Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
An integrated detection system against false data injection attacks in the Smart Grid
- Pages: 91-109
- First Published: 04 March 2014
In this paper, we develop a system for the smart grid for detecting false data injection attacks that integrates two complementary techniques that are each tailored to a particular type of attacks. Anomaly-based detection detects strong attacks that inject large amounts of spurious measurement data over a very short time. We integrate the anomaly detection mechanism with a watermarking-based detection scheme that prevents stealthy attacks that involve subtle manipulation of measurement data over a long period.
A novel image steganography scheme based on morphological associative memory and permutation schema
- Pages: 110-121
- First Published: 12 February 2014
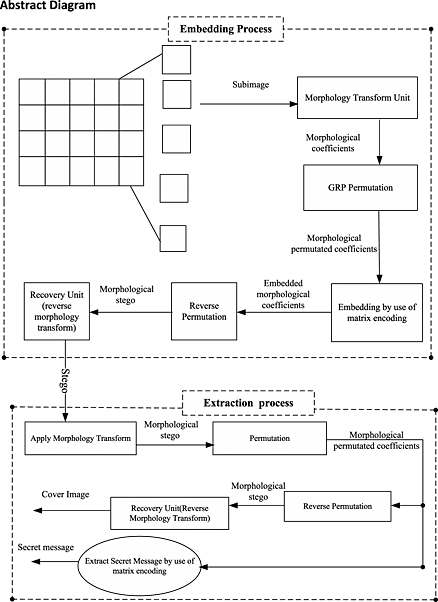
In this paper, a new image steganography algorithm based on morphological associative memory, GRP permutation, and matrix encoding is proposed. The secret message is embedded into the permutated morphological coefficients via the matrix encoding method. The proposal algorithm was compared with two known steganography algorithms, F5 and morphological steganography, in terms of peak signal to noise ratio, visual distortion, time complexity, and robustness against steganalysis attacks.
Cryptanalysis of a certificateless identification scheme
- Pages: 122-125
- First Published: 19 February 2014
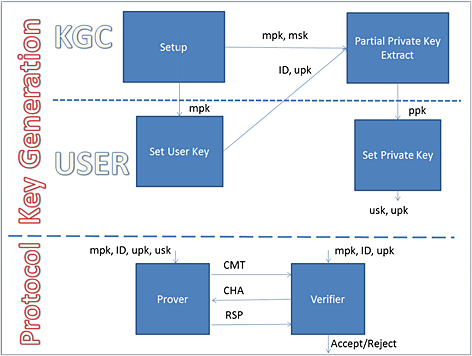
In 2013, Dehkordi and Alimoradi proposed a certificateless identification scheme using supersingular elliptic curves. This proposal came independent of the parallel work of Chin et al. in proposing the first known security models for certificateless identification with provable security. In this paper, we show that there are some design flaws in the Dehkordi-Alimoradi scheme and present attacks of both Type-1 and Type-2 adversaries against certificateless identification schemes. These attacks lead one to conclude that their scheme is insecure.
Enhancement on strongly secure group key agreement
- Pages: 126-135
- First Published: 19 February 2014
In this article, two security weaknesses on a strongly secure group key agreement protocol are pointed out because it must rely on a signature scheme with existential unforgeability under adaptive chosen message attacks (UF-ACMA) to achieve the security goals of authenticated key exchange and mutual authentication. We define a novel security notion for signature, called existential UF-ACM and ephemeral secret leakage attacks. We point out that some existing UF-ACMA secure signature schemes are not secure under the new security notion while presenting a UF-ACM and ephemeral secret leakage attacks secure signature scheme.
Analyses of several recently proposed group key management schemes
- Pages: 136-148
- First Published: 05 March 2014
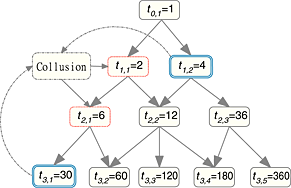
In this paper, we review three schemes recently proposed, including Kayam's scheme for groups with hierarchy, Piao's group KM scheme, and Purushothama's group KM schemes. We point out the problems in each scheme. The first two schemes have security flaws, and the last one has efficiency issue. We also analyze the underlying reasons and give suggestions on how to avoid those problems.
Cryptanalysis and security enhancement of Zhu's authentication scheme for Telecare medicine information system
- Pages: 149-158
- First Published: 10 March 2014
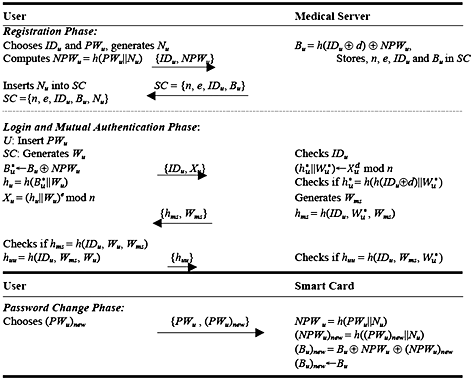
The concept of Telecare Medicine Information systems has evolved to provide better health care to the masses. Recently, some researchers have proposed authentication protocols for Telecare Medicine Information systems. However, in this paper, the author presents a novel authentication technique to overcome the discrepancies of previous protocols. Analysis shows the robustness as well as the simplicity of the proposed scheme.
A high-capacity and low-distortion 3D polygonal mesh steganography using surfacelet transform
- Pages: 159-167
- First Published: 04 March 2014
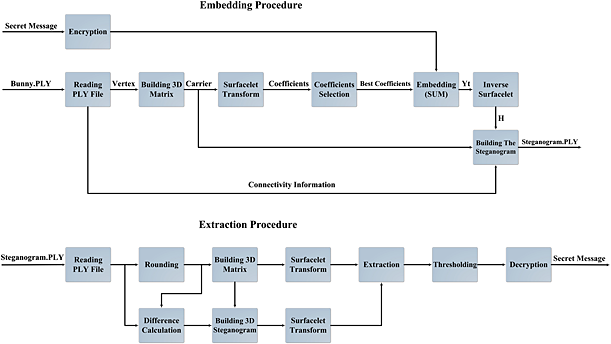
A novel steganography algorithm for three-dimensional polygon models is introduced based on surfacelet transform. The experimental results show that the proposed method causes the lowest distortion into the carrier compared with other methods. The capacity of our algorithm is 3 bits/vertex, which is the maximum capacity among transform domain methods.
A lightweight trust management based on Bayesian and Entropy for wireless sensor networks
- Pages: 168-175
- First Published: 21 March 2014
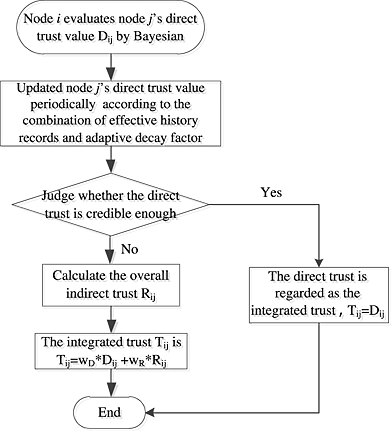
Based on Bayesian and Entropy, this paper proposes a lightweight trust management for wireless sensor networks. Lightweight trust management based on Bayesian and Entropy adopts two strategies to make the model lightweight. One is using effective history records rather than all the records when updating trust value, which saves nodes' memory. The other is using indirect trust only when the direct trust is not credible enough to be the integrated trust, which reduces the network energy consumption. In addition, the Entropy Theory is adopted to distribute weights to different trust values, which can improve the problems caused by distributing weights subjectively and also enhance adaptability of the model.
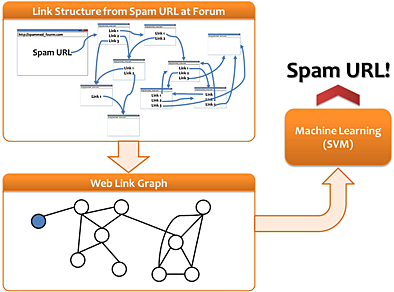
A link graph-based approach to identify forum spam
- Pages: 176-188
- First Published: 10 March 2014
A flexible hierarchical access control mechanism enforcing extension policies
- Pages: 189-201
- First Published: 04 March 2014

This figure is an example of access control in a hierarchy with explicit transitive exception and antisymmetric arrangement. In this work, an access control mechanism, providing explicit transitive exception and antisymmetric arrangement, is proposed to provide flexible and appropriate solutions to hierarchical relationships. The proposed mechanism employs an elliptic curve cryptosystem and a two-layer hash approach to ensure security and computation efficiency.
A new multi-use multi-secret sharing scheme based on the duals of minimal linear codes
- Pages: 202-211
- First Published: 19 March 2014
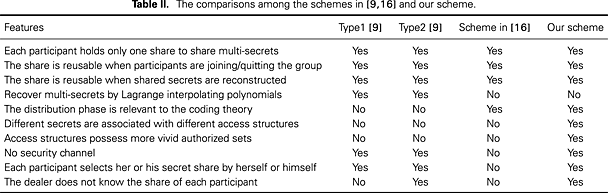
In general, it is very hard to determine the minimal access structures of the schemes based on linear codes. In this paper, we first propose the concept of minimal linear codes so as to make it easier to determine the access structures of the schemes based on the duals of minimal linear codes. Then, we devise a new multi-use multi-secret sharing scheme based on the dual code of a minimal linear code, where each participant has to carry only one share. Furthermore, we study the minimal access structures of the multi-secret sharing scheme and present specific examples through programming.
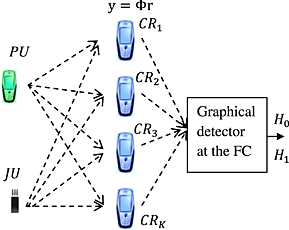
Fast anomaly detection using Boxplot rule for multivariate data in cooperative wideband cognitive radio in the presence of jammer
- Pages: 212-219
- First Published: 10 March 2014
Efficient centralized approach to prevent from replication attack in wireless sensor networks
- Pages: 220-231
- First Published: 10 March 2014
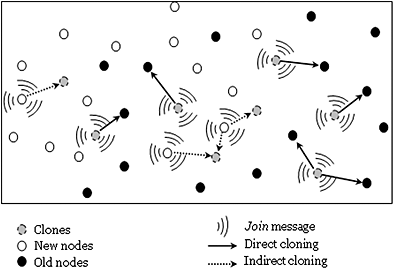
The majority of key management schemes suffer from the physical compromising of nodes. We propose, in this paper, a solution based on the digital signature of the base station, to perfectly secure network maintenance against the cloning attack. Our solution is based on the agreement that the base station should give to a new node to share a pairwise key with its neighbors.
Towards cross-layer approaches to coping with misbehavior in mobile ad hoc networks: an anatomy of reputation systems
- Pages: 232-244
- First Published: 17 March 2014
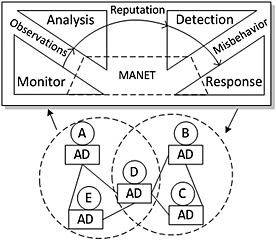
Reputation systems help to establish mutual trust between entities of autonomic networking paradigms such as mobile ad hoc networks (MANET). This paper provides a deep look into the capabilities and limitations of those available reputation systems in the deployment context of MANET, exploring their effectiveness and usability to handle misbehaviors in MANETs.
An improved and provable remote user authentication scheme based on elliptic curve cryptosystem with user anonymity
- Pages: 245-260
- First Published: 10 March 2014

We point out that Li's scheme is insecure and propose an improved scheme based on elliptic curve cryptosystem. Also, we enhance the notion of forward security to strong forward security to satisfy this kind of scheme and present a security proof model. Our scheme is secure and efficient via analysis.
A new secure Internet voting protocol using Java Card 3 technology and Java information flow concept
- Pages: 261-283
- First Published: 12 March 2014
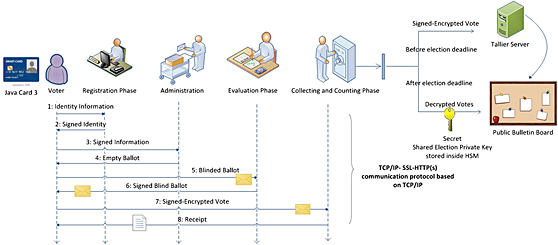
Our study proposes an Internet voting system, which addresses major problems of i-voting systems such as uncoercibility/bribery, collusion, and specially voter insecure platform. For securing voter-side platform, we have introduced Java Card 3 for the first time. We have used Java information flow for providing confidentiality and integrity of stored vote. We also have proposed an implementation of the proposed protocol with the use of Java Card 3, which is the first implementation of an i-voting protocol with Java Card 3 (not only is the first implementation of an i-voting with Java Card 3 but also is the first one in e-services).
Fair two-party computation with rational parties holding private types
- Pages: 284-297
- First Published: 21 March 2014
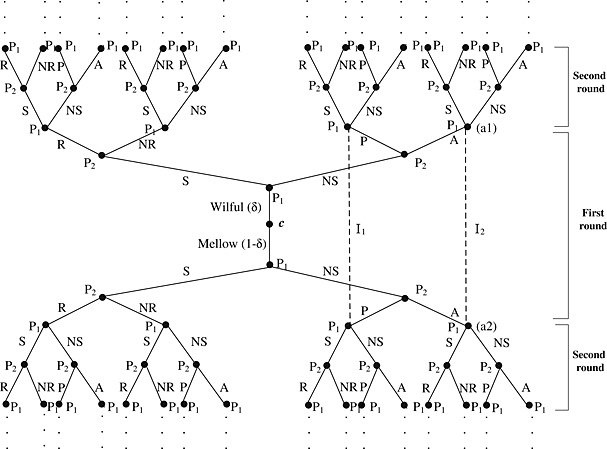
We consider a complex but practical rational secure two-party computation protocol under asymmetric information where previous equilibriums are inadequate to guarantee fairness. We propose a stronger equilibrium named computationally sequential equilibrium to guarantee fairness under asymmetric information. Furthermore, our protocol only requires small constant communication rounds.
An efficient batch verification system and its effect in a real time VANET environment
- Pages: 298-310
- First Published: 18 March 2014
Efficient video frame insertion and deletion detection based on inconsistency of correlations between local binary pattern coded frames
- Pages: 311-320
- First Published: 10 March 2014
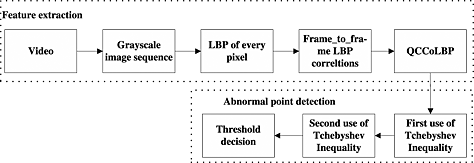
Frame insertion and deletion are common inter-frame forgery in digital videos. The proposed method is composed of two parts: feature extraction and abnormal point detection. In the feature extraction, quotients of correlation coefficients among sequential local binary pattern coded frames are calculated. In the abnormal point detection, insertion and deletion localization is achieved by using Tchebyshev inequality twice followed by abnormal points detection based on decision-thresholding. Experimental results show that our method has high detection accuracy and low computational complexity.
On query execution over encrypted data
- Pages: 321-331
- First Published: 12 March 2014
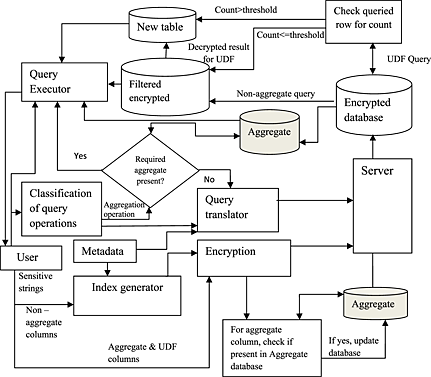
This paper proposes a framework for improving the performance of different query operations, that is, non-aggregate, aggregate and user-defined query operations, on encrypted data in Database-as-a-Service model. The performance of these query operations over the encrypted data is compared with that of the available methods, in terms of the execution time, and it is found that the efficiency of the proposed approach is better than that of the traditional approach. Effectiveness of different types of non-aggregate query operations is identified in terms of filter ratio and false ratio. The analysis has shown that the filter ratio increases and the false ratio decreases with an increase in the size of sensitive string and the reachability matrix generated for the non-aggregate attribute.
A survey on secret key generation mechanisms on the physical layer in wireless networks
- Pages: 332-341
- First Published: 04 March 2014
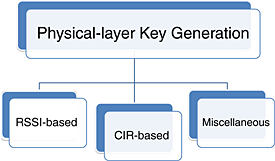
This paper reviews secret key generation mechanisms on the physical layer in wireless networks. After a theoretical overview, most recent approaches based on the received signal strength indicator or the channel impulse response are summarized. Finally, other proposed key generation methods are also discussed.