Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
A systematic review of present and future pharmaco-structural therapies for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- First Published: 03 January 2024
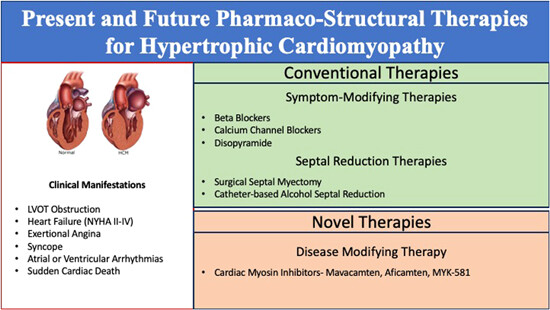
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is an increasingly recognized genetic condition that is accompanied by a heterogeneous phenotype. The presence of outflow tract obstruction carries an increased risk for the development of heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. Here, we review conventional and novel disease-modifying therapies for HCM.
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
QRS fragmentation does not predict mortality in survivors of acute myocardial infarction
- First Published: 19 January 2024
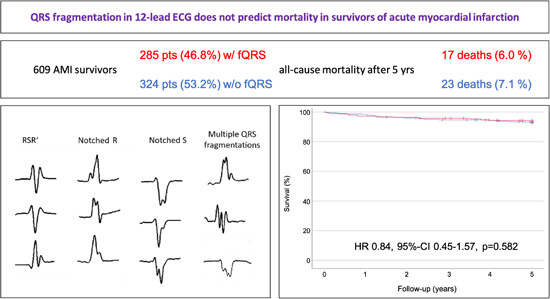
The aim of this study was to assess whether fragmented QRS (fQRS) was a mortality predictor in acute myocardial infarction survivors. Six hundred nine patients were included and followed for 5 years. fQRS prevalence was 46.8%. These patients had no increased hazard of all-cause death (hazard ratio: 0.84, 95% confidence interval: 0.45–1.57, p = .582) with a mortality rate of 6.0% compared to 7.1% in those without fQRS.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
Multiplex analysis of inflammatory proteins associated with risk of coronary artery disease in type-1 diabetes patients
- First Published: 11 October 2023
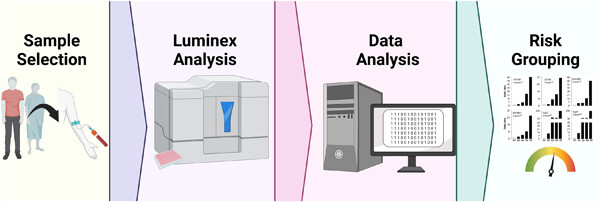
Serum levels of 22 proteins were measured in type-1 diabetes (T1D) patients with and without coronary artery disease (CAD) in a high-throughput manner using multiplex immunoassays. Machine learning-based scores can stratify CAD patients into low, medium, and high-risk groups. Our findings have translational potential to identify T1D patients at higher risk of CAD.
REVIEWS
Principles of artificial intelligence and its application in cardiovascular medicine
- First Published: 18 September 2023
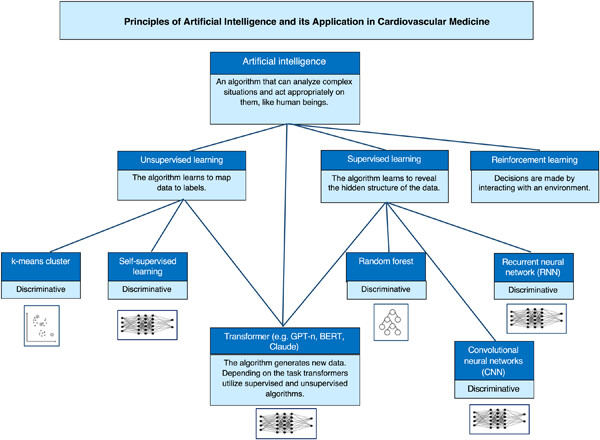
Artificial intelligence (AI) represents a rapidly developing field. This review will present the basics of AI. Different classifications of AI, like supervised versus unsupervised and discriminative versus generative AI, are given. Analogies to human intelligence are discussed as far as algorithms are oriented toward it. The second step will present the most common models like random forest, k-means clustering, convolutional neural networks, and transformers to understand the underlying ideas. Corresponding medical applications in cardiovascular medicine will be named for all models.
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
Cardiovascular risk and biopsychosocial interplay: Association among hypertension, anxiety, and emotional dysregulation—observational study in primary care setting for efficient self-care
- First Published: 28 September 2023
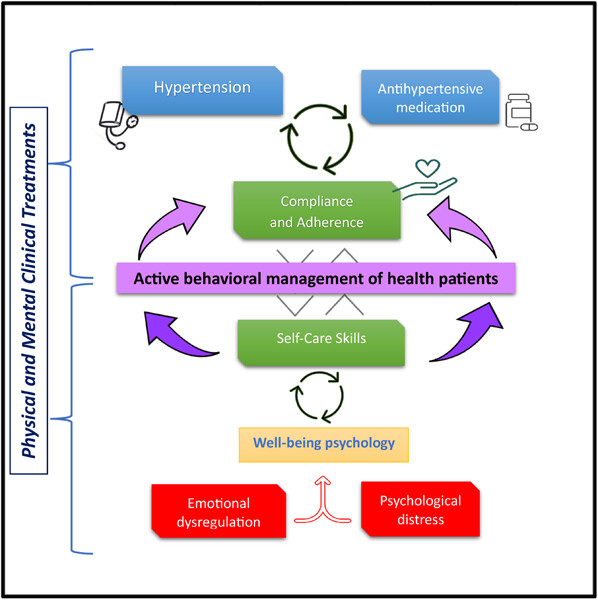
The study focused on the health management of the hypertensive patients over the time considering the emotional perspective on the self-care skills. As expected, anxiety resulted a co-morbidity in hypertension; interesting results was to detect the related association between psychological and health management factors. In particular, emotional dysregulation and psychological distress were correlated to self-care.
REVIEWS
Association of living alone with clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 22 September 2023
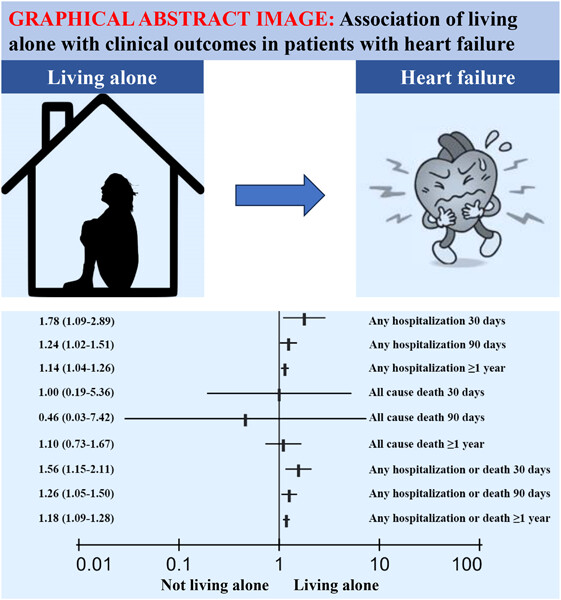
This study sought to explore the association between living alone and adverse outcomes in patients with heart failure (HF). Pooled data showed that HF patients living alone had a higher risk of any hospitalization and any hospitalization or death during the 30-day, 90-day, and ≥1-year follow-up periods compared with living with others. Whereas in terms of all-cause mortality, there was no difference in risk between the two groups.
Application of Mendelian randomization in the discovery of risk factors for coronary heart disease from 2009 to 2023: A bibliometric review
- First Published: 19 September 2023
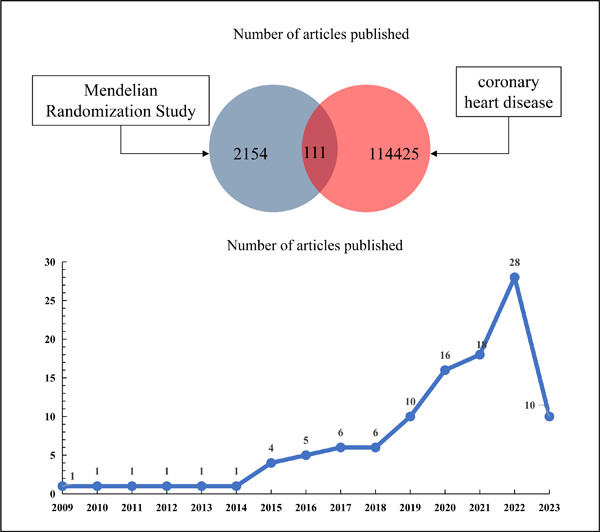
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a life-threatening condition that poses a significant risk to individuals. Mendelian randomization (MR) is an emerging epidemiological research method that offers substantial advantages in identifying risk factors for diseases. Currently, there are ongoing CHD-related MR studies. To gain comprehensive insights into the focal areas and trends of CHD-related MR research, this study utilizes bibliometrics to conduct an in-depth analysis of CHD-related MR articles published in the core database of Web of Science (WOS) from 2009 to 2023. A search was performed to identify CHD-related MR articles published between 2009 and 2023 in WOS. The data, including publication countries, research institutions, journals, citations, and keywords, were analyzed using the Bibliometrix R-4.0 software package. A total of 111 articles published in 71 journals were included in the analysis. The journal with the highest impact factor (IF) was the New England Journal of Medicine. The articles were distributed across 24 categories within the 71 journals, with the highest number of publications falling under Cardiac & Cardiovascular Systems, Medicine, General & Internal, and Genetics & Heredity. Among the articles, 57 were published in Q1 journals, 42 in Q2 journals, 9 in Q3 journals, and 2 in Q4 journals. The most frequently published journals on CHD-related MR were Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, Frontiers in Genetics, and the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. A total of 963 authors participated in the 111 articles, with the majority affiliated with institutions in the United Kingdom, the US, and China. The national cooperation network revealed close collaborations between the UK and the US, as well as between the UK and China. The publication of the 111 articles involved 453 research institutions, with Oxford University, Bristol University, and Cambridge University being the most frequently involved institutions. Out of the 111 articles, only 62 were directly related to CHD and MR, with CHD being the outcome factor in 61 of them. These 61 articles investigated 47 exposure factors across eight categories. Among these factors, 10 had been studied in more than 2 articles. The findings concerning the impact of serum uric acid and omega-6 fatty acids on CHD risk were not entirely consistent. Research in MR related to CHD has been gradually gaining recognition, with an increase in both its academic credibility and collaborative efforts within this field. Indeed, MR has facilitated the identification of risk factors associated with CHD. However, the relationship between these disease risk factors and CHD requires further investigation for clarification. Future MR studies on CHD could prioritize the elucidation and validation of contentious disease risk factors, thereby paving the way for a more comprehensive exploration of additional factors contributing to the onset of CHD.
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
ECG left ventricular hypertrophy in aortic stenosis: Relationship with cardiac structure, invasive hemodynamics, and long-term mortality
- First Published: 23 September 2023
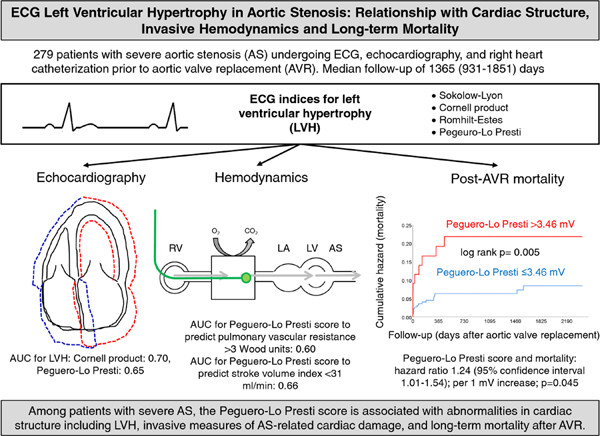
In 279 severe AS patients undergoing ECG, echocardiography, and cardiac catheterization, the Peguero-Lo Presti score and three other LVH scores were assessed. The Peguero-Lo Presti score had the greatest AUC for the prediction of key hemodynamics. After a median post-AVR follow-up of 1365 days only the Peguero-Lo Presti score was significantly associated with mortality.
Comparison of machine-learning models for the prediction of 1-year adverse outcomes of patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- First Published: 18 September 2023
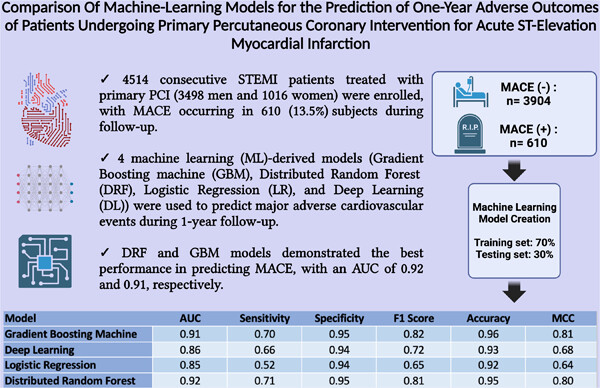
This study assessed the performance of four machine learning models for predicting adverse outcomes in acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Among the models tested, the Distributed Random Forest and Gradient Boosting Machine exhibited superior predictive accuracy for major adverse cardiovascular events during a 1-year follow-up. These models hold the potential for enhancing personalized treatment strategies and improving clinical outcomes in high-risk STEMI patients.
CLINICAL TRIAL
Antianginal effects of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and refractory angina; a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial (EMPT-ANGINA Trial)
- First Published: 18 September 2023
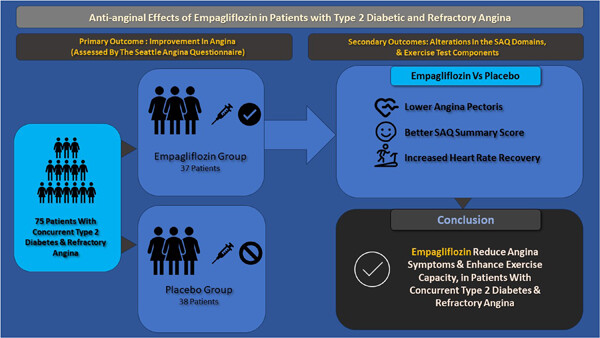
The EMPT-ANGINA randomized trial evaluated the effect of empagliflozin, a sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, on angina symptoms and exercise capacity in patients with both type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and refractory angina (RA). Patients were divided into two groups: one received empagliflozin (n = 37), and the other received a placebo (n = 38). The primary outcome, assessed by the Seattle Angina Questionnaire Summary Score, showed significant improvement in the empagliflozin group. Secondary outcomes, including various exercise test components, also improved significantly in the empagliflozin group. The study concluded that adding empagliflozin to routine anti-hyperglycemic therapies in patients with T2DM and RA could significantly reduce angina symptoms and improve exercise capacity with minimal side effects.
Relationship between ideal cardiovascular health score and perioperative acute kidney injury: A case-control study
- First Published: 19 September 2023
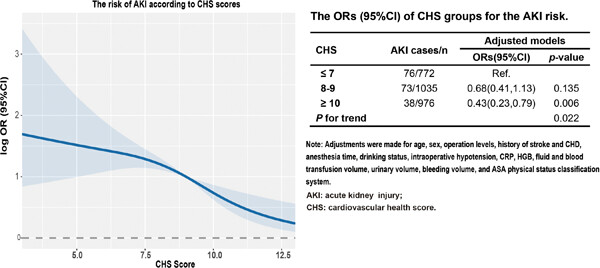
In the current study, we found that cardiovascular health scores (CHS) score strongly associated with the risk of perioperative acute kidney injury (AKI), with higher CHS scores associated with a lower risk of AKI, These findings provide a theoretical basis and clinical evidence for preventing perioperative AKI.
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
Epidemiology of arrhythmogenic ventricular cardiomyopathy in China
- First Published: 01 November 2023
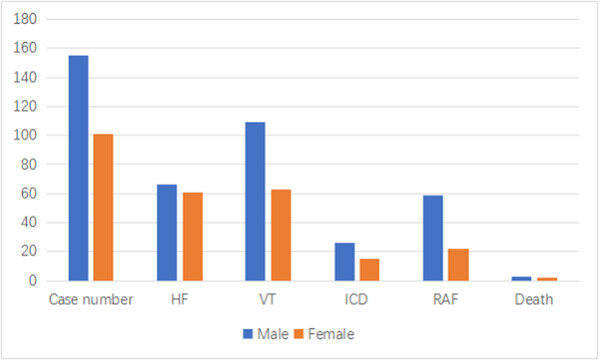
We studied 15 888 adults from the Beijing Municipal Health Commission Information Center (BMHCIC) registry database in China from January 2010 to December 2020, there were a total of 256 newly diagnosed AVC patients. Males had higher incidence of AVC than females. Males had similar VT prevalence (70.32% vs. 62.38%) and mortality (1.94% vs. 1.98%) but lower HF prevalence (42.58% vs. 60.40%), when compared with females.
CLINICAL TRIAL
Cardioversion strategy impacts rate control during recurrences in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A subanalysis of the RACE 7 ACWAS trial
- First Published: 23 October 2023
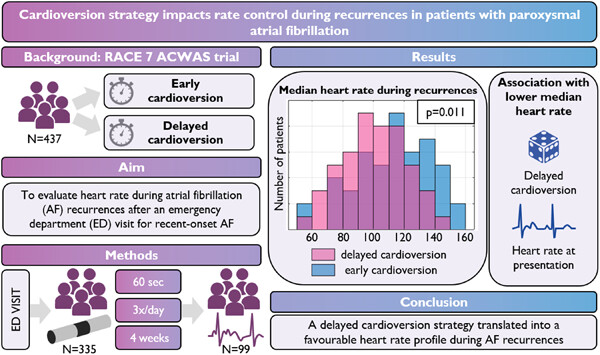
In the RACE 7 ACWAS trial, patients with recent-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) were randomized to either early or delayed cardioversion. This prespecified sub-analysis evaluating heart rate during AF recurrences after an emergency department visit showed that a delayed cardioversion strategy translated into a favorable heart rate profile during AF recurrences.
Abbreviations: AF = atrial fibrillation, ED = emergency department, RACE 7 ACWAS trial = Rate Control versus Electrical Cardioversion Trial 7–Acute Cardioversion versus Wait and See.
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
Appropriate time for ejection fraction reassessment after revascularization in patients with left ventricular dysfunction for risk stratification of sudden cardiac death
- First Published: 07 November 2023
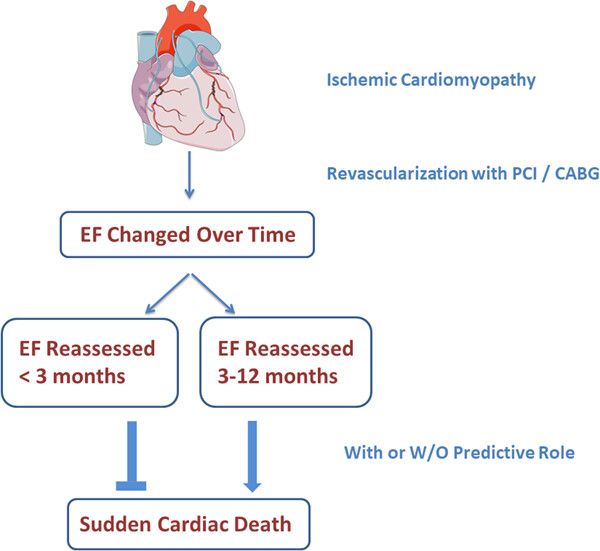
Ejection fraction (EF) changed over time after revascularization in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. When EF was reassessed early (<3 months) after revascularization, EF ≤ 35% predicted the risk of all-cause death but not sudden cardiac death (SCD). By contrast, when EF was reassessed within 3–12 months, EF ≤ 35% was associated with higher risks of both SCD and all-cause death.
CLINICAL ARTICLES
Association of red blood cell distribution width and hemoglobin-to-RDW ratio with contrast-associated acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary angiography: A retrospective study
- First Published: 04 October 2023
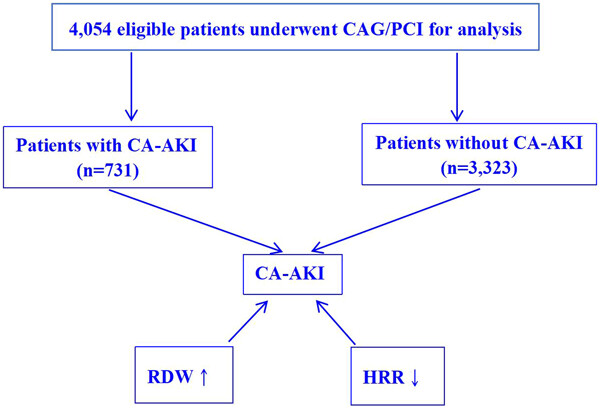
Both high red blood cell distribution width (RDW) and low hemoglobin-to-RDW ratio (HRR) demonstrated robust and independent associations with contrast-associated acute kidney injury (CA-AKI). These findings suggest that tracking RDW and HRR could be valuable for the early identification of CA-AKI risk.
CLINICAL STUDY DESIGN
Adjunctive posterior wall isolation for the treatment of persistent and longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation (CORNERSTONE AF) trial: Design and rationale
- First Published: 11 October 2023
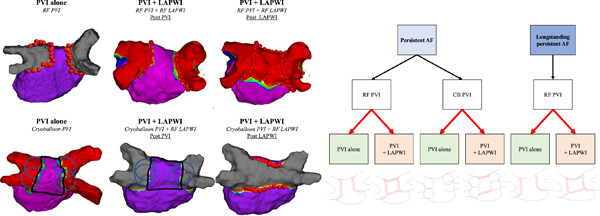
Patients with persistent AF or longstanding persistent AF will be randomized to a PVI alone or a PVI + LAPWI in a 1:1 manner. The PVI will be performed either by a radiofrequency catheter or cryoballoon. The left images show sample 3D mapping images after the procedure. AF, atrial fibrillation; LAPWI, left atrial posterior wall isolation; PVI, pulmonary vein isolation.
CLINICAL ARTICLES
Sex-related association of modifiable risk factors with hypertension: A national cross-sectional study of NHANES 2007–2018
- First Published: 05 October 2023
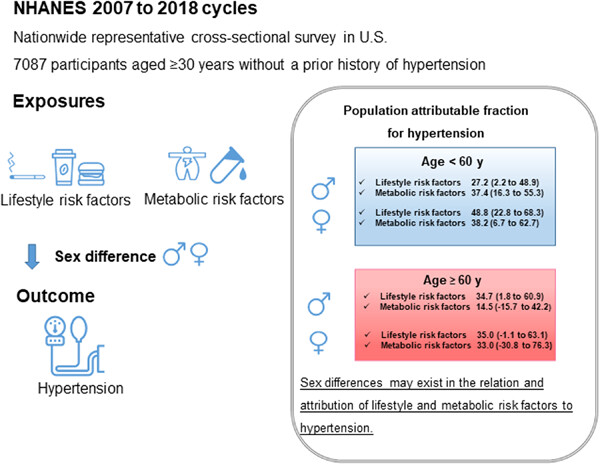
This study included 7087 participants aged ≥30 years from NHANES and showed that men had 84% increased risk of prevalence of hypertension than women. The sex difference was more evident in those aged <60 years and lifestyle and metabolic risk factors accounted for different attribution to hypertension between men and women.
Troponin level at presentation as a prognostic factor among patients presenting with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
- First Published: 19 October 2023
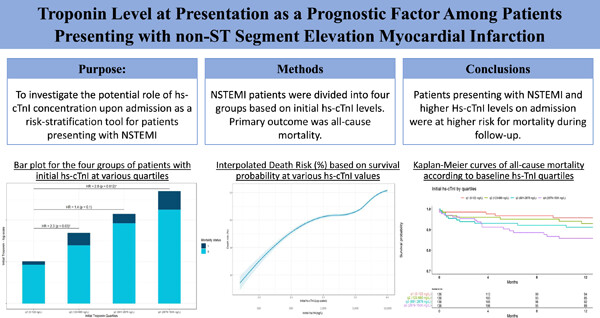
In a study of 544 NSTEMI patients (mean age: 68; 22% females), we explored hs-cTnI levels on admission as a prognostic marker. The highest hs-cTnI quartile showed increased mortality (16.2% vs. 7.3%). Adjusted HR for mortality was 2.06 (p = .047). Further prospective studies are essential to assess reperfusion strategies based on initial troponin levels.
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
Effects of using primary percutaneous coronary interventions on the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation following an acute myocardial infarction
- First Published: 25 October 2023
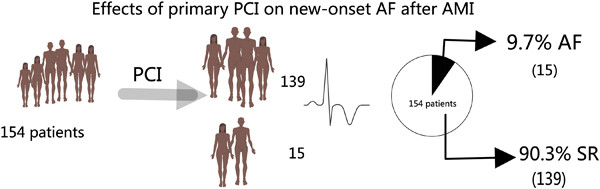
Using primary percutaneous coronary interventions (PCIs) on the incidence of new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) following an acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Age and left atrial diameter were independent risk factors of new-onset AF in patients undergoing a PCl following an AMI, while primary PCI was a protective factor.
CLINICAL ARTICLES
A model for predicting postoperative persistent acute kidney injury (AKI) in AKI after cardiac surgery patients with normal baseline renal function
- First Published: 08 October 2023
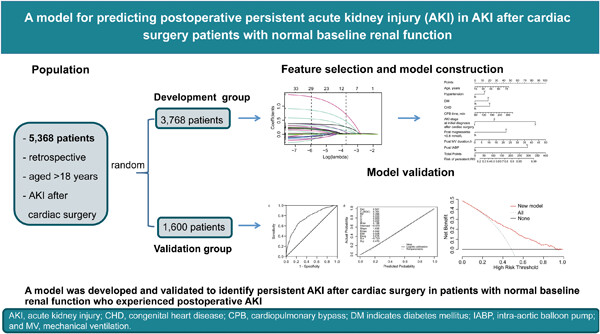
Among 5368 patients with baseline normal renal function and acute kidney injury (AKI) after cardiac surgery, 3768 patients were randomly used for model development and the rest for validation. We developed a model for predicting postoperative persistent AKI. The model's performance was good in the validation group.
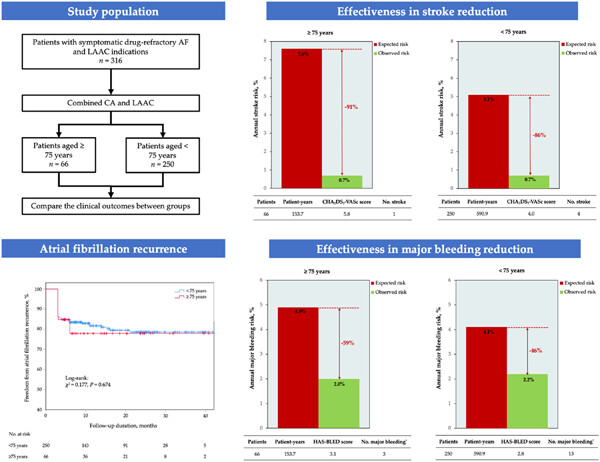
Clinical outcomes of combined catheter ablation and left atrial appendage closure in elderly patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation
- First Published: 07 October 2023
Risk factor profile and outcomes of premature acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention: A 1-year prospective design
- First Published: 11 October 2023
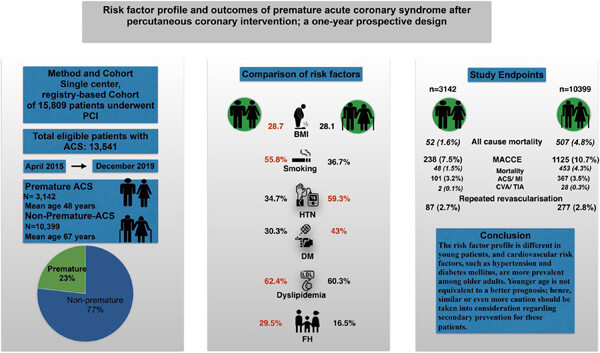
Our study compared risk factors, all-cause mortality, and major cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in premature and nonpremature patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention. Younger patients exhibited distinct risk factors, with higher in-hospital mortality but similar long-term outcomes. This highlights the need for caution in secondary prevention for younger patients.
CLINICAL TRIAL
Impact of heart failure and preoperative platelet count on the postoperative short-term outcome in infective endocarditis patients
- First Published: 10 October 2023
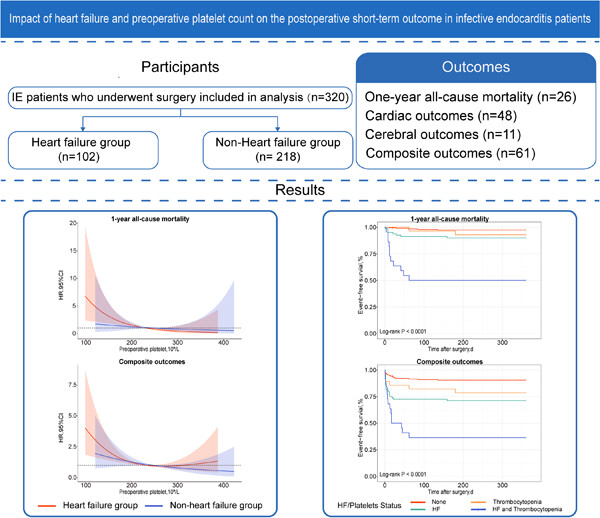
In this study, we found a mutual promoting effect between heart failure (HF) and thrombocytopenia. Platelets had a greater impact on the prognosis of HF patients than of non-HF patients. Event-free survival in patients with both HF and thrombocytopenia was significantly shorter than that in other patients.
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
Effects of intensive blood-pressure treatment on myocardial work in elderly hypertensive patients: A subcenter study of the STEP randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 11 October 2023
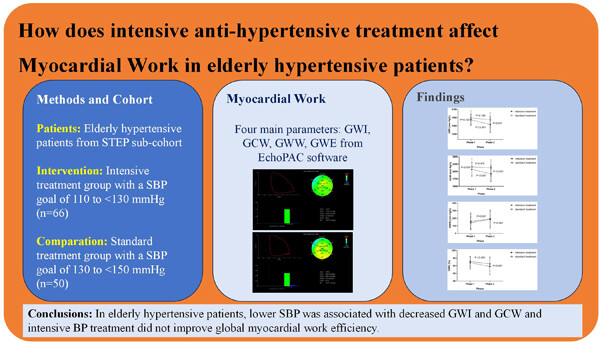
We investigated MW parameters and intensive antihypertensive treatment. We found that intensive antihypertensive treatment significantly reduced GWI and GCW from phase 1 to phase 2. Both treatment groups’ GWW increased and GWE decreased from phase 1 to phase 2. Intensive antihypertensive treatment did not reverse myocardial work in elderly hypertensives.
REVIEWS
Navigating the Sotatercept landscape: A meta-analysis of clinical outcomes
- First Published: 11 October 2023
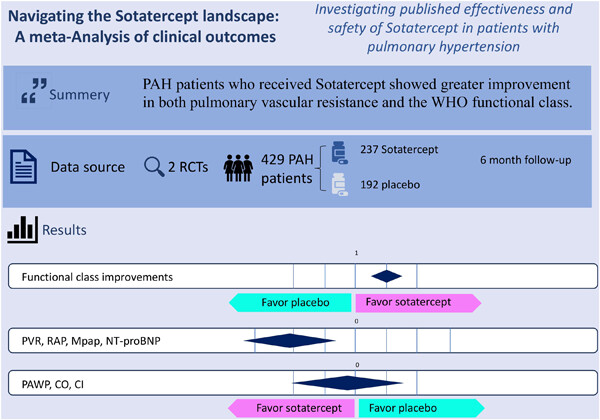
In this study, we performed a meta-analysis on two randomized clinical trials to assess the impact of Sotatercept on PAH patients. The included papulation were 429 patients with PAH, of which 237 received Sotatercept and 192 received placebo. They were followed for 6 months.
Our findings revealed that those treated with Sotatercept showed greater improvement in pulmonary vascular resistance, right atrial pressure, mean pulmonary artery pressure, change in N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide, and World Health Organization functional class compared with placebo recipients.
CLINICAL ARTICLES
The significance of heart rate variability in patients with frequent premature ventricular complex originating from the ventricular outflow tract
- First Published: 19 October 2023
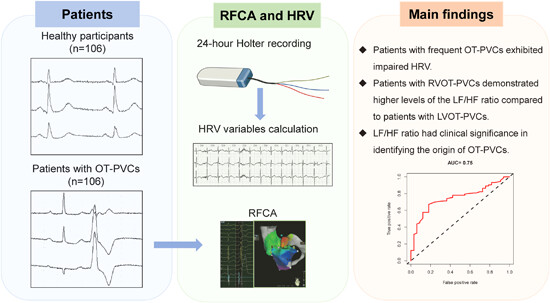
A total of 106 frequent outflow tract premature ventricular complexes (OT-PVCs) patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation and 106 healthy participants were included in the study to examine the significance of heart rate variability (HRV) in patients with frequent OT-PVCs. Patients with OT-PVCs showed impaired HRV, while those with RVOT-PVCs exhibited higher low frequency to high frequency ratios compared to patients with LVOT-PVCs.
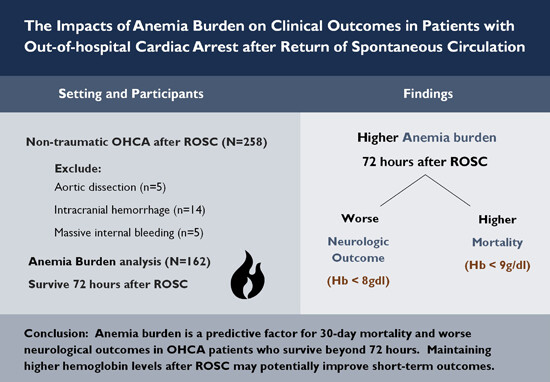
The impacts of anemia burden on clinical outcomes in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
- First Published: 24 October 2023
REVIEWS
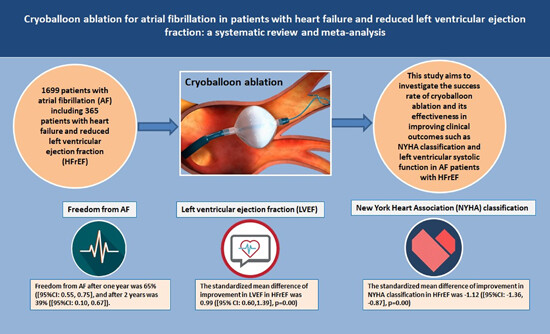
Cryoballoon ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 25 October 2023
CLINICAL TRIAL
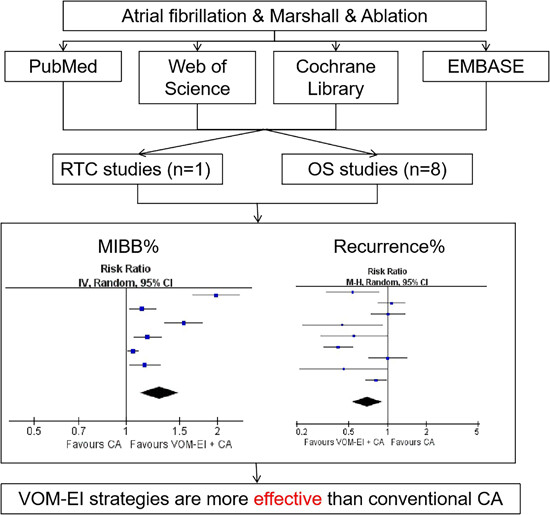
Efficacy and feasibility of vein of Marshall ethanol infusion during persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 06 November 2023
CLINICAL ARTICLES
The comparison between the novel technique and conventional method in the catheter ablation of premature ventricular contractions originating from the free wall of tricuspid annulus
- First Published: 25 October 2023
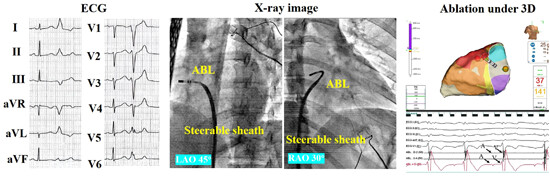
This study focus on the safety and effectiveness of the reversed S-curve technique under the support of a steerable sheath for catheter ablation in patients with premature ventricular contraction (PVC) from free wall of tricuspid annulus (TV). The data showed that the reserved S-curve technique, supported by a steerable sheath, is a feasible and effective method for ablating PVC originating from the free wall of TV.
Safety and efficacy of catheter ablation of para-Hisian accessory pathway via a direct superior vena cava approach: A multicenter study
- First Published: 27 October 2023
Characterization and LDL-C management in a cohort of high and very high cardiovascular risk patients: The PORTRAIT-DYS study
- First Published: 06 November 2023
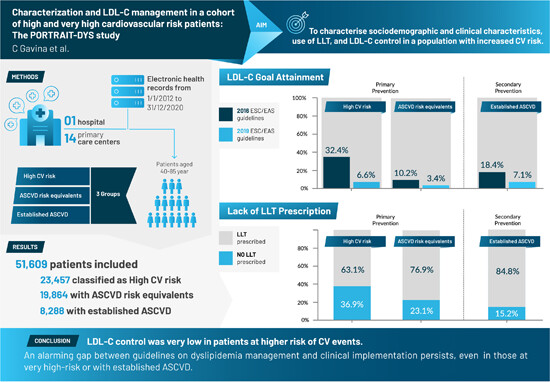
We analyzed electronic health records of 51 609 patients from one hospital and 14 primary care centers in Portugal, assessing sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, lipid-lowering therapies usage, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) control. Our findings show suboptimal LDL-C control in high-risk patients, emphasizing the need for improved strategies.
Is it time for Heart–Brain clinics? A clinical survey and proposition to improve current care for cognitive problems in heart failure
- First Published: 06 January 2024
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
How to assess the epidemiology of arrhythmogenic ventricular cardiomyopathy
- First Published: 12 January 2024
CORRESPONDENCE
Efficacy and safety of torsemide versus furosemide in heart failure patients: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials
- First Published: 22 August 2023
REVIEWS
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement: Past, present, and future
- First Published: 14 January 2024
In this review, we provide an updated overview of the TAVR procedure, the main aspects of preprocedural patient assessment, and the key complications of the procedure. We also summarize the current evidence comparing TAVR and SAVR, before exploring the potential future directions for TAVR. Created with BioRender.
CLINICAL ARTICLES
Fatty acid-binding protein-3 and renal function decline in patients with chronic coronary syndrome
- First Published: 15 January 2024
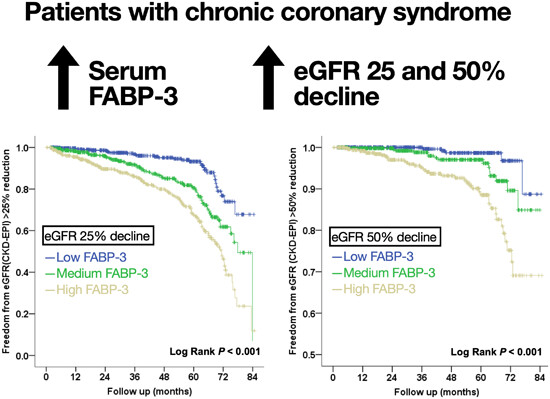
For patients with chronic coronary syndrome, early detection and prevention of kidney injury are crucial. We found that a higher serum FABP-3 level was correlated to an increased risk of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline. Serum FABP-3 may serve as a novel biomarker to predict eGFR decline in these patients.
REVIEWS
Effects of flaxseed supplementation on weight loss, lipid profiles, glucose, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in patients with coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- First Published: 16 January 2024
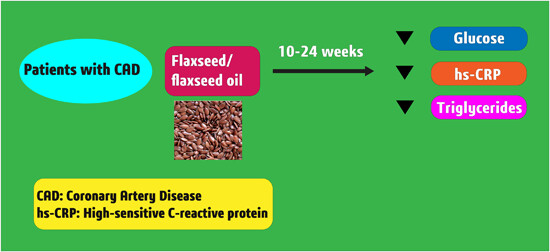
This meta-analysis assessed the efficacy of flaxseed supplementation in improving anthropometric, glycemic, lipid, and inflammatory indices in individuals with coronary artery disease (CAD). Pooled data showed that 10–24 weeks of flaxseed or flaxseed oil supplementation led to a statistically significant decrease in glucose, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and triglyceride levels in individuals with CAD.
CLINICAL TRIAL RESULT
Time-weighted blood pressure with cardiovascular risk among patients with or without diabetes
- First Published: 16 January 2024
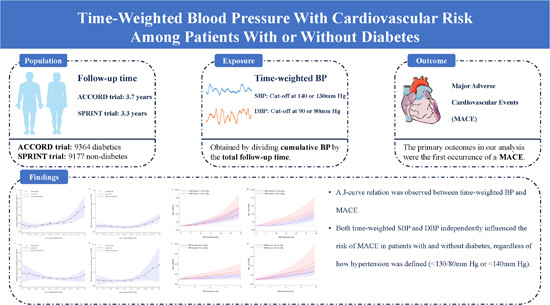
This study employed data sourced from the ACCORD and SPRINT clinical trials to unveil the correlation between time-weighted blood pressure and the incidence of significant adverse cardiovascular events in individuals with diabetes and those without diabetes. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
CLINICAL ARTICLES
Elevated uric acid/albumin ratio as a predictor of poor coronary collateral circulation development in patients with non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction
- First Published: 16 January 2024
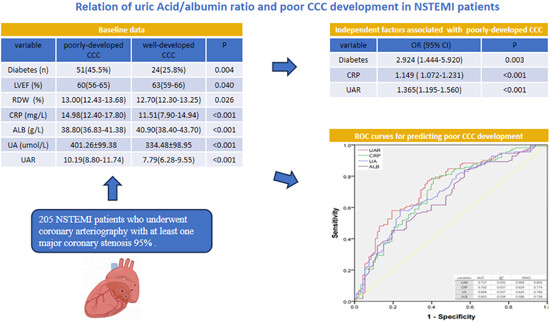
Analysis of 205 non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction patients reveals the uric acid/albumin ratio (UAR) as a strong predictor of poor coronary collateral circulation development, outperforming UAR, C-reactive protein, uric acid, and albumin levels in predictive value, as evidenced by receiver operating characteristic curves.
Contractility, ventriculoarterial coupling, and stroke work after acute myocardial infarction using CMR-derived pressure-volume loop data
- First Published: 16 January 2024
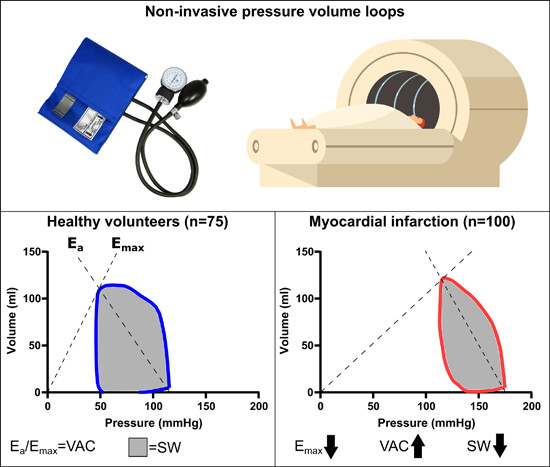
Contractility, ventriculoarterial coupling, and SW in healthy volunteers and myocardial infarction (MI) patients using noninvasive pressure-volume (PV) loop measurements. The top box illustrates generation of PV loops non-invasively by sphygmomanometry and CMR. Variables such as Emax (used as a measure of contractility), ventriculoarterial coupling, and SW were calculated. The left graph shows an example of a PV loop in a healthy volunteer where Ea and Emax have been illustrated as the slope of the dotted lines and SW as the gray area filling the PV loop. The right graph shows an example of a PV loop in a patient during the first week after MI and is representative of the mean difference in Emax (lower), VAC (higher), and SW (lower) compared to the healthy volunteers. CMR, cardiovascular magnetic resonance, Ea, arterial elastance; Emax, maximal elastance; PV, pressure volume; SW, stroke work; VAC, ventriculoarterial coupling. Image of MRI scanner by macrovector on Freepik.com. Image of sphygmomanometer cuff by www.medisave.co.uk
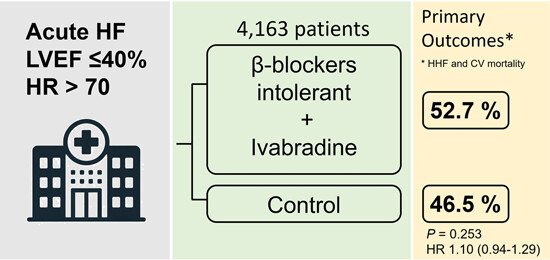
Evaluating the applicability of ivabradine in acute heart failure
- First Published: 28 December 2023