Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
CLINICAL ARTICLES
Predictors of developing renal dysfunction following diagnosis of transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis
- First Published: 14 June 2024
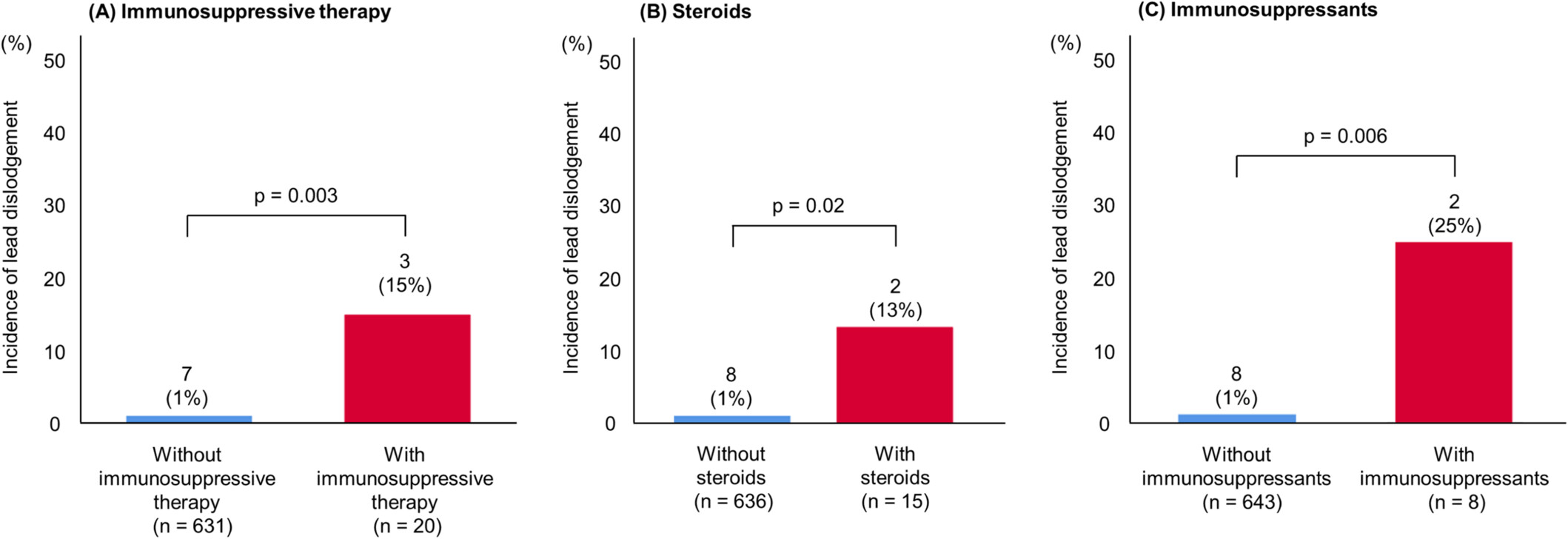
Our study demonstrated that the development of de novo renal dysfunction or worsening renal function is common following the diagnosis of ATTR-CA. Additionally, we identified worse NYHA class and no history of IHD as significant predictors associated with developing worsening renal function, while receiving SGLT2i therapy appeared to be protective.
The relationship between ambulatory arterial stiffness index and incident atrial fibrillation
- First Published: 14 June 2024
PREDICT HF: Risk stratification in advanced heart failure using novel hemodynamic parameters
- First Published: 05 June 2024
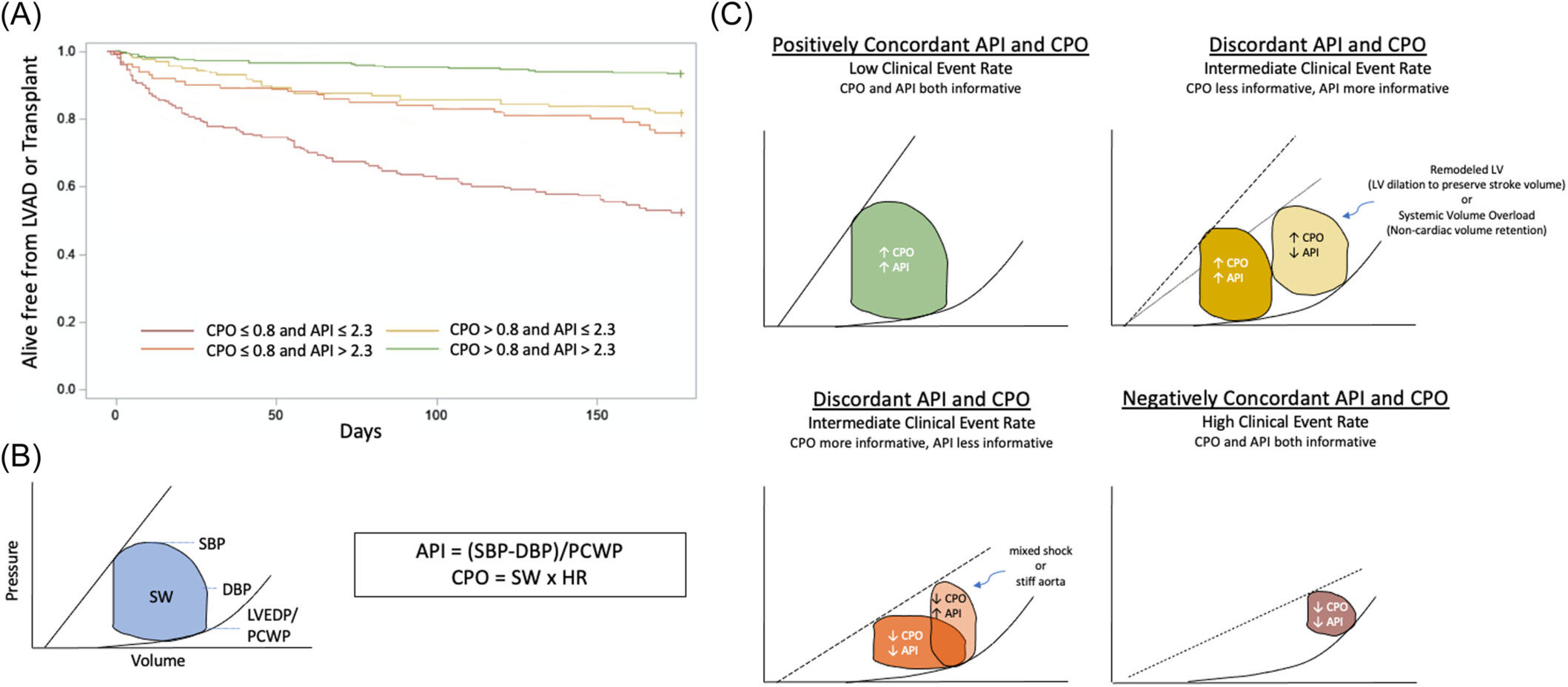
(A) Improved risk stratification of advanced heart failure using the advanced hemodynamic parameters, aortic pulsatility index (API), and cardiac power output (CPO). The simultaneous incorporation of API and CPO into risk models defines three patient populations ([1] concordantly high API and CPO [best prognosis], [2] discordant API and CPO [intermediate prognosis], [3] concordantly low API and CPO [worst prognosis]) with incremental risk of the combined end-point of death, left ventricular assist device or transplant at 6 months. (B) API and CPO measurements depicted utilizing pressure−volume loops. C. Pressure−volume loops demonstrating the relationship and utility of API and CPO in different clinical states.
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
CLINICAL ARTICLES
The Plaque Analysis Classifies the Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS) Stenosis and Plaque Burden Categories: Association of the Plaque Features, Fat Attenuation Index, Coronary Computed Tomography Fractional Flow Reserve, and the Combination of Stenosis and Calcification
- First Published: 17 June 2024
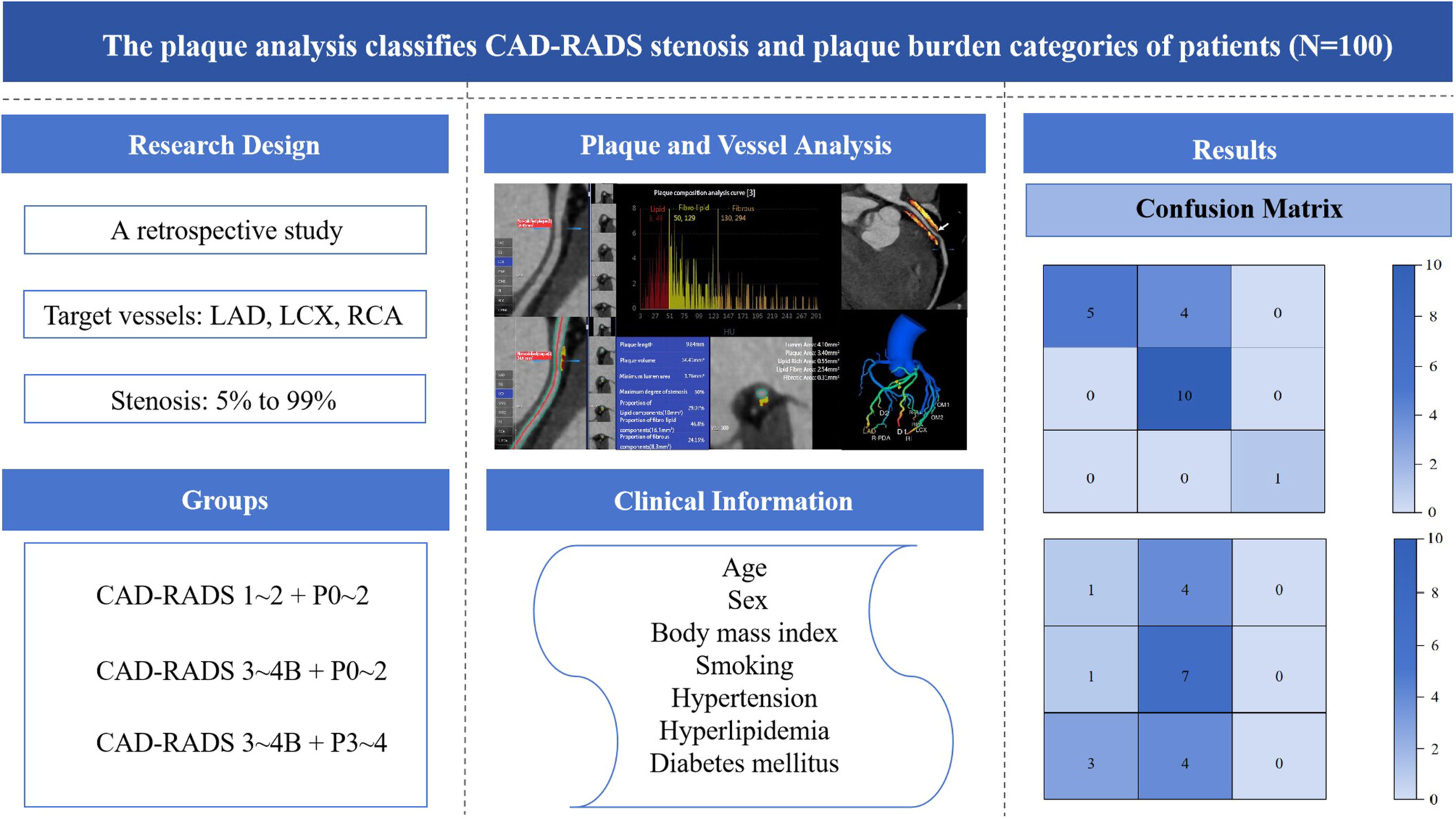
Computed tomography fractional flow reserve, volume and proportion of lipid and fibro-lipid components of plaques, proportion of calcified components, and plaque type were valuable for coronary artery disease-reporting and data system stenosis + plaque burden classification. Notably, the above model built using random forest is better than clinical model (area under curve: 0.874 vs. 0.647).
Home Heart Hospital Associated With Reduced Hospitalizations and Costs Among High-Cost Patients With Cardiovascular Disease
- First Published: 14 June 2024
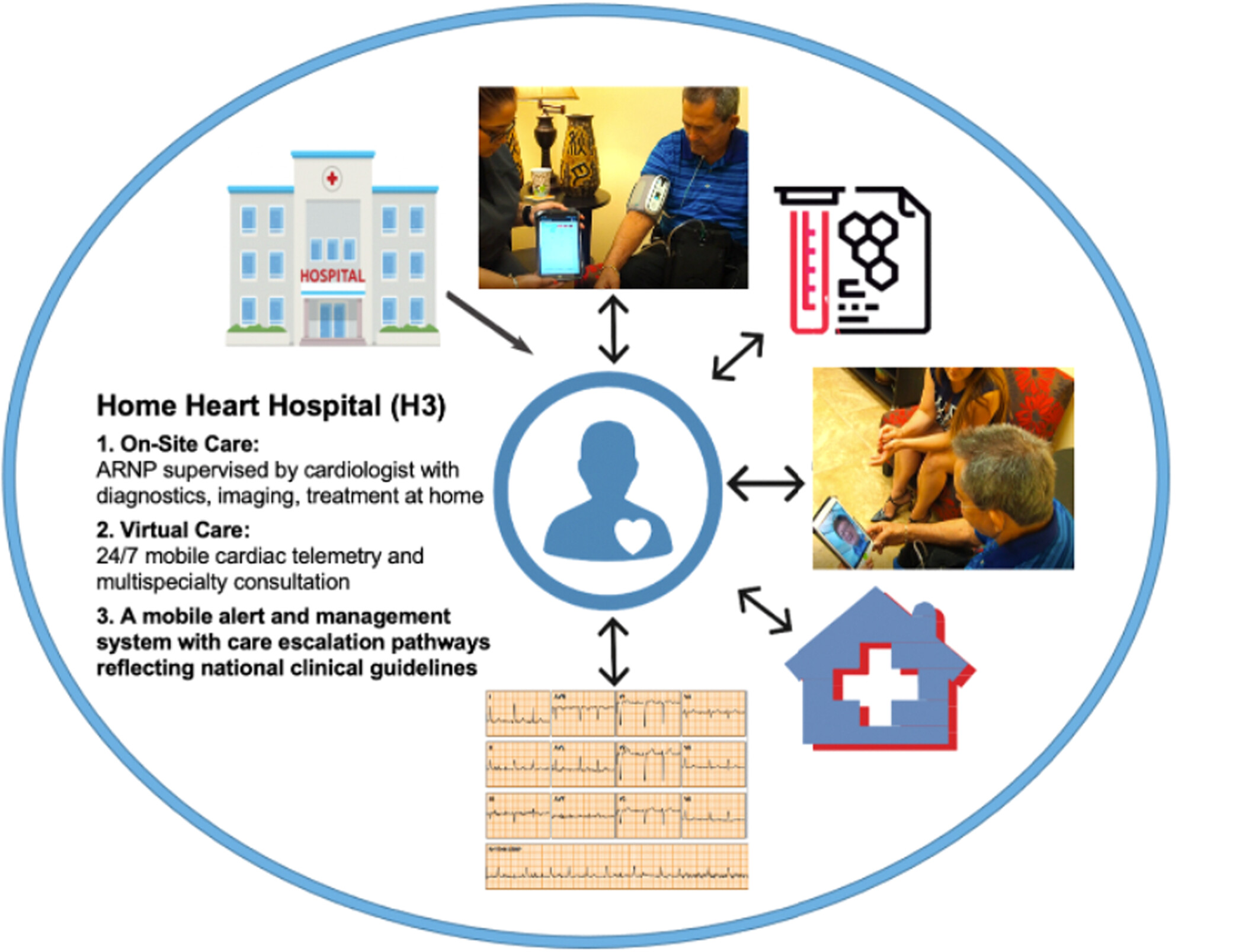
The H3 care model is designed to provide acute care services in the patient's home, including cardiac telemetry, which is utilized at the discretion of the treating cardiologist. The included photos display the use of 4G-connected devices as part of the remote patient monitoring bundle of sensors provided to each patient.
The Effect of Different Statin-Based Lipid-Lowering Strategies on C-Reactive Protein Levels in Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease
- First Published: 19 June 2024
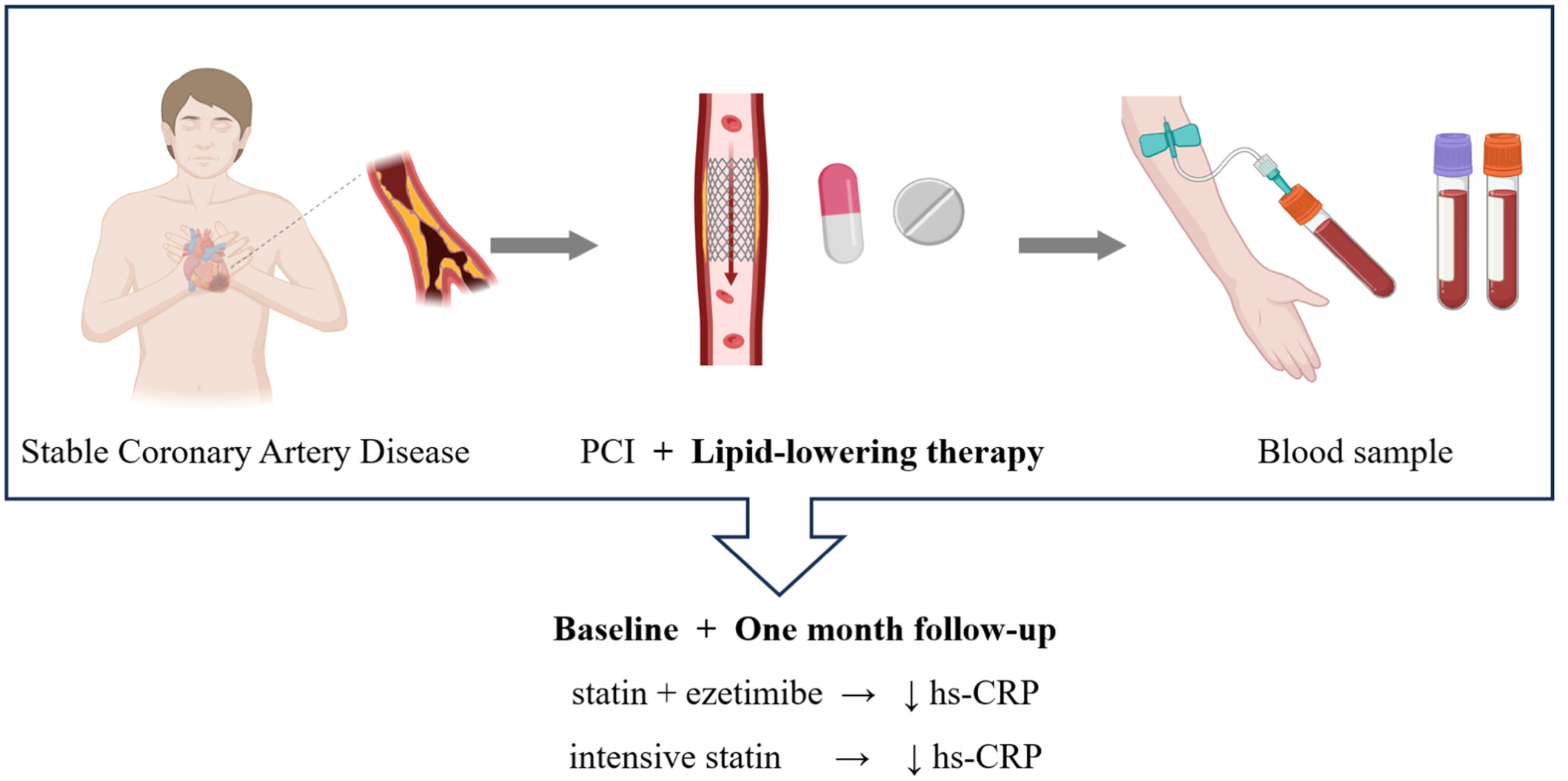
This study included stable coronary artery disease patients who underwent PCI and following treatment with statins. During treatment, hs-CRP, LDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, non-HDL-C, total cholesterol, and triglycerides were measured at baseline and 1 month of lipid-lowering therapy. In conclusion, statin combined with ezetimibe therapy and intensive statin therapy could further reduce hs-CRP levels by lowering LDL-C levels.
Clinical ARTICLES
Impact of Immunosuppressive Therapy on Lead Dislodgement After Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Implantation
- First Published: 18 June 2024
REVIEWS
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD): A contemporary review
- First Published: 11 June 2024
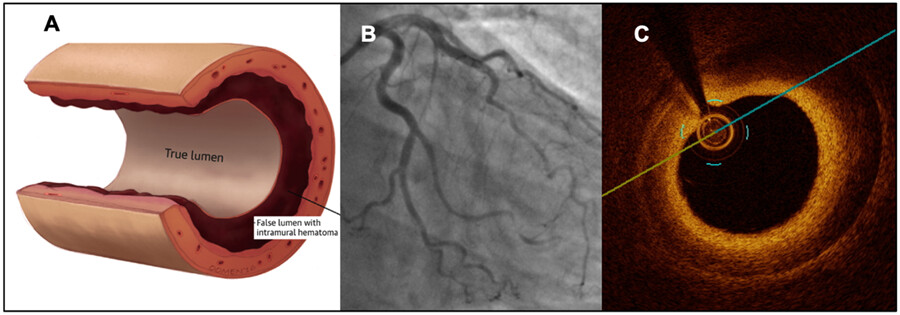
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection (SCAD) is an increasingly recognized cause of myocardial infarction that most frequently affects younger women, making it an important cause of morbidity and mortality within these demographics. The evolution of intracoronary imaging (C - OCT image of IMH), improved diagnosis with coronary angiography (B - Type 2 A SCAD in an obtuse marginal artery), and ongoing research efforts and attention via social media, has led to increasing recognition of this previously underdiagnosed condition (A - IMH as the important pathophysiologic mechanism in SCAD).
OCT, optical coherence tomography; IMH, intramural hematoma; SCAD, Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection.
CLINICAL ARTICLES
The involvement of circulating miR-146a and miR-27a in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection
- First Published: 17 June 2024
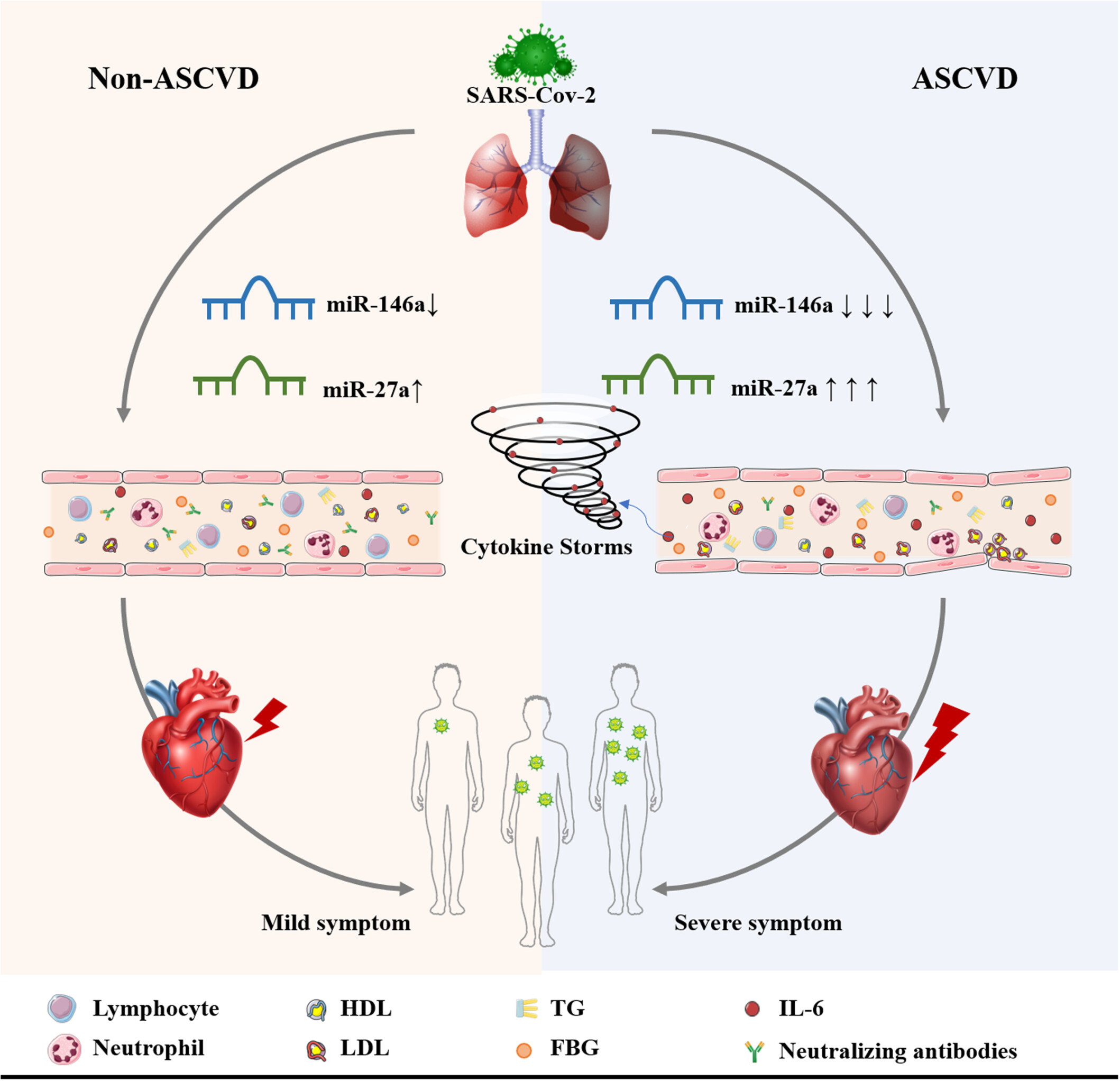
Patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease are more vulnerable to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and suffer more severe conditions and outcomes, miR-146a and miR-27a are involved in bidirectional interactions between ASCVD and SARS-CoV-2 infections, and are associated with metabolism, inflammation, and immune levels.
REVIEWS
Temporal Trends in the Outcomes of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention With Zotarolimus Eluting Stents Versus Everolimus Eluting Stents: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- First Published: 18 June 2024
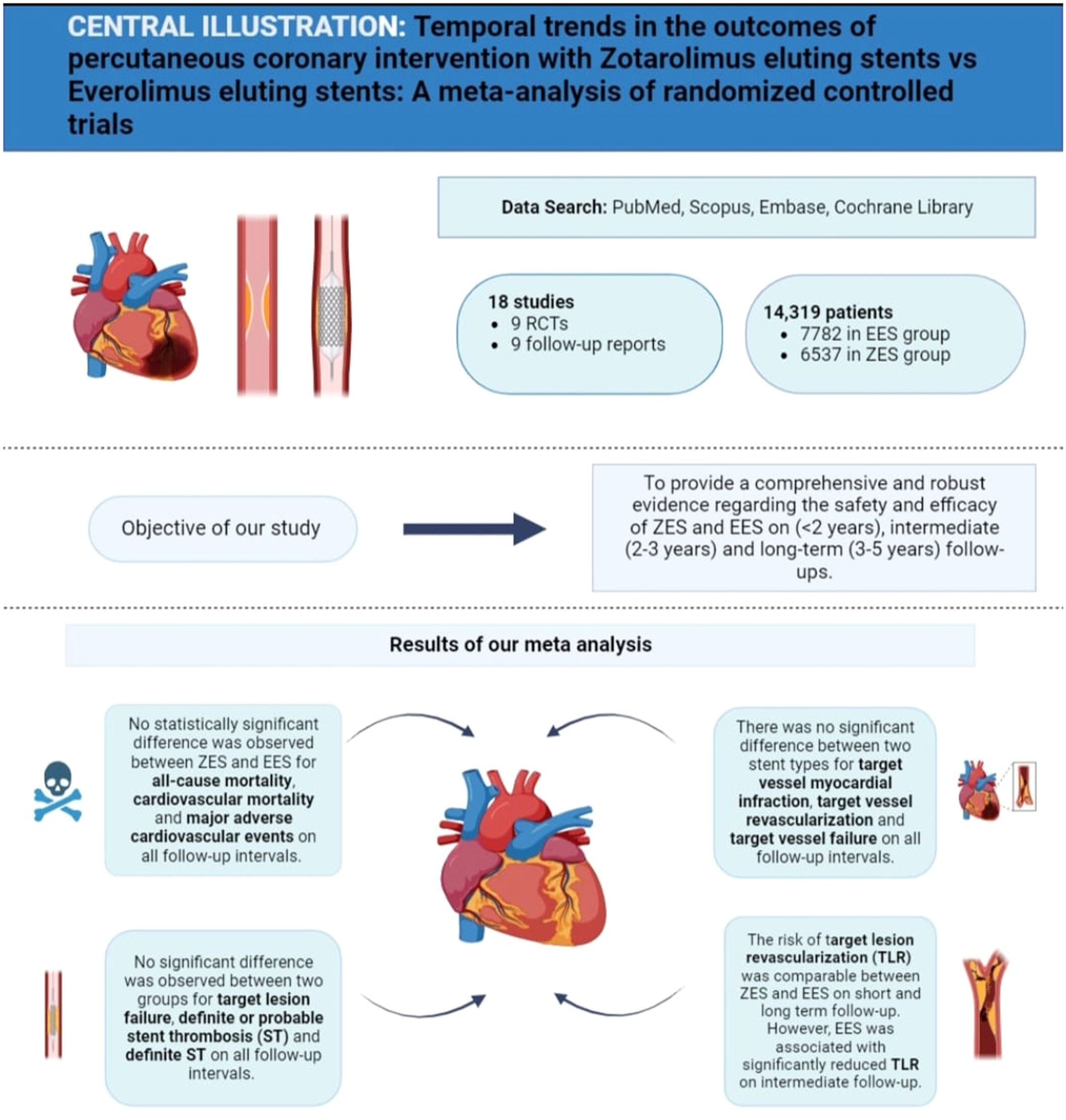
A meta-analysis comparing the outcomes of percutaneous coronary intervention with Everolimus eluting stents versus Zotaralimus eluting stents. EES and ZES showed similar efficacy and safety at short-, mid-, and long-term follow-up. EES was found to be superior to ZES for target lesion revascularization at intermediate follow-up.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Incorporating multiple biomarkers to assess mortality risk in non-ST elevation myocardial infarction
- First Published: 14 June 2024
CLINICAL ARTICLES
Plasma triglyceride is associated with the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after radiofrequency catheter ablation: A retrospective study
- First Published: 30 May 2024
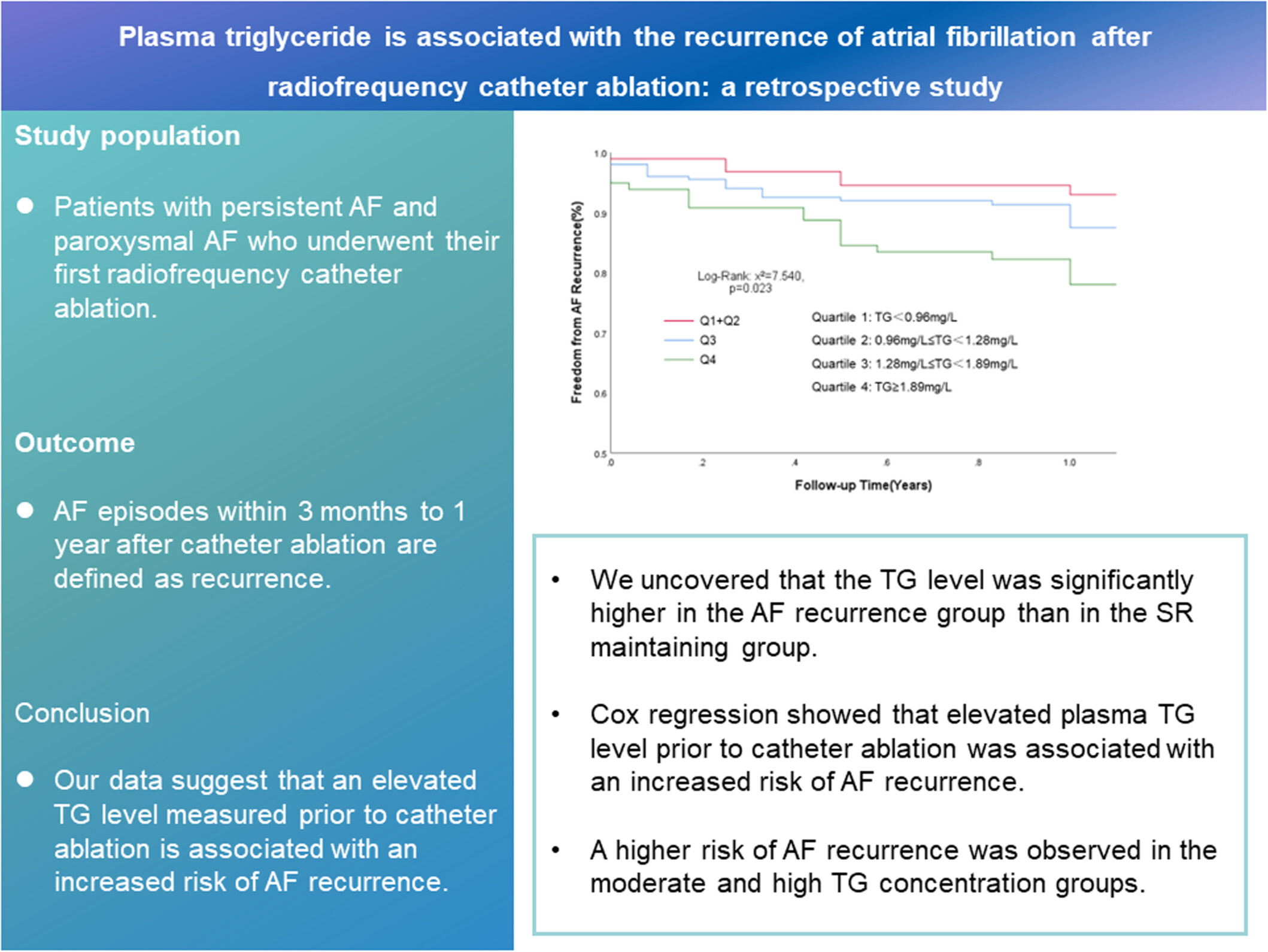
We uncovered that the triglyceride (TG) level was significantly higher in the atrial fibrillation (AF) recurrence group than in the sinus rhythm-maintaining group. Cox regression showed that elevated plasma TG level before catheter ablation was associated with an increased risk of AF recurrence. A higher risk of AF recurrence was observed in the moderate and high TG concentration groups.