Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Success of 2013–2020 World Health Organization action plan to control non-communicable diseases would require pollutants control
- Pages: 621-622
- First Published: 24 June 2014
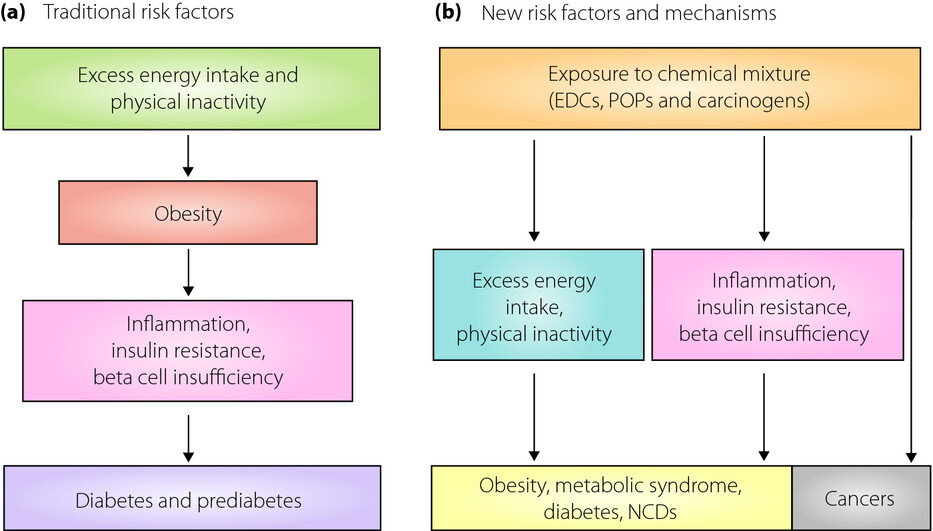
To control diabetes epidemic and NCDs, WHO has been promoting its action plans since 2000, but diabetes epidemic is continuing. New action plan for 2013-2020 aim to reduce shared risk factors of NCDs, such as tobacco use, unhealthy (i.e., high fat) diet, physical inactivity and harmful use of alcohol and is strengthening the risk reduction measures, such as taxing on tobacco, alcohol and sugary beverages, banning advertisements of unhealthy foods. However it might fail because it did not consider the contribution of environmental pollution on the pathogenesis of diabetes and NCDs.
Review Article
Diabetic cardiomyopathy and its mechanisms: Role of oxidative stress and damage
- Pages: 623-634
- First Published: 15 July 2014
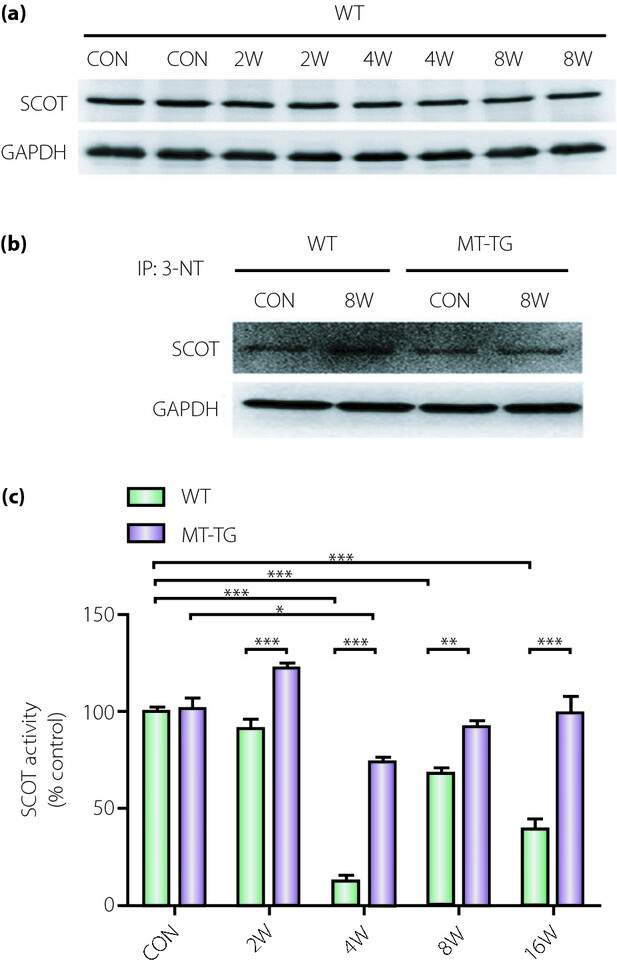
Although several pathological mechanisms responsible for diabetic cardiomyopathy have been proposed, oxidative stress is widely considered as one of the major causes for the pathogenesis of the disease. Hyperglycemia-, hyperlipidelima-, hypertension-, and inflammation-induced oxidative stress is a major risk factor for the development of micro-vascular pathogenesis in the diabetic myocardium, which results in abnormal gene expression, altered signal transduction, and the activation of pathways leading to programmed myocardial cell deaths.
Commentaries
Glycated hemoglobin variability: A potential new risk marker for diabetes complications?
- Pages: 635-636
- First Published: 02 April 2014
Look Action for Health in Diabetes trial: What we have learned in terms of real world practice and clinical trials
- Pages: 637-638
- First Published: 05 May 2014
Articles
Basic Science and Research
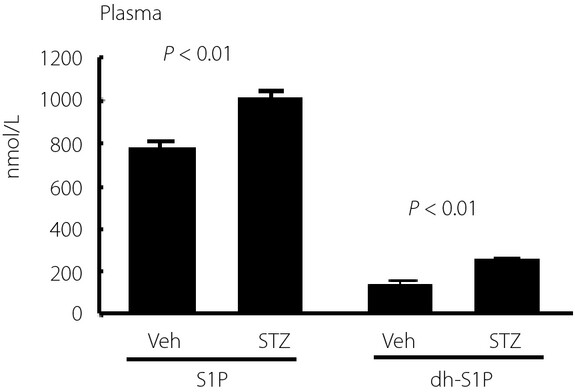
Modulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate and apolipoprotein M levels in the plasma, liver and kidneys in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
- Pages: 639-648
- First Published: 21 April 2014
Epidemiology
Identification of novel risk genes associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a genome-wide gene-based association analysis
- Pages: 649-656
- First Published: 02 April 2014
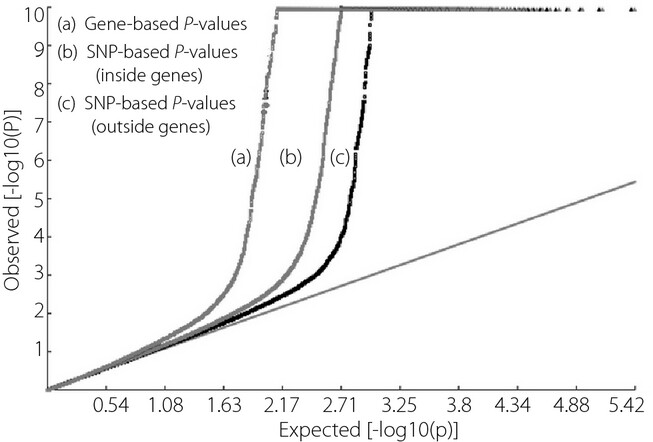
We found more disease-susceptibility genes by using Genome-wide Gene-Based Association Study than SNP-base association test. Our findings point to the involvement of previously unsuspected new pathways in the pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, and provide novel insights into the genetic basis of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.
Clinical Science and Care
Clinical characteristics of hyperglycemic crises in patients without a history of diabetes
- Pages: 657-662
- First Published: 05 March 2014
Relationship and factors responsible for regulating fasting and post-challenge plasma glucose levels in the early stage development of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 663-670
- First Published: 12 May 2014
Increasing risk of diabetes mellitus according to liver function alterations in electronic workers
- Pages: 671-676
- First Published: 28 March 2014
Application of a health-related quality of life conceptual model in community-dwelling older Chinese people with diabetes to understand the relationships among clinical and psychological outcomes
- Pages: 677-686
- First Published: 11 February 2014
Is persistence of metabolic syndrome associated with poor health-related quality of life in non-diabetic Iranian adults? Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
- Pages: 687-693
- First Published: 25 March 2014
Decreased serum CA19-9 is associated with improvement of insulin resistance and metabolic control in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
- Pages: 694-700
- First Published: 26 February 2014
Efficacy of glimepiride/metformin fixed-dose combination vs metformin uptitration in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled on low-dose metformin monotherapy: A randomized, open label, parallel group, multicenter study in Korea
- Pages: 701-708
- First Published: 16 March 2014
Median neuropathy at the wrist as an early manifestation of diabetic neuropathy
- Pages: 709-713
- First Published: 28 March 2014
Prevalence and risk factors of development of peripheral diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus in a tertiary care setting
- Pages: 714-721
- First Published: 02 April 2014
Mild-to-moderate intensity exercise improves cardiac autonomic drive in type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 722-727
- First Published: 20 May 2014
Variations in 7-day/24-h circadian pattern of ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate of type 2 diabetes patients
- Pages: 728-733
- First Published: 02 April 2014
Comparison of carotid and lower limb atherosclerotic lesions in both previously known and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 734-742
- First Published: 11 March 2014
Severity of hearing impairment is positively associated with urine albumin excretion rate in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 743-747
- First Published: 05 March 2014
Letter to the Editor
Case of fulminant type 1 diabetes with coronary microcirculatory dysfunction
- Pages: 748-749
- First Published: 27 October 2014