Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Original Articles
The average copy number variation (CNVA) of chromosome fragments is a potential surrogate for tumor mutational burden in predicting responses to immunotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer
- First Published: 04 January 2021
Short Communication
Successful identification of predictive profiles for infection utilising systems-level immune analysis: a pilot study in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma
- First Published: 07 January 2021
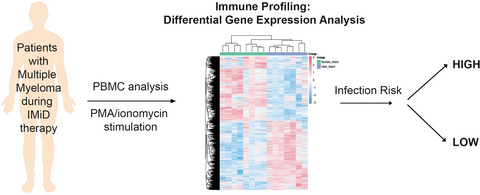
Patients with multiple myeloma (MM) are at increased risk for infection, and clinical assessment of infection risk is increasingly challenging in the era of immune-based therapy. A pilot systems-level immune analysis identified gene expression immune signatures that may predict future infection risk in patients with relapsed and/or refractory MM.
DOCK8 deficiency diminishes thymic T-regulatory cell development but not thymic deletion
- First Published: 07 January 2021
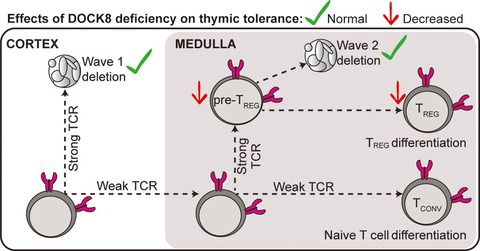
Deleterious mutations in DOCK8 cause a severe immune deficiency syndrome, but whether thymic self-tolerance mechanisms are affected has been unclear. In this study, we found that DOCK8-deficient mice have normal clonal deletion of self-reactive T cells at two stages of development in the thymus. However, DOCK8 deficiency conferred a T-cell-intrinsic defect in the intrathymic differentiation of Foxp3+ T-regulatory cells.
Original Articles
Nalfurafine reduces neuroinflammation and drives remyelination in models of CNS demyelinating disease
- First Published: 17 January 2021
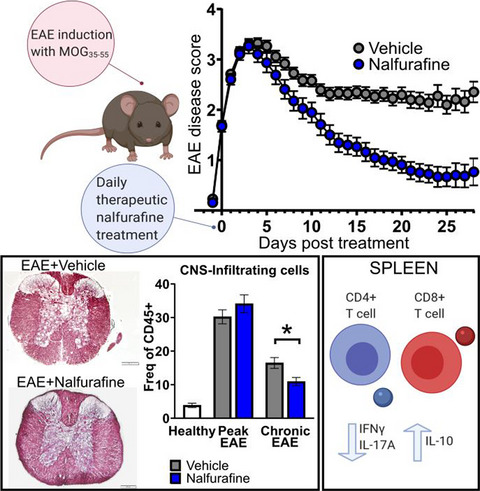
Nalfurafine enabled recovery and remyelination during chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by targeting the kappa opioid receptor. Furthermore, nalfurafine reduced immune cell infiltration into the central nervous system, altered peripheral immune responses, and enabled remyelination after chronic non-immune demyelination. Our findings support the potential of nalfurafine to promote recovery and remyelination and highlight its promise for clinical use in multiple sclerosis.
Special Feature Review
Arrested development: suppression of NK cell function in the tumor microenvironment
- First Published: 10 January 2021
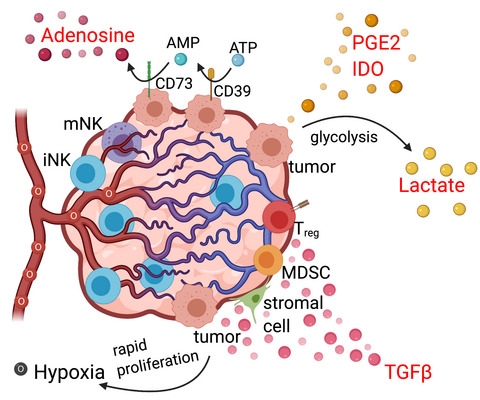
In this review, we provide a summary of the current literature profiling intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms of NK cells that promote dysfunctional responses in solid tumor microenvironments. We critically analyse the current literature and propose open questions as well as new directions for NK-cell-based immunotherapies in cancer.
Reviews
Designing the next-generation therapeutic vaccines to cure chronic hepatitis B: focus on antigen presentation, vaccine properties and effect measures
- First Published: 15 January 2021
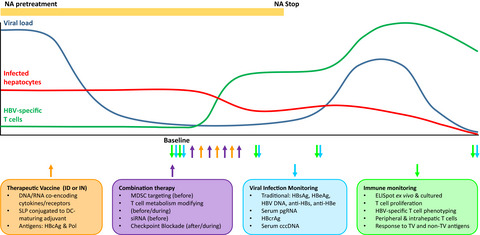
Therapeutic vaccination exploiting the antigen presentation capacity of dendritic cells to prime and/or boost HBV-specific T-cell responses was deemed highly promising but has not yet delivered its promise. In this review, we summarize what has been clinically tested in terms of antigen targets and vaccine forms, how the immunological and therapeutic effects were assessed and what clinical and immunological findings were reported. We combine this information with the most recent insights on HBV antigen presentation, T-cell responses, vaccine composition, antiviral and immune-modulatory drugs and disease biomarkers to derive novel opportunities for the next generation of therapeutic vaccines.
Original Articles
An acetate-yielding diet imprints an immune and anti-microbial programme against enteric infection
- First Published: 15 January 2021
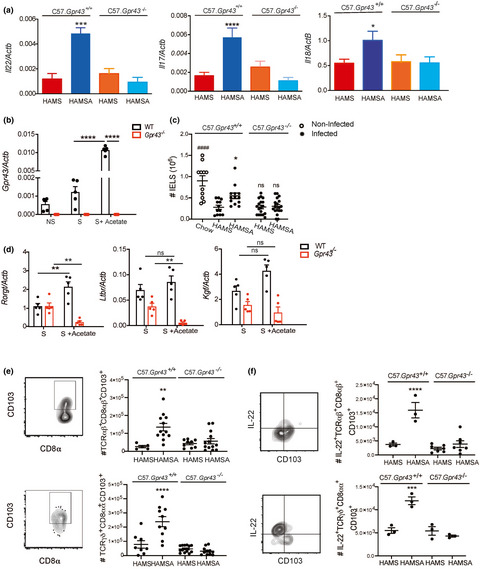
Specialised diets that produce high concentrations of acetate are a novel approach to protect against intestinal bacterial infections. We show that modified starches yielding short-chain fatty acids delivered during gut infection mediate functional microbiota changes and intraepithelial lymphocyte expansion and activation via GPR43 central to aid in preserving epithelial barrier integrity and bacterial clearance.
Special Feature Review
Regulation of the human NK cell compartment by pathogens and vaccines
- First Published: 18 January 2021
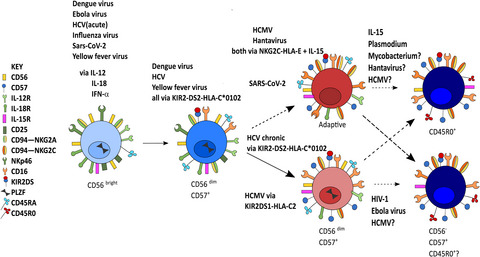
Natural killer (NK) cells integrate signals from both innate and adaptive immune components to act as regulatory and effector cells in the immune response to pathogens. Here, we review how distinct viruses, malaria parasites and emerging infections interact with NK cells and influence the differentiation of NK cells and the consequences for their phenotypic and functional characteristics.
Original Articles
Vaccine-related major cutaneous reaction size correlates with cellular-mediated immune responses after tularaemia immunisation
- First Published: 19 January 2021
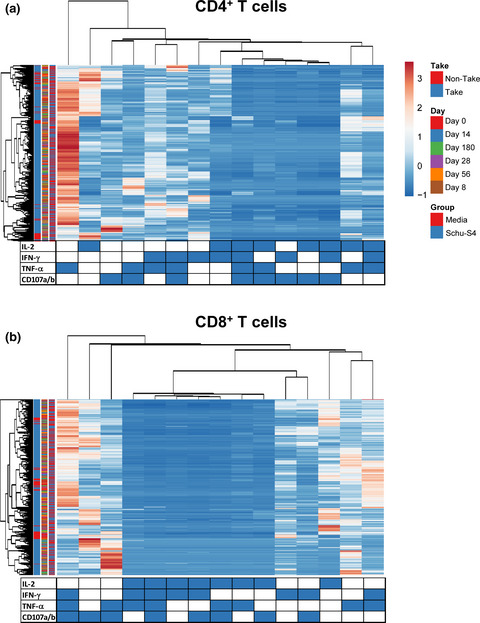
The actual immunological correlate(s) of protection from tularaemia in humans remain(s) unknown. As with smallpox, take is widely accepted as a clinical correlate of protection against tularaemia. We report, for the first time, a correlation between take-lesion size and cellular-mediated immune responses in humans after tularaemia immunization.
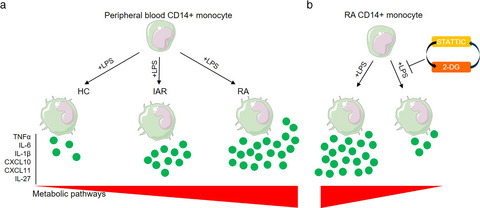
Rheumatoid arthritis CD14+ monocytes display metabolic and inflammatory dysfunction, a phenotype that precedes clinical manifestation of disease
- First Published: 19 January 2021
Influenza, but not SARS-CoV-2, infection induces a rapid interferon response that wanes with age and diminished tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells
- First Published: 26 January 2021
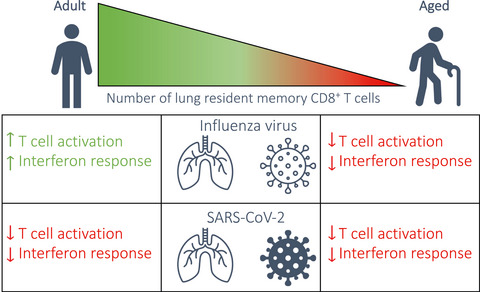
We observed an age-associated decline of lung-resident memory CD8+ T cells in the elderly. The loss of the resident memory T-cell pool that occurs with advanced age coincided with an impairment in the early antiviral immune response following exposure to influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2, a phenomenon that may, in part, explain the increased vulnerability of the elderly to respiratory infections.