Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Simultaneous bilateral cochlear implants: Developmental advances do not yet achieve normal cortical processing
- First Published: 28 February 2017
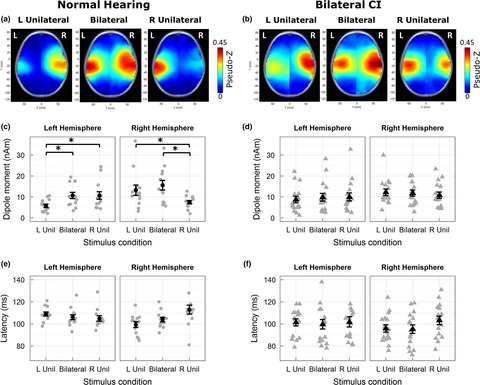
Early bilateral implantation in children promotes normal symmetric cortical activity to unilateral input, supporting calls to eliminate the aural preference syndrome through this treatment. Yet, persistent differences from normal in the implanted group included smaller differences between unilateral and bilateral listening, weaker-than normal preference for contralateral stimuli, and greater recruitment of the occipital areas to process bilateral sounds. Limited differences between conditions in implant users reflect effects of deafness, electrical hearing, and/or use of uncoordinated devices, and may explain reduced spatial acuity in children using bilateral cochlear implants.
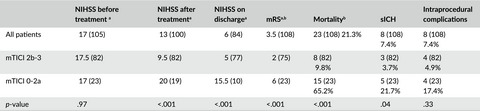
Endovascular stroke treatment in a small-volume stroke center
- First Published: 28 February 2017
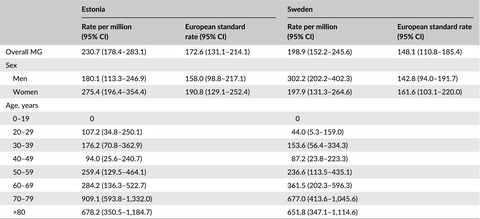
Diversity in mental fatigue and social profile of patients with myasthenia gravis in two different Northern European countries
- First Published: 01 March 2017
Lifelong neurogenesis in the cerebral ganglion of the Chinese mud snail, Cipangopaludina chinensis
- First Published: 03 March 2017
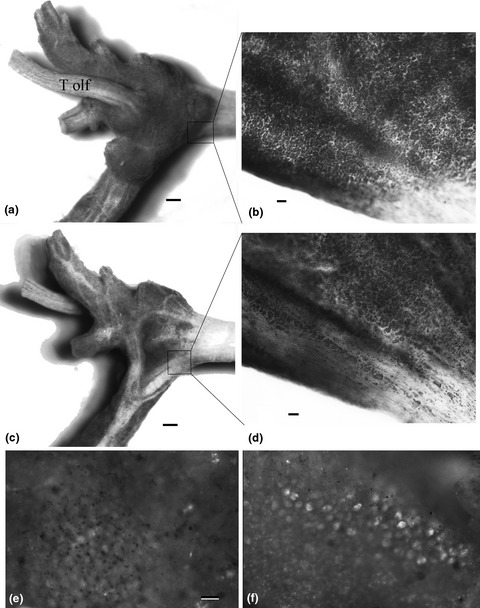
We document neurogenesis across the lifespan in the Chines Mud Snail Cipangopaludina chinensis using direct cell counts and Edu staining. The rate of neurogenesis remains constant across the lifespan and total neuron number in the cerebral ganglion increases with age. New neurons arise mainly near the anterior portion of the cerebral ganglion and especially at the base of nerve roots.
Disrupting dorsolateral prefrontal cortex by rTMS reduces the P300 based marker of deception
- First Published: 03 March 2017
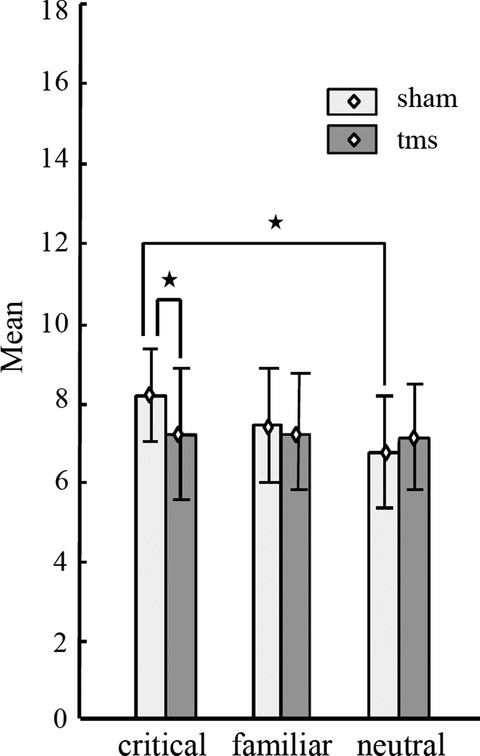
Event-related potential component, P300, is widely considered as the main EEG recorded signature associated with deception: when people deceive, P300 amplitude relatively increases in response to a critical stimulus item (e.g., the name or picture of a stolen merchandise). For the first time, we show that repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation targeted at the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex effectively eliminates this critical difference in the P300 amplitude. Thus, magnetic stimulation of the brain can be used in order to desensitize a subject to critical stimuli in the context of lie detection.
Awareness, apathy, and depression in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment
- First Published: 06 March 2017
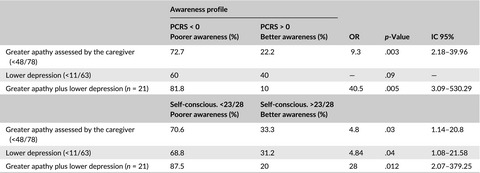
Awareness in 20 patients with Alzheimer's disease and 20 amnestic mild cognitive impairment has been assessed with a clinical rating scale and a patient versus caregiver report scale. The main results of this study showed (1) that the groups were comparable on the two awareness scales and (2) that the correlates of awareness were mainly affective and behavioral whatever the stage of the disease (mild cognitive impairment vs. mild Alzheimer's disease) and irrespective of the assessment method (clinical rating vs. patient-caregiver report). So, greater apathy and lower depression were associated with poorer awareness on both awareness scales.
White matter connections of the inferior parietal lobule: A study of surgical anatomy
- First Published: 08 March 2017
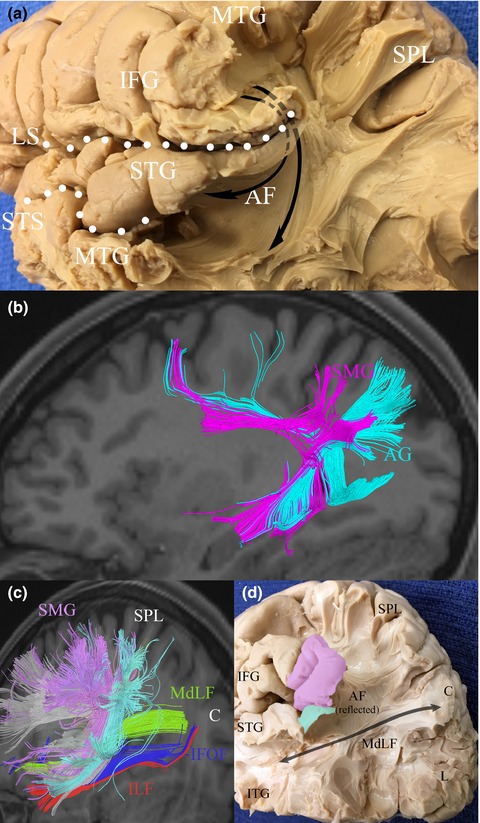
A basic understanding of the nuanced white-matter anatomy of the inferior parietal lobule may be useful to preserving the semantic network when operating in this region of the brain. We identified three major types of connections in this region. This study highlights the principle white-matter pathways and highlights key underlying connections.
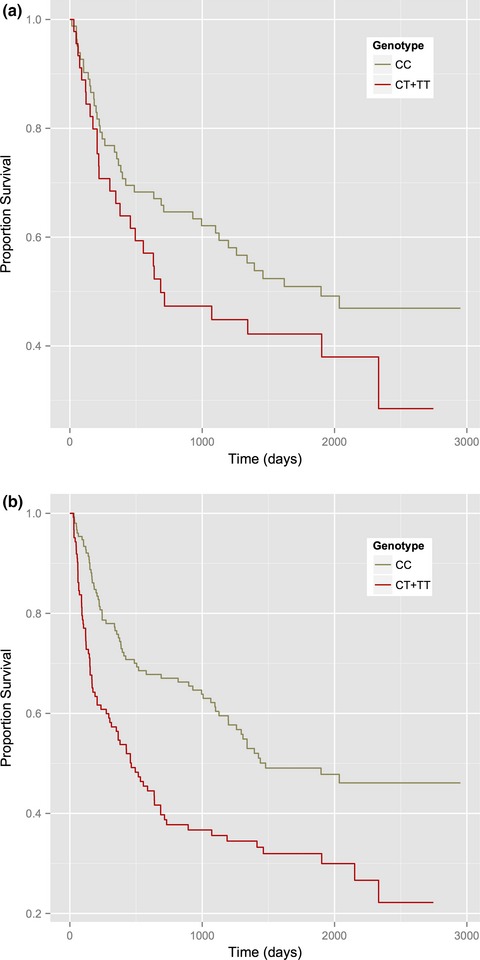
Variation within MBP gene predicts disease course in multiple sclerosis
- First Published: 09 March 2017
Elevated C-X-C motif ligand 13 and B-cell-activating factor levels in neuromyelitis optica during remission
- First Published: 10 March 2017
Basic taste processing recruits bilateral anteroventral and middle dorsal insulae: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of fMRI studies
- First Published: 10 March 2017
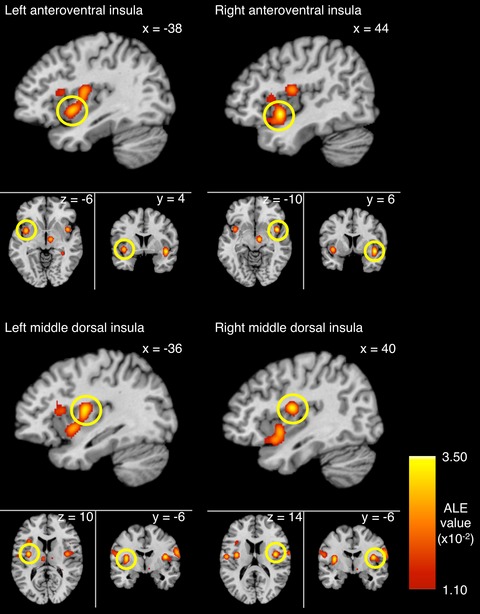
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first meta-analytic research paper specific to taste processing that evaluates the contribution of each basic taste to the activated clusters. Results indicated that taste processing employs bilateral cortical regions, and these regions are connected with other regions responsible for attentiveness and emotion. Sweet taste is the predominant taste being studied.
Catastrophic outcome of patients with a rebound after Natalizumab treatment discontinuation
- First Published: 14 March 2017
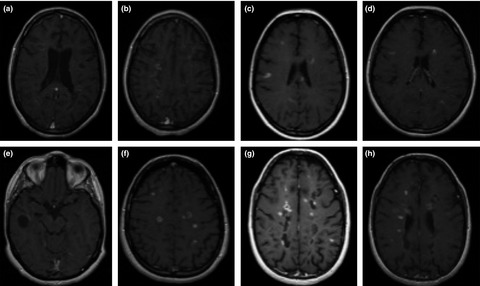
In this article, we presented four cases and analyzed the actual evidence of rebound after Natalizumab (NTZ) withdrawal, clinical and radiological features are discussed. We think it is important to asses carefully the risk/benefit of withdrawing NTZ in MS patients in order to prevent severe and permanent sequelaes.
Targeted sequencing identifies genetic polymorphisms of flavin-containing monooxygenase genes contributing to susceptibility of nicotine dependence in European American and African American
- First Published: 15 March 2017
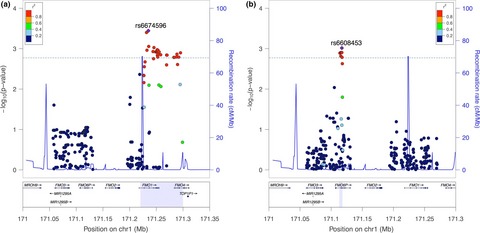
In this study, we investigated the potential of FMO genes to confer risk of nicotine dependence via deep targeted sequencing in 2,820 study subjects comprising 1,583 nicotine dependents and 1,237 controls from European American and African American. Specifically, we focused on the two genomic segments including FMO1, FMO3, and pseudo gene FMO6P, and aimed to investigate the potential association between FMO genes and nicotine dependence. We identified different clusters of significant common variants in European (with most significant SNP rs6674596, p = .0004, OR = 0.67, MAF_EA = 0.14) and African Americans (with the most significant SNP rs6608453, p = .001, OR = 0.64, MAF_AA = 0.1).
Acute stroke alert activation, emergency service use, and reperfusion therapy in Sweden
- First Published: 15 March 2017
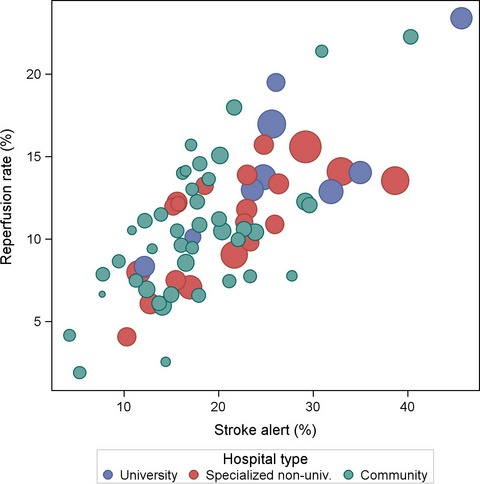
This nationwide study included 49,907 patients admitted with acute stroke who were registered in The Swedish Stroke Register (Riksstroke) in 2011–2012. Acute stroke alerts have a significant potential to improve stroke reperfusion rates. Prehospital stroke management varies conspicuously between hospitals and patient groups, and the elderly and patients living alone have a markedly reduced likelihood of stroke alerts.
Neural evidence for phonologically based language production deficits in older adults: An fMRI investigation of age-related differences in picture-word interference
- First Published: 15 March 2017
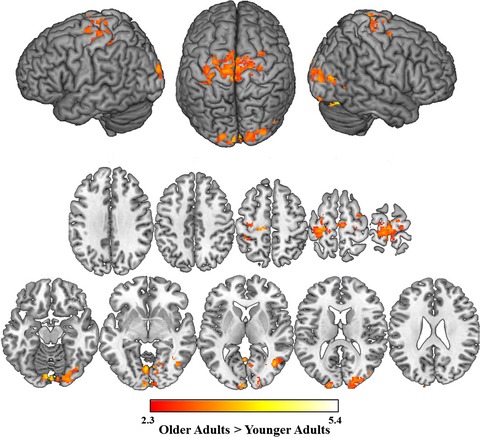
Older adults often show declines in phonological aspects of language production, particularly for low-frequency words, but maintain strong semantic systems. Here, we used fMRI with a picture-word interference task to demonstrate that older adults show less activation during phonological processing and more activation during semantic processing compared with younger adults. Moreover, older adults were more sensitive to changes in picture frequency than younger adults.
Combination of standard axial and thin-section coronal diffusion-weighted imaging facilitates the diagnosis of brainstem infarction
- First Published: 15 March 2017
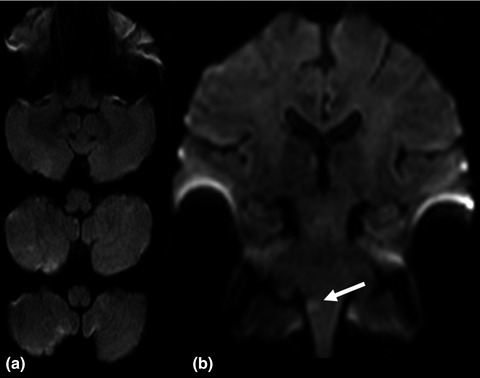
Although diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a very sensitive technique for the detection of small ischemic lesions in the human brain, in particular in the brainstem it may fail to demonstrate acute ischemic infarction. In this study, we demonstrate that in approximately 2% of patients with brainstem infarction the ischemic lesion was detected only on thin-section coronal DWI and in one quarter of patients the ischemic lesion was more easily identified on coronal DWI. Thus, we conclude that combination of axial and thin-section coronal DWI may facilitate the diagnosis of brainstem infarction, and suggest the inclusion of coronal DWI in standard stroke MRI protocols.
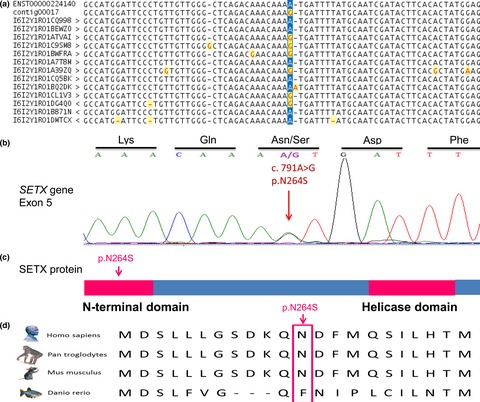
High-throughput sequencing revealed a novel SETX mutation in a Hungarian patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- First Published: 15 March 2017
Prevalence of potential sports-associated risk factors in Swiss amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients
- First Published: 16 March 2017
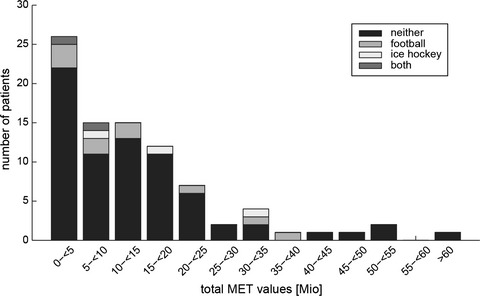
The role of extrinsic risk factors as physical activity, head trauma, and drug/pesticide-exposure in the pathophysiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) remains controversial. We retrospectively studied exposure to extrinsic factors in 92 ALS patients in the presymptomatic stage, using metabolic equivalents. History of head injuries was the only extrinsic risk factor associated with accelerated neurodegeneration in ALS, supporting the hypothesis that not increased physical activity per se, but rather a—yet unknown—genetic profile or lifestyle-promoting physical fitness increases ALS susceptibility.
Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma β-endorphin levels in children with cerebral malaria
- First Published: 17 March 2017
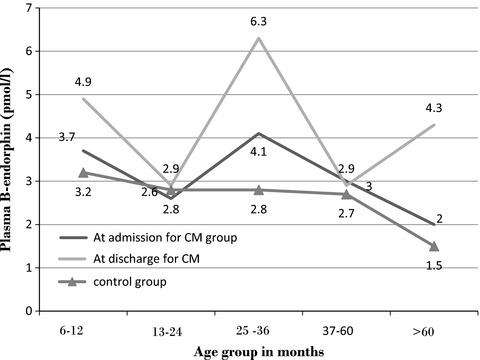
This study on cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma β-endorphin levels in cerebral malaria (CM) was carried out on forty children with CM which is the most lethal form of malaria. It was a cross-sectional study where these 40 children were studied along with 40 age- and sex-matched controls. We found that children with CM had higher plasma β-endorphin levels than the controls with increased production during the course of the illness.
Brain serotonin 4 receptor binding is inversely associated with verbal memory recall
- First Published: 17 March 2017
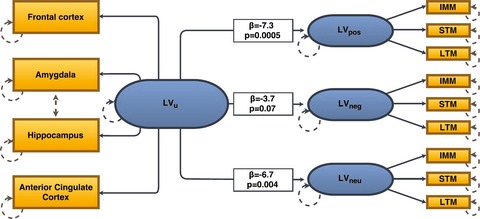
We here present novel evidence of a significant inverse relation between cerebral serotonin 4 receptor (5-HT4R) binding and affective memory performances in healthy volunteers. These findings support the relevance of 5-HT4R in relation to affective components of memory and provide insight into molecular mechanisms that may contribute to the risk architectures for affective disorders and antidepressants effects.
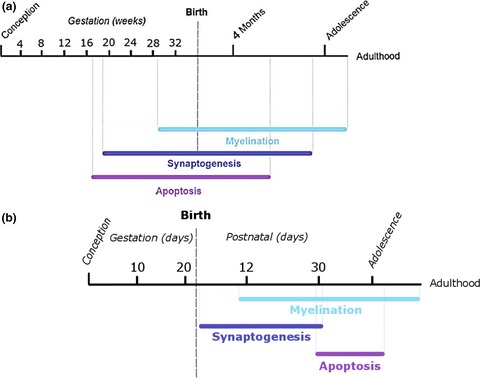
Acute ethanol exposure during late mouse neurodevelopment results in long-term deficits in memory retrieval, but not in social responsiveness
- First Published: 21 March 2017
Data-driven regions of interest for longitudinal change in three variants of frontotemporal lobar degeneration
- First Published: 23 March 2017
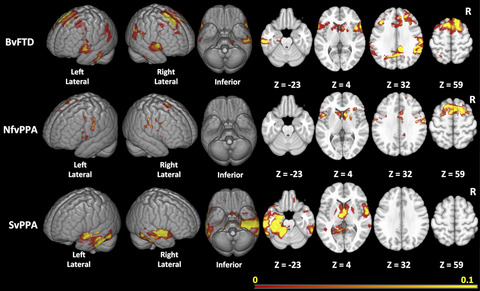
This work describes a process for creating optimized data-driven regions of interest (ROIs) for measuring change in cortical volume in three major variants of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Estimated sample sizes that should be achievable using these ROIs are compared with sample sizes for tracking change in clinical variables.