Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Original Article
Mesenchymal stem cells prevent overwhelming inflammation and reduce infection severity via recruiting CXCR3+ regulatory T cells
- First Published: 30 September 2020
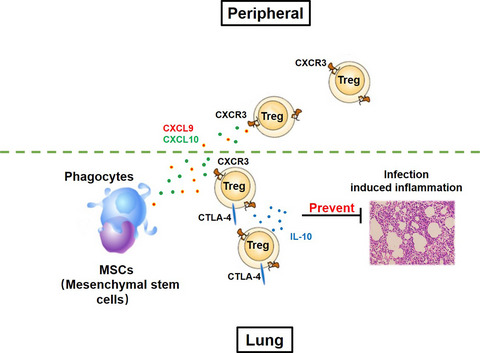
Unlike traditional immunosuppressants, which inadvertently impair a patient's antimicrobial immunity during therapy, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) reduce the incidence and duration of respiratory infection. MSCs are phagocytosed by lung cells and recruit CXCR3+ Tregs which could prevent overwhelming inflammation and accelerate bacterial clearance. Our study highlights the application of MSCs in treating patients who need a long-term immunosuppressive regimen.
Reviews
Immune contexture analysis in immuno-oncology: applications and challenges of multiplex fluorescent immunohistochemistry
- First Published: 07 October 2020
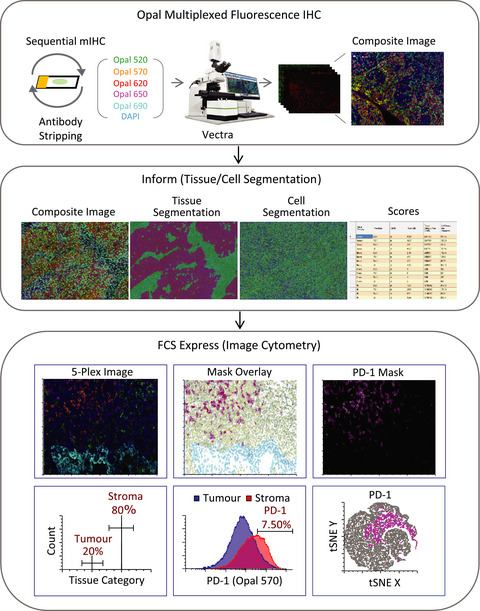
This review discusses current developments in multiplexed fluorescent immunohistochemistry for immune contexture analysis, and their application in immuno-oncology, and discusses challenges to effectively use this technology in clinical settings. We also present a multiplexed image analysis workflow to analyse fluorescence multiplexed stained tumor sections using the Vectra Automated Digital Pathology System together with FCS express flow cytometry software.
Original Articles
Immunosuppression and cardiovascular dysfunction in patients with severe versus mild coronavirus disease 2019: a case series
- First Published: 01 October 2020
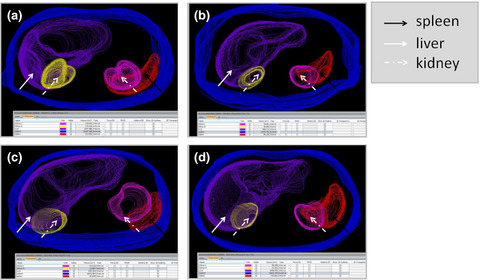
In addition to pulmonary manifestations, our study demonstrated that other organ systems can also be affected during COVID-19 infection. The injuries in COVID-19 patients could lead to immunosuppression and cardiovascular dysfunction, which might contribute to increased mortality in critically ill patients.
Theoretical Article
Is glaucoma an autoimmune disease?
- First Published: 06 October 2020
In this paper, we discuss the concept that glaucoma is an autoimmune disease and review emerging evidence for this concept. There is increasing experimental data that some types of normal-pressure glaucoma may involve immune mechanisms directed at self-antigens, such as HSP, but proof of the concept that glaucoma is an autoimmune disease remains to be conclusively demonstrated.
Reviews
Emerging insights on the role of gasdermins in infection and inflammatory diseases
- First Published: 04 October 2020
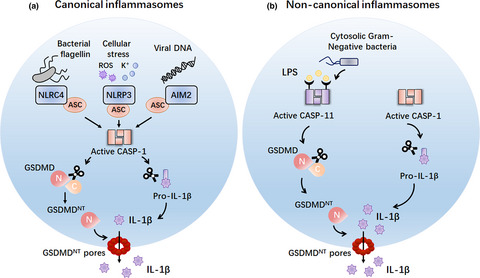
This review summarises the latest advances in several aspects of mode of activation of gasdermins, which finally drives pyroptosis, NETosis, secondary necrotic death and apoptosis. Here, we also highlight the current understanding of gasdermin involvement in infections and autoimmunity disorders, providing a promising translational approach to the treatment of infectious and autoinflammatory diseases.
Original Article
Age-related remodelling of the blood immunological portrait and the local tumor immune response in patients with luminal breast cancer
- First Published: 03 October 2020
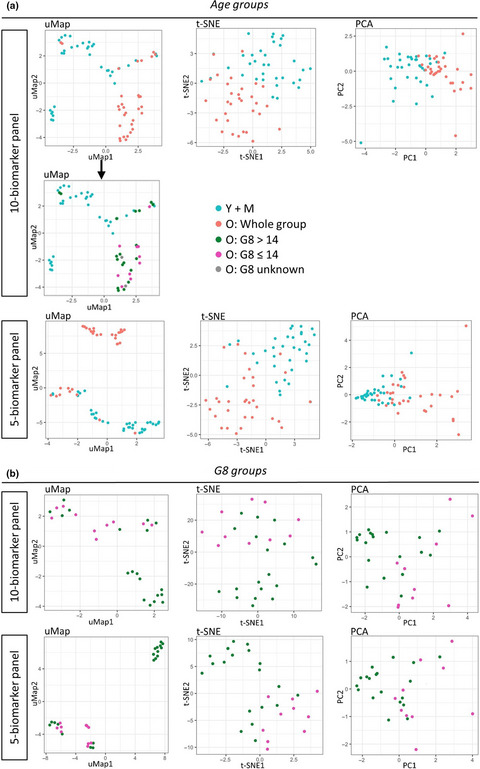
In this study, apart from age-related changes in the immune profile of patients with luminal breast cancer, remarkable frailty-related changes within the subgroup of older patients were observed. Our data support age-dependent remodelling of both systemic immunity features and anti-tumor immune responses.
Systematic analysis of the transcriptome in small-cell carcinoma of the oesophagus reveals its immune microenvironment
- First Published: 05 October 2020
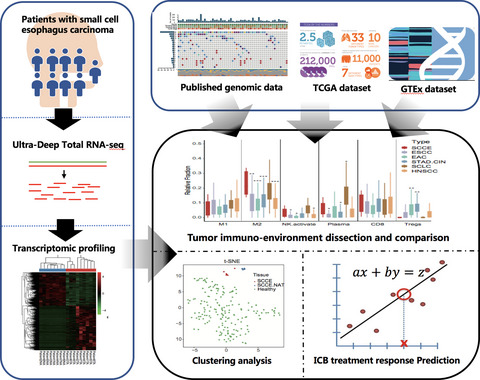
In this study, transcriptomic aberrance and immune microenvironment of small-cell carcinoma of the esophagus (SCCE) was comprehensively characterized with transcriptome and immunohistochemistry analysis. Assessment of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) treatment biomarkers provides a rationale for use of ICB treatment in patients with SCCE.
Reviews
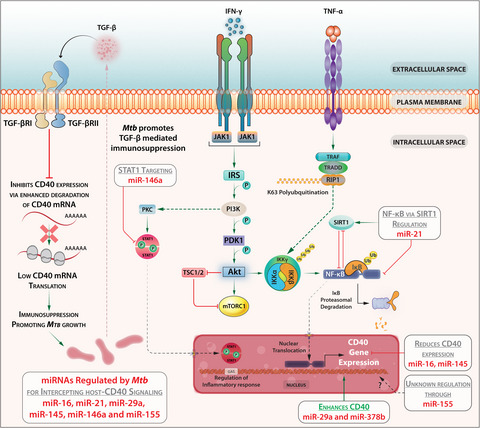
March of Mycobacterium: miRNAs intercept host cell CD40 signalling
- First Published: 07 October 2020
Original Articles
Kinetics and isotype assessment of antibodies targeting the spike protein receptor-binding domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 in COVID-19 patients as a function of age, biological sex and disease severity
- First Published: 07 October 2020
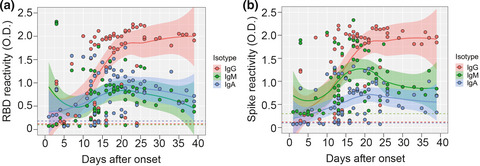
Antibodies to severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronaviruses-2 spike arise within 1 week after COVID-19 symptoms and are not affected by patient age or biological sex. Neutralising activity correlates with receptor-binding domain reactivity and may reflect viral replication rather than acute protection.
Case Reports
Severe delayed pulmonary toxicity following PD-L1–specific CAR-T cell therapy for non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 09 October 2020

We studied the circulating PD-L1–specific CAR-T cells in a patient with non-small cell lung cancer. Circulating PD-L1–specific CAR-T cells accounted for 3.30% of the patient’s peripheral blood T cells detected by FACS in the first follow-up (Day +29), and a chest CT scan showed subtle shrinkage of tumors (stable disease). However, the patient was immediately transferred to the ICU on Day +47 because he deteriorated quickly into respiratory failure in three days. This case might represent a unique clinical manifestation of solitary organ damage secondary to PD-L1–specific CAR-T cell therapy.
Original Article
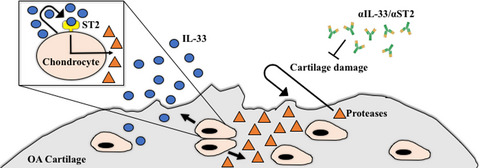
Blockade of IL-33 signalling attenuates osteoarthritis
- First Published: 23 October 2020
Limited effect of duration of CMV infection on adaptive immunity and frailty: insights from a 27-year-long longitudinal study
- First Published: 14 October 2020
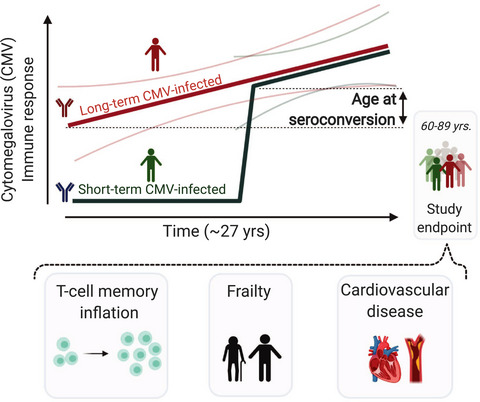
We conducted a retrospective longitudinal study spanning ~27 years, which enabled us to identify cytomegalovirus (CMV) seroconverters in an ageing population and to quantify duration of CMV infection. We found that age-related effects other than duration of CMV infection are important to CMV-induced changes in the immune system, such as T-cell responses and the expansion of the T-cell memory pool. Although CMV-specific immunity is not evidently linked to frailty, it tends to associate with higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease.
Original Articles
Endothelial, pericyte and tumor cell expression in glioblastoma identifies fibroblast activation protein (FAP) as an excellent target for immunotherapy
- First Published: 14 October 2020
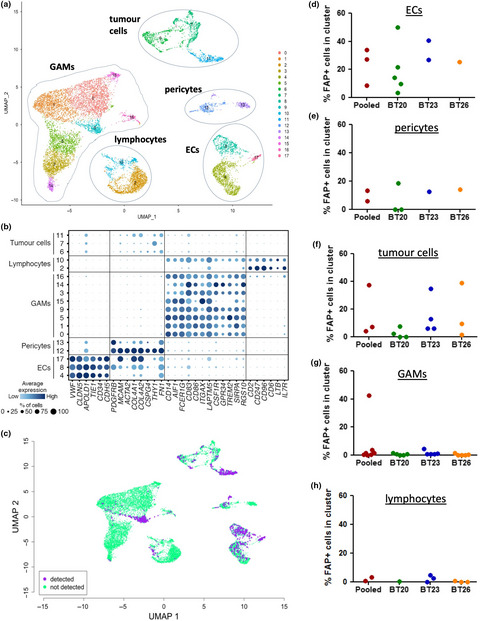
This detailed analysis of the expression patterns of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) reveals it to be an important new target antigen for immunotherapy of glioblastoma. Immunostaining of tissue sections, flow cytometry and single-cell RNA sequencing reveal broad expression of FAP by not only glioblastoma tumour cells but also endothelial cells and pericytes within the tumour microenvironment.
Clinical efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in critical ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 14 October 2020
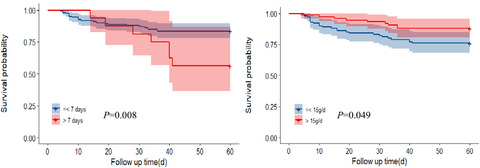
Early administration of a high dose of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) improves the prognosis of critical-type patients with COVID-19. This study provides important information on clinical application of IVIG in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection, including patient selection and administration dosage and timing.
A novel autoantibody targeting calreticulin is associated with cancer in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies
- First Published: 15 October 2020
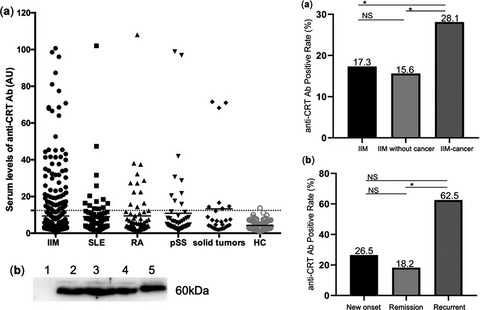
To our knowledge, this is the first report to describe the prevalence and clinical significance of serum anti-calreticulin autoantibodies (anti-CRT Ab) in a large cohort of adult-onset idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) patients. Serum anti-CRT Ab could serve as a novel candidate marker of cancer in IIM patients, and detection of anti-CRT Ab could be valuable in monitoring cancer recurrence in IIM patients with a history of solid tumors.
News & Commentary
Intravenous immunoglobulin immunotherapy for coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19)
- First Published: 16 October 2020
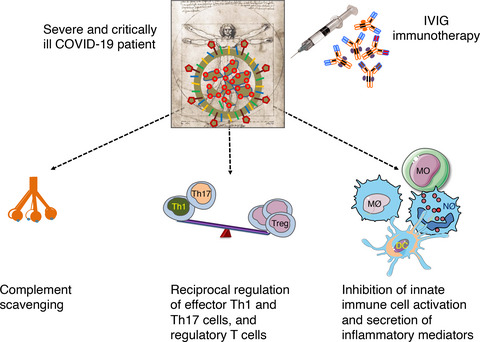
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), a pooled normal IgG from several thousand healthy donors and one of the commonly used immunotherapeutic molecules for the management of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, has been explored for the treatment of coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19). Although placebo-controlled, double-blind randomised clinical trials are lacking, current data from either retrospective, case series or open-label randomised controlled trials provide an indicator that IVIG immunotherapy could benefit severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients. See alsoShao et al.
Original Articles
Narrowband UVB phototherapy reduces TNF production by B-cell subsets stimulated via TLR7 from individuals with early multiple sclerosis
- First Published: 15 October 2020
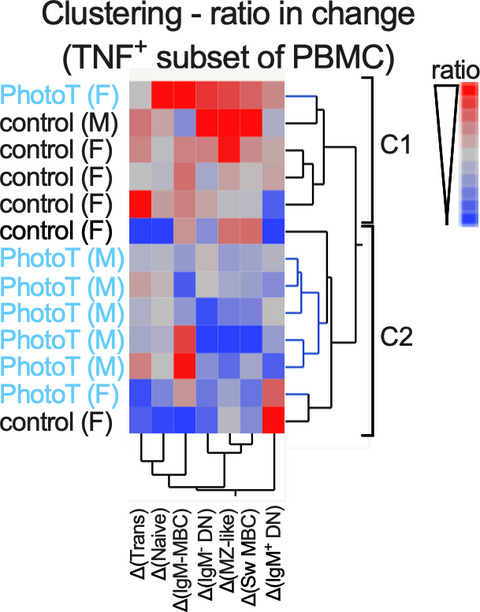
Phototherapy was tested to prevent or delay individuals with clinically isolated syndrome converting to multiple sclerosis. This study investigated the functional impact of phototherapy on circulating B cells. In addition to modulating the proportion of circulating B-cell subsets, phototherapy reduced the ability of B cells to respond to TLR7 stimulation with pro-inflammatory TNF production suggesting that phototherapy may limit polyclonal B-cell activation.
Inverse correlation between serum complement component C1q levels and whole blood type-1 interferon signature in active tuberculosis and QuantiFERON-positive uveitis: implications for diagnosis
- First Published: 16 October 2020
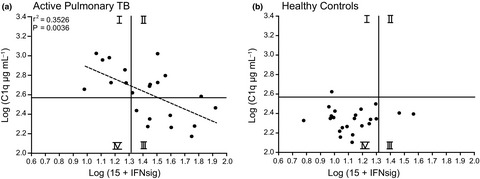
Serum C1q is elevated in active pulmonary tuberculosis, especially in those cases with uveitis. Serum C1q correlated inversely with type-1 IFN signature scores in APTB (P = 0.0036, r2 = 0.3526), revealing that these biomarkers for active TB disease can be mutually exclusive. We propose that combined measurement of blood type-1 IFN signature and serum C1q may provide added value in the diagnosis of active TB disease, which might be especially beneficial in often hard-to-diagnose TB-associated uveitis cases.
Influenza-specific IgG1+ memory B-cell numbers increase upon booster vaccination in healthy adults but not in patients with predominantly antibody deficiency
- First Published: 16 October 2020
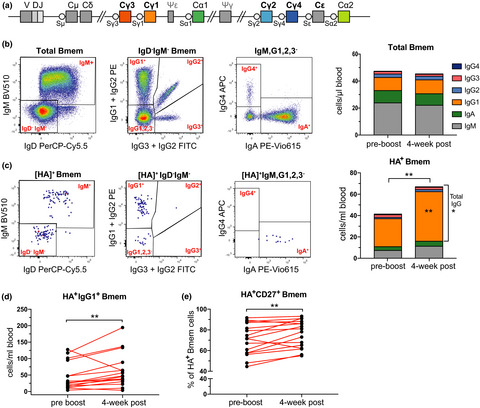
We here developed an extensive flowcytometry panel to examine influenza-specific memory B cells using fluorescently labeled recombinant haemagglutinin (HA) tetramers. Influenza-specific memory B cells were predominantly IgG1+, and these were increased following booster vaccination in healthy controls, but not in patients with predominantly antibody deficiency.
Integrative immunogenomic analysis of gastric cancer dictates novel immunological classification and the functional status of tumor-infiltrating cells
- First Published: 17 October 2020
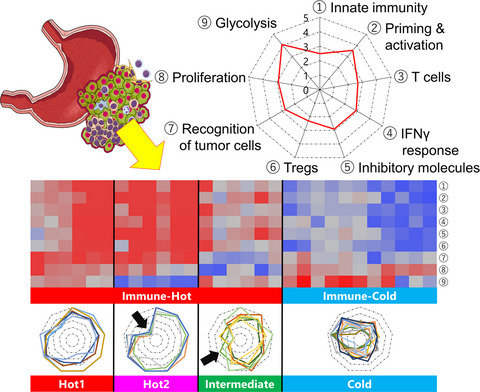
In this study, an integrative immunogenomic analysis of gastric cancer was performed. The immunological classification of gastric cancer resulted in immune signatures of four main types, designated Hot1, Hot2, Intermediate and Cold, in which the functional status of T cells was different. Early administration of anti-PD-1 therapy might be recommended for patients with Hot1 tumors.
Ex vivo enrichment of PRAME antigen-specific T cells for adoptive immunotherapy using CD137 activation marker selection
- First Published: 21 October 2020

Adoptive immunotherapy with ex vivo expanded tumor-specific T cells has potential as anticancer therapy. Preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma (PRAME) is an attractive target overexpressed in several cancers including melanoma and acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), with low expression in normal tissue outside the gonads. We developed a GMP-compliant manufacturing method for PRAME-specific T cells from healthy donors for adoptive immunotherapy.