
Our analysis identifies significant predictors of poor prognosis in anterior circulation acute large vessel occlusive stroke (ALVOS) patients after endovascular reperfusion. Specifically, ASPECTS-net water uptake (ASPECTS-NWU), combined with NIHSS and large vessel occlusion (LVO), demonstrates strong prognostic value. These findings highlight ASPECTS-NWU as a promising biomarker for individualized risk assessment and provide insights into optimizing post-reperfusion outcomes in ALVOS patients.
Advancing Nutritional Status Classification With Hybrid Artificial Intelligence: A Novel Methodological Approach
- First Published: 13 May 2025
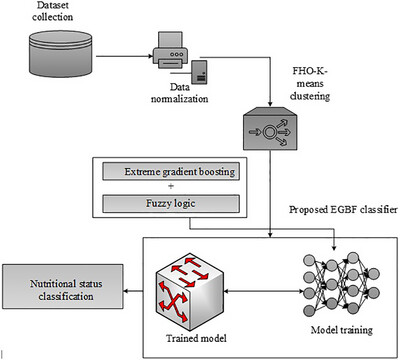
This graphical abstract illustrates a novel hybrid AI framework that integrates Fire Hawk Optimizer-based K-Means clustering with Extreme Gradient Boosting Fuzzy classification to accurately identify and classify childhood nutritional statuses, enabling data-driven interventions for malnutrition in developing nations.
Effect of Probucol and Atorvastatin Treatment on the Self-Care Ability of Acute Cerebral Infarction Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study
- First Published: 13 May 2025
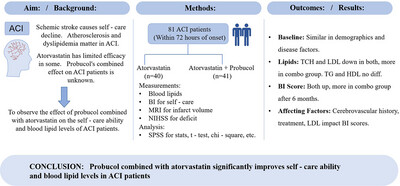
This study assessed the effects of combining probucol with atorvastatin on self-care ability and blood lipids in acute cerebral infarction (ACI) patients. Eighty-one patients within 72 h of onset were assigned to receive either atorvastatin alone or atorvastatin plus probucol. Key measures included blood lipid levels, Barthel Index (BI) for self-care, and MRI for infarct volume. The combination group showed greater reductions in total cholesterol and LDL, with improved BI scores after 6 months. These results suggest that probucol combined with atorvastatin enhances lipid control and self-care in ACI patients.
The Relationship Between Childhood Maltreatment and Insomnia in Depressed Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Rumination
- First Published: 13 May 2025
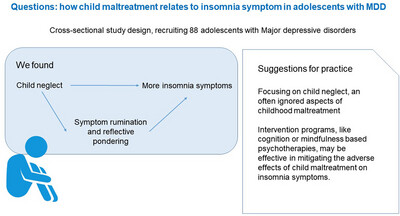
We suggested an early screening and prevention of child maltreatment to prevent the onset of insomnia symptoms in adolescents with major depressive disorders. Special attention should be given to the child neglect, which is often ignored and difficult to detect in practice. Moreover, this study found symptom rumination and reflective pondering may mediate the association between childhood maltreatment and insomnia, which may be intervention targets to reduce the adverse effects of child neglect on insomnia symptoms.
Machine Learning-Based Identification of Children With Intermittent Exotropia Using Multiple Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features
- First Published: 13 May 2025
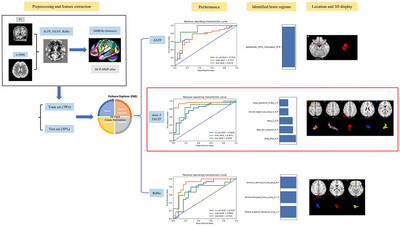
The machine learning methods combined with resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging parameters (ALFF, slow-5 fALFF, and ReHo) had good classification performance in distinguishing intermittent exotropia (IXT) children from healthy controls (HCs). Among several parameters, the slow-5 fALFF showed the best classification performance. The slow-5 fALFF can be a promising biomarker for distinguishing IXT children from HCs.
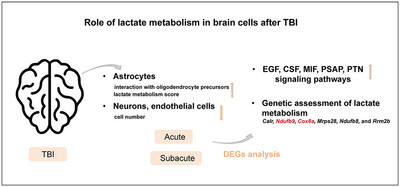
Single-Cell RNA and Transcriptome Sequencing to Analyze the Role of Lactate Metabolism in Traumatic Brain Injury Astrocytes
- First Published: 21 May 2025
REVIEW
Evolution Trend of Brain Science Research: An Integrated Bibliometric and Mapping Approach
- First Published: 21 May 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
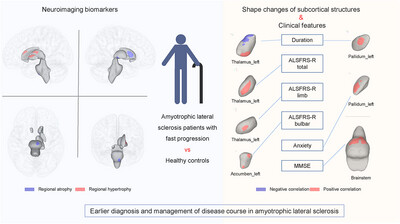
Shape Alterations of Subcortical Nuclei Correlate With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Progression
- First Published: 19 May 2025
Associations Between Cortical Iron Accumulation and Memory in Patients With Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and in Cognitively Normal Individuals
- First Published: 19 May 2025
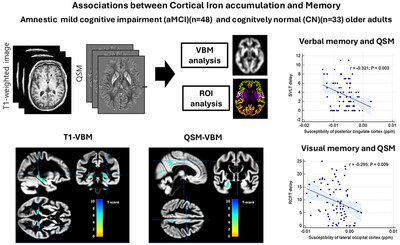
The T1-weighted VBM analysis revealed significant hippocampal atrophy in the aMCI group. QSM-VBM showed increased iron accumulation in multiple brain regions (FWE-corrected p < 0.05). Lower hippocampal volume and higher posterior cingulate cortex susceptibility predicted verbal memory, while higher lateral occipital susceptibility predicted visual memory. These findings suggest iron accumulation may precede atrophy, serving as a potential early marker of neurodegeneration.
Infralimbic GABAergic May be the Target of Asiaticoside on Alleviating Bone Cancer Pain
- First Published: 19 May 2025
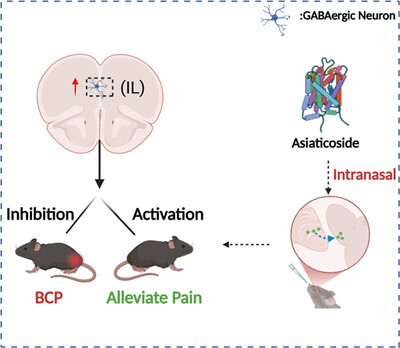
Our study demonstrates that AS alleviates BCP by selectively targeting GABAergic neurons in the infralimbic cortex (IL). These findings highlight the pivotal role of IL GABAergic signaling in pain modulation. Furthermore, this study provides preclinical evidence supporting AS to be a promising pharmacological agent with a targeted delivery strategy for clinical pain intervention. Further research is needed to elucidate the downstream neural circuits involved in AS-mediated analgesia.
REVIEW
When Silence Breaks: The Influence of Pure Tones and White Noises on Conditioned Flight Responses
- First Published: 19 May 2025
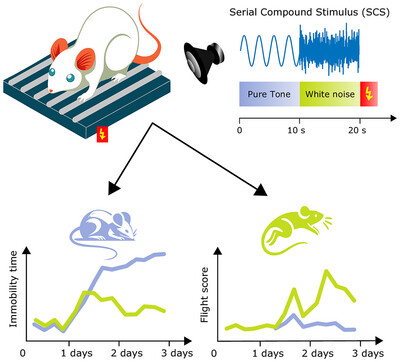
A novel behavioral paradigm by Fadok et al. (2017) pairs a sequence of pure tone and white noise with footshock. After learning, the mouse shows freezing during pure tones and jumps during white noise. This discovery produced shows great potential for the study of fear learning and maladaptive responses.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
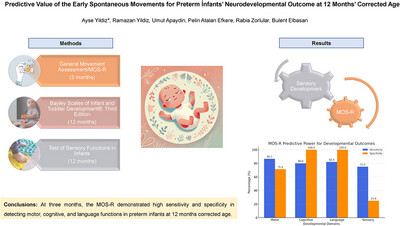
Predictive Value of the Early Spontaneous Movements for Preterm Infants’ Neurodevelopmental Outcome at 12 Months’ Corrected Age
- First Published: 19 May 2025
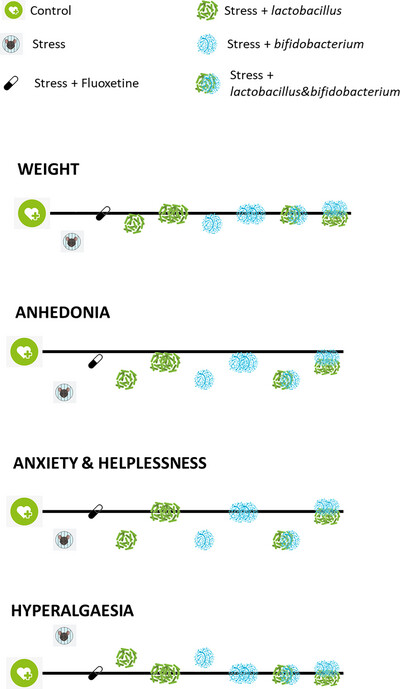
Combined Administration of Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium Offers Enhanced Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Activity in a Dose Dependent Manner
- First Published: 18 May 2025
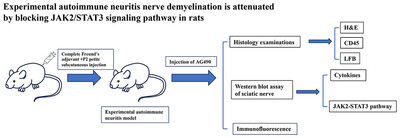
Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis Nerve Demyelination Is Attenuated by Blocking JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Rats
- First Published: 18 May 2025
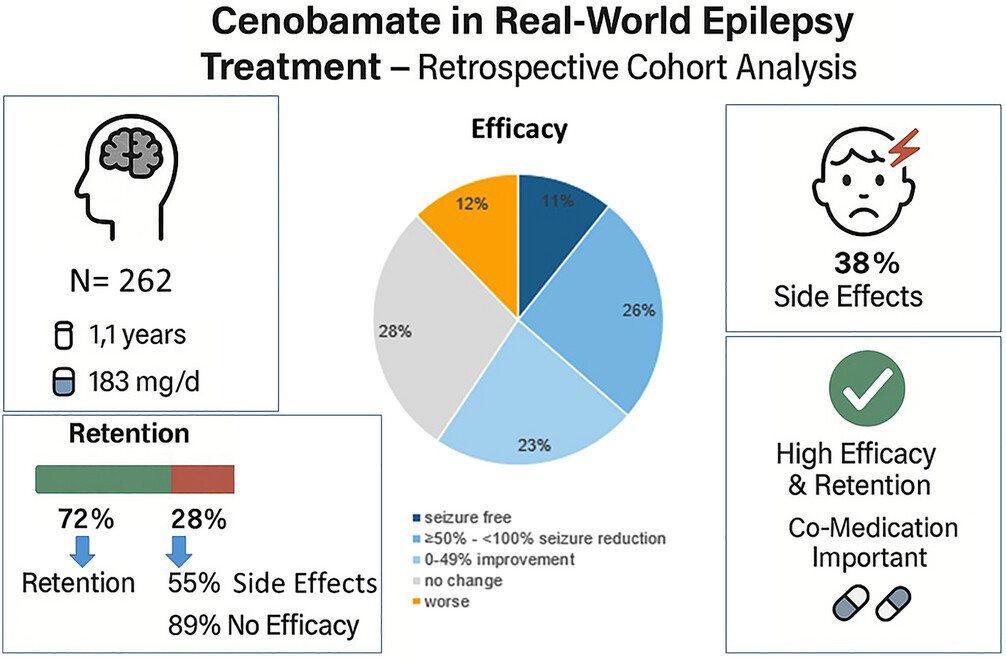
Cenobamate in Real-Word Scenario: Results on Efficacy, Side Effects, and Retention Rate in a Single Center Retrospective Study
- First Published: 18 May 2025
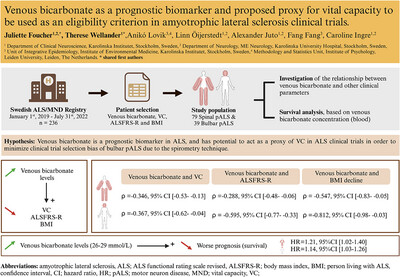
Venous Bicarbonate as a Prognostic Biomarker and Proposed Proxy for Vital Capacity to Be Used as an Eligibility Criterion in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Clinical Trials
- First Published: 18 May 2025
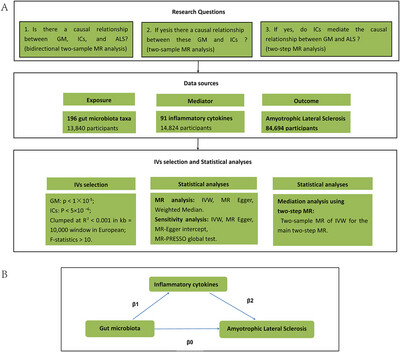
Causal Relationships Between the Gut Microbiota, Inflammatory Cytokines, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis
- First Published: 18 May 2025
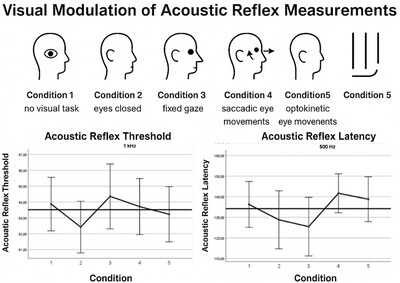
Visual Modulation of Acoustic Reflex Measurements: Insights Into Sensory Integration
- First Published: 18 May 2025
Latent Default Mode Network Connectivity Patterns: Associations With Sleep Health and Adolescent Psychopathology
- First Published: 19 May 2025
A Single Session of tDCS Stimulation Can Modulate an EEG Microstate Associated With Anxiety in Patients With Depression
- First Published: 19 May 2025
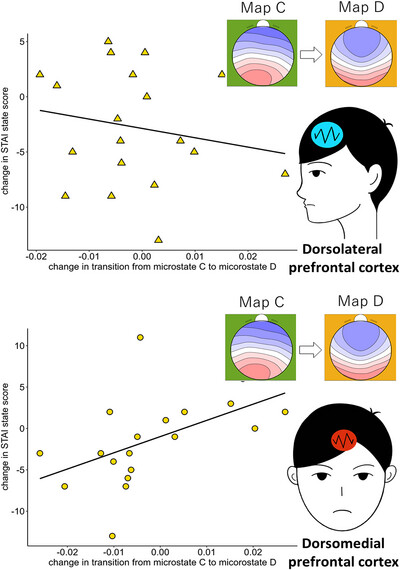
The findings demonstrated a significant increase in the duration of microstate class D following stimulation, while no changes were observed in class C. Moreover, transitions from microstate class C to D exhibited a correlation with the state-trait anxiety inventory-state anxiety (STAI-SA) scores following dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (DMPFC) stimulation. In contrast, transitions from class D to C were linked to left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) stimulation, albeit without a significant correlation. These results underscore the distinct and site-specific effects of neural stimulation on anxiety-related brain states.
CORRECTION
Correction to “Evaluation of Risk Factors in Patients with Chronic Daily Headache and Medication-Overuse Headache”
- First Published: 21 May 2025
REVIEW
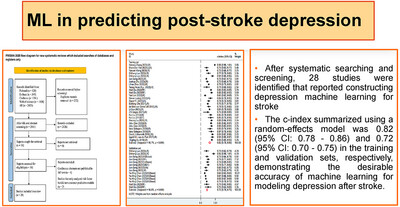
Accuracy of Machine Learning in Predicting Post-Stroke Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 26 May 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Effects of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Upper Limb Motor Function and Serum Lipid Metabolomics in Patients With Ischemic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Study
- First Published: 26 May 2025
Both low- and high-frequency rTMS enhance upper limb motor function/self-care in ischemic stroke, with low-frequency showing superior motor gains. Lipidomics revealed upregulated diacylglycerol phosphoinositide (DAG-PI) and triacylglycerol (TAG) and reduced dialkyl glycerol (DAG) levels post-intervention.
The Causal Relationship Between Asthma and Hippocampal Volume: A Study Based on Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Analysis
- First Published: 26 May 2025
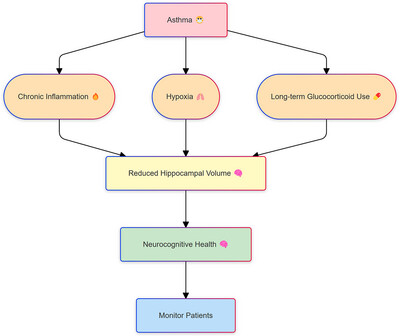
This study reveals a causal relationship between asthma and reduced hippocampal volume using Mendelian randomization analysis. Asthma may negatively impact hippocampal structure via chronic inflammation, hypoxia, and long-term glucocorticoid use, suggesting the need for monitoring neurocognitive health in asthma patients.
Examining the Relationship Between Physical Function and Anxiety/Depression in Parkinson's
- First Published: 26 May 2025
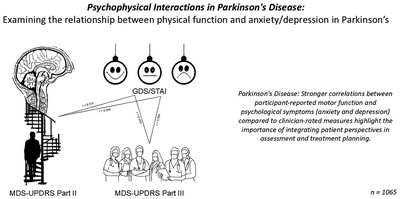
This study reveals significant correlations between participant-reported motor function and psychological symptoms of anxiety and depression in Parkinson's disease. Weaker associations were found between anxiety/depression and clinician-rated measures of physical function. Factors such as age and cognition appear to influence these relationships, emphasizing the importance of integrating patient perspectives in treatment planning. This approach can inform assessment and referral practices, potentially enhancing patient-centered care and improving outcomes.
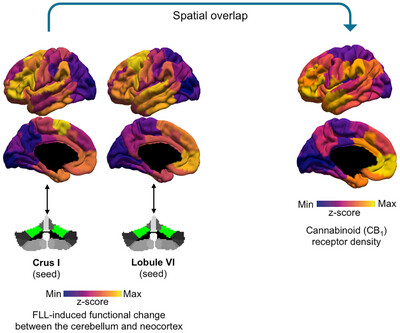
Learning a Foreign Language in Older Adults Shapes the Functional Connectivity of Distinct Cerebellar Sub-Regions With Cortical Areas Rich in CB1 Receptor Expression
- First Published: 26 May 2025
MicroRNA Signatures Predict Brain Amyloidosis and Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease: Insights from [18F] AV45 and FDG PET Imaging
- First Published: 26 May 2025
![MicroRNA Signatures Predict Brain Amyloidosis and Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease: Insights from [18F] AV45 and FDG PET Imaging](/cms/asset/68e1643d-b09e-4d1b-be1d-cf09c58d8a85/brb370572-gra-0001-m.jpg)
This study leverages data from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) to examine differential microRNA expression in patients with MCI or mild AD. This graphical abstract illustrates key findings, including a significant positive correlation between CSF levels of miR-210-3p and Aβ accumulation (B = 4.69). Negative correlations were identified between- several microRNAs (let-7g-5p, miR-423-5p, and miR-660-5p) and glucose reuptake as measured by FDG-PET. These results suggest that specific microRNAs may serve as potential biomarkers for AD progression.
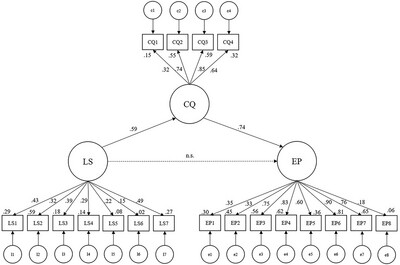
Expatriates' Cultural Intelligence Mediates the Relationship Between Lifestyle and Performance: A Cross-Sectional Analysis and a Longitudinal Pilot Study
- First Published: 26 May 2025
Predictive Model for Early Neurological Deterioration in Acute Ischemic Stroke Utilizing Novel Thrombotic Biomarkers
- First Published: 26 May 2025
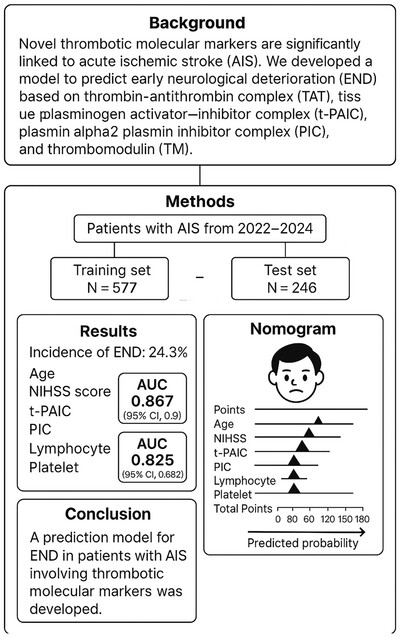
This study developed a predictive nomogram for early neurological deterioration (END) in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) using serum biomarkers tissue plasminogen activator–inhibitor complex (t-PAIC) and plasmin -α2 plasmin inhibitor complex (PIC), age, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score, lymphocyte (lymph), and platelet (PLT). The model demonstrated strong predictive accuracy with well-calibrated and clinical utility for END risk assessment.
Enhancing Teacher Training Through Self-Efficacy and Emotional Intelligence: A Conditional Process Model of Pre-Service Teachers’ Well-Being and Academic Achievements
- First Published: 26 May 2025

Psychological well- being significantly boosts academic achievements among pre- service teachers, especially when supported by strong academic self- efficacy. Emotional intelligence enhances this relationship, highlighting the need to develop both confidence and emotional skills to foster academic success in teacher education.
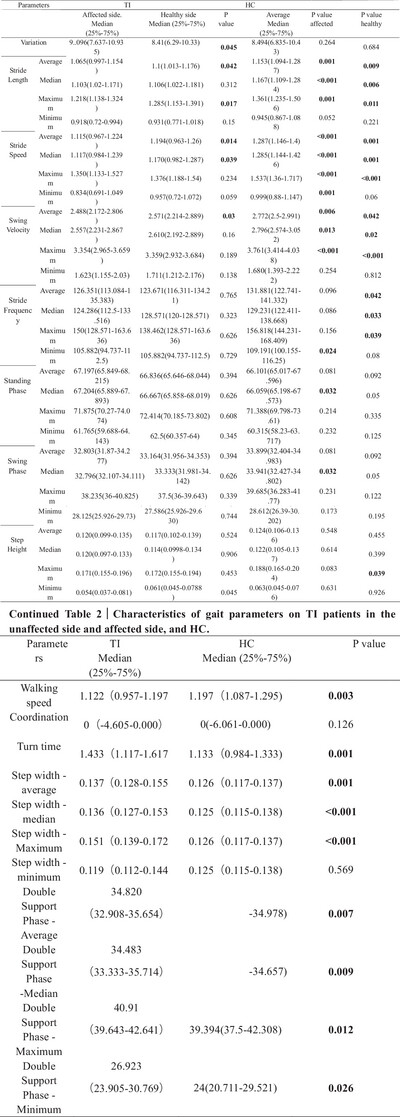
Discrepant Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Gait Impairments in Thalamic Infarction Patients
- First Published: 26 May 2025