Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Short Communication
Dupilumab improves outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps irrespective of gender: results from the SINUS-52 trial
- First Published: 08 June 2024
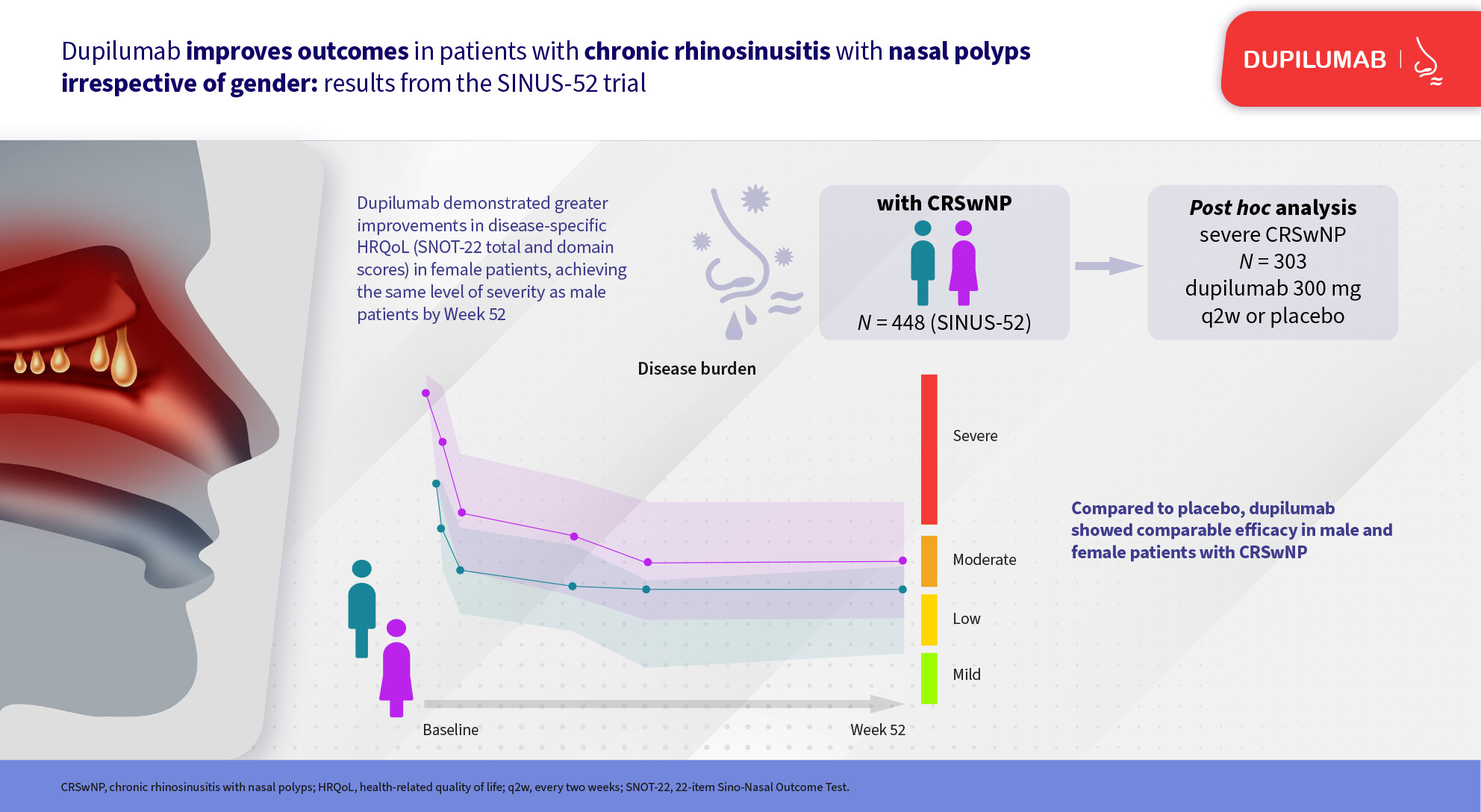
This post hoc analysis of SINUS-52 (NCT02898454) assessed disease characteristics and response to dupilumab treatment in male and female patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. The analysis found female patients had greater asthma, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease and health-related quality-of-life burden at baseline than male patients. Dupilumab treatment significantly improved objective and subjective outcomes compared with placebo through 52 weeks, irrespective of gender.
Original Article
Plasma EBV quantification is associated with the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade and disease monitoring in patients with primary pulmonary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma
- First Published: 03 June 2024
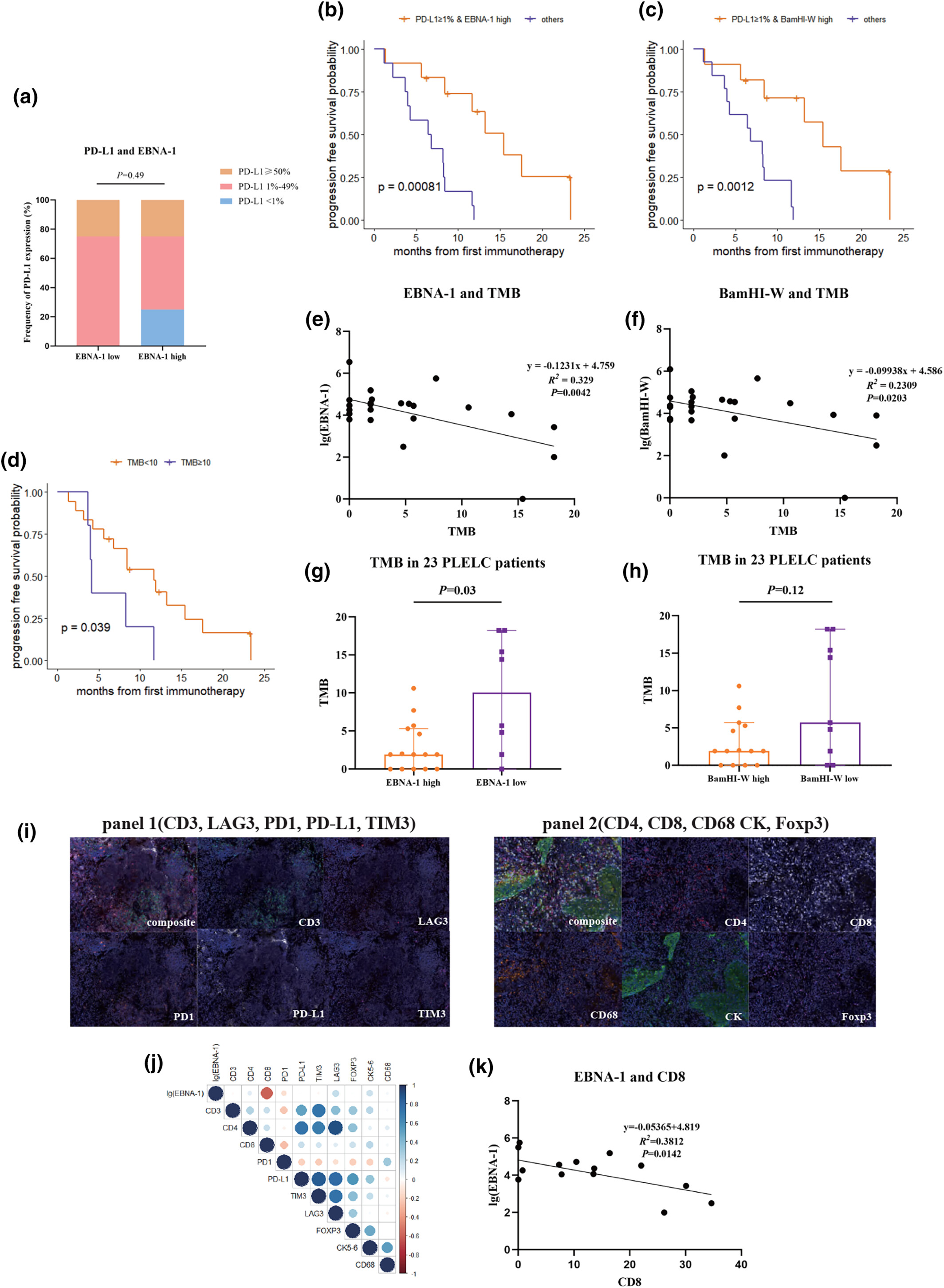
In this study, we found that patients with higher Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) DNA showed longer progression-free survival in pulmonary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma patients treated with immune checkpoint blockade. Plasma EBV DNA could be a useful biomarker to monitor disease progression and predict the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade.
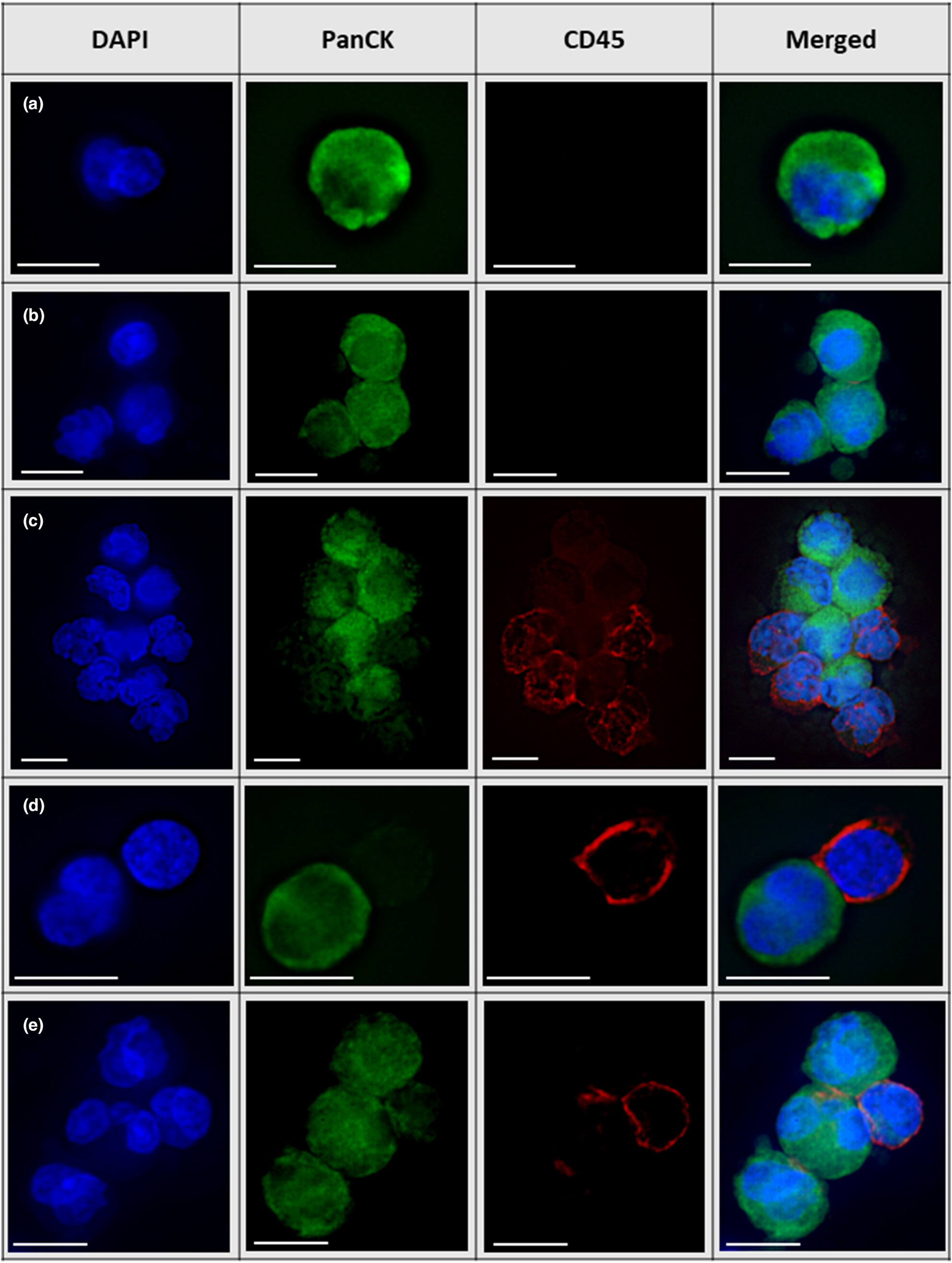
Characterisation of circulating tumor-associated and immune cells in patients with advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 03 June 2024
Serum AZD7442 (tixagevimab–cilgavimab) concentrations and in vitro IC50 values predict SARS-CoV-2 neutralising antibody titres
- First Published: 13 June 2024
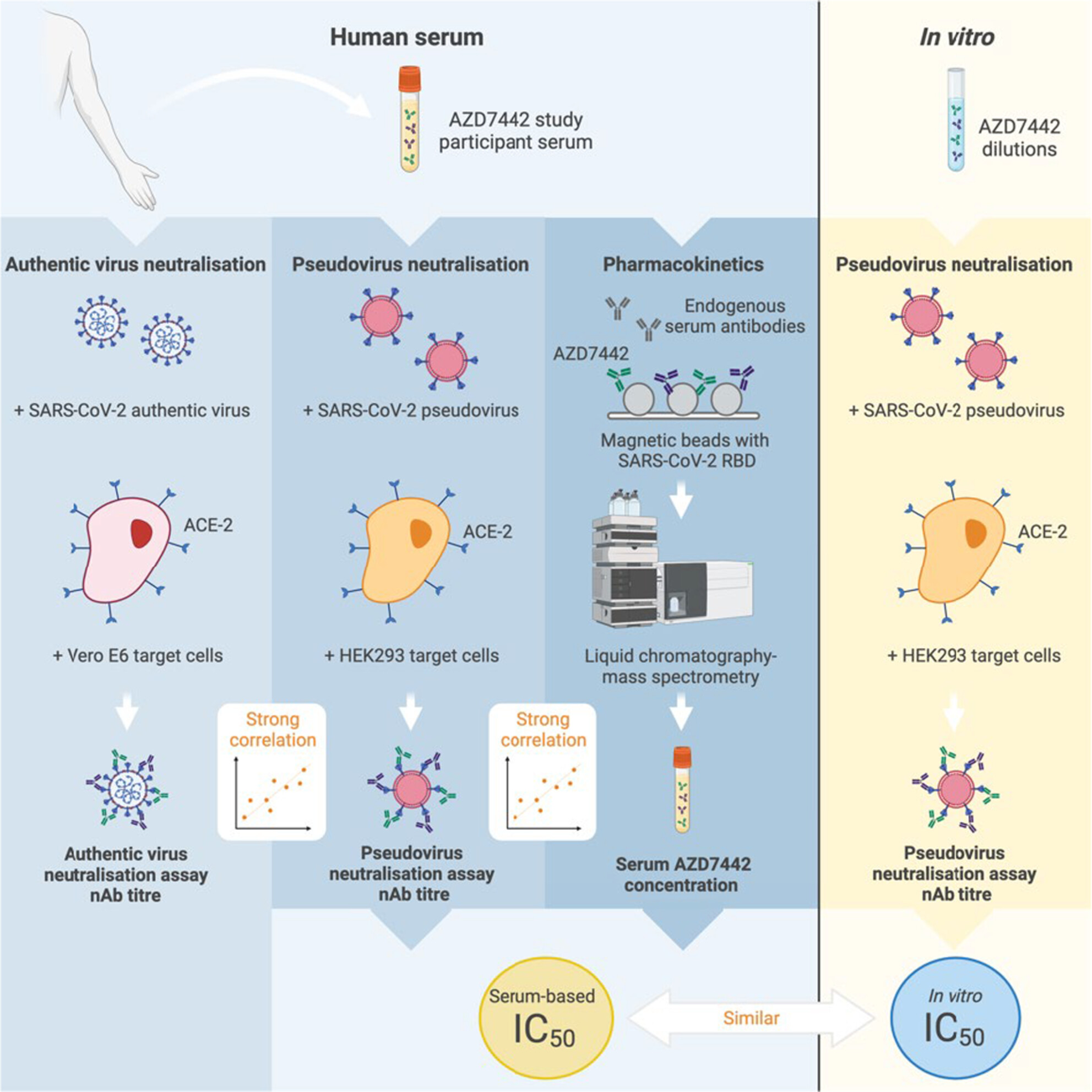
In the analyses reported herein, we use data from clinical studies of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) monoclonal antibody (mAb) combination AZD7442 (tixagevimab–cilgavimab) to demonstrate the utility of pseudovirus neutralisation assay data in conjunction with mAb serum concentrations to predict neutralising antibody titres against emergent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants. Our findings offer a strategy to streamline the clinical evaluation of mAbs targeting SARS-CoV-2 and have the potential to significantly decrease the time from discovery to clinical deployment of the next generation of COVID-19 mAbs.